
Describe the major events in sexual reproduction.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Sexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which new organisms are created, by combining the genetic information from two individuals of different sexes.
Complete answer:
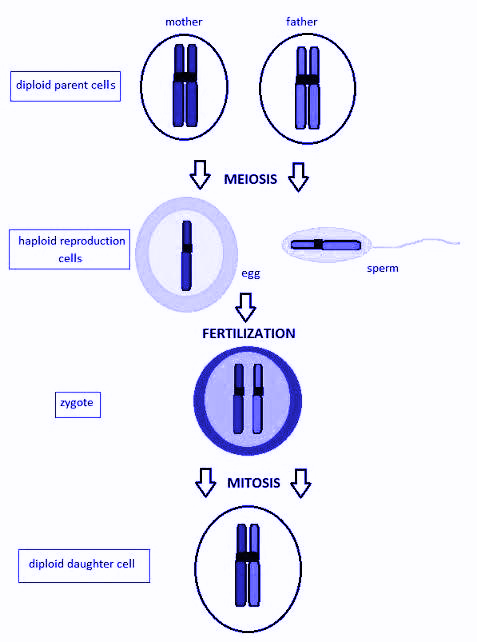
In multicellular eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in animals, fungi, and plants. Sexual reproduction involves a complex life cycle. It consists of a set of events that are divided into the following three stages:
1. Pre-fertilization: (Formation & Transfer of Gametes)
This stage comprises the events before fertilization. The two events that take place during this stage are:
2. Gametogenesis of gamete formation
In eukaryotes, diploid mother cells divide to produce haploid cells known as gametes, in a process called meiosis. This process involves the recombination of genetic materials.
3.Transfer of gametes
Since the female gametes are immotile, male gametes are transferred for fertilization. In plants, this is achieved by pollination. Unisexual animals transfer gametes by sexual intercourse.
4. Fertilization: (Fusion of Gametes)
Two haploid gametes combine into one diploid cell to form a zygote, which is the precursor to an embryo offspring, in the process called fertilization. This zygote incorporates the genetic material from both the gametes. It is also known as syngamy.
5. Post-fertilization: (Embryogenesis)
Fertilization results in multiple cell divisions mitotically, without any change in the number of chromosomes, and forms a multicellular diploid phase that leads the zygote to develop into an embryo. This process is called embryogenesis.
Note:
1. The genetic diversity arising from sexual reproduction gives the species a better chance of survival. Sexual reproduction increases the diversity of genotypes and phenotypes within a population and allows natural selection to select for the individuals best suited to an environment.
2. Fertilization occurs either outside the body called external fertilization or inside the body called internal fertilization.
Complete answer:
In multicellular eukaryotes, sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in animals, fungi, and plants. Sexual reproduction involves a complex life cycle. It consists of a set of events that are divided into the following three stages:
1. Pre-fertilization: (Formation & Transfer of Gametes)
This stage comprises the events before fertilization. The two events that take place during this stage are:
2. Gametogenesis of gamete formation
In eukaryotes, diploid mother cells divide to produce haploid cells known as gametes, in a process called meiosis. This process involves the recombination of genetic materials.
3.Transfer of gametes
Since the female gametes are immotile, male gametes are transferred for fertilization. In plants, this is achieved by pollination. Unisexual animals transfer gametes by sexual intercourse.
4. Fertilization: (Fusion of Gametes)
Two haploid gametes combine into one diploid cell to form a zygote, which is the precursor to an embryo offspring, in the process called fertilization. This zygote incorporates the genetic material from both the gametes. It is also known as syngamy.
5. Post-fertilization: (Embryogenesis)
Fertilization results in multiple cell divisions mitotically, without any change in the number of chromosomes, and forms a multicellular diploid phase that leads the zygote to develop into an embryo. This process is called embryogenesis.

Note:
1. The genetic diversity arising from sexual reproduction gives the species a better chance of survival. Sexual reproduction increases the diversity of genotypes and phenotypes within a population and allows natural selection to select for the individuals best suited to an environment.
2. Fertilization occurs either outside the body called external fertilization or inside the body called internal fertilization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




