
Describe the construction and working theory of cyclotron.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint- Here, we will proceed by telling what is the function of a cyclotron. Then, we will discuss the principle on which this device is based. Also, the construction of this device along with its working theory will be explained.
Complete step-by-step solution:
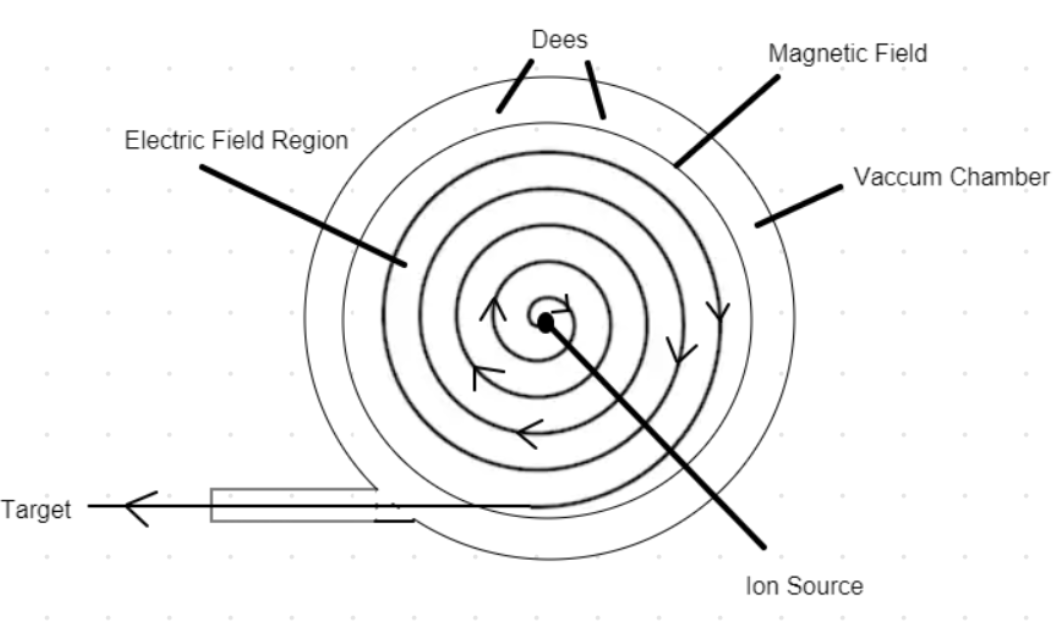
Cyclotron is a device used to accelerate charged particles to high energies.
Principle
Cyclotron works on the principle that a charged particle moving normal to a magnetic field experiences magnetic Lorentz force due to which the particle moves in a circular path.
Construction
It consists of a hollow metal cylinder divided into two sections D1 and D2 called Dees, enclosed in an evacuated chamber. The Dees are kept separated and a source of ions is placed at the centre in the gap between the Dees. They are placed between the pole pieces of a strong electromagnet. The magnetic field acts perpendicular to the plane of the Dees. The Dees are connected to a high frequency oscillator.
Working Theory
When a positive ion of charge q and mass m is emitted from the source, it is accelerated towards the Dee having a negative potential at that instant of time. Due to the normal magnetic field, the ion experiences magnetic lorentz force and moves in a circular path. By the time the ion arrives at the gap between the Dees, the polarity of the Dees gets reversed. Hence the particle is once again accelerated and moves into the other Dee with a greater velocity along a circle of greater radius. Thus the particle moves in a spiral path of increasing radius and when it comes near the edge, it is taken out with the help of a deflector plate (D.P). The particle with high energy is now allowed to hit the target T.
Note: According to the concept of magnetic lorentz force, when the particle moves along a circle of radius r with a velocity v then the magnetic lorentz force provides the necessary centripetal force which means that here the magnetic lorentz force will be equal to the centripetal force i.e., Bqv = $\dfrac{{{\text{m}}{{\text{v}}^2}}}{{\text{r}}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution:

Cyclotron is a device used to accelerate charged particles to high energies.
Principle
Cyclotron works on the principle that a charged particle moving normal to a magnetic field experiences magnetic Lorentz force due to which the particle moves in a circular path.
Construction
It consists of a hollow metal cylinder divided into two sections D1 and D2 called Dees, enclosed in an evacuated chamber. The Dees are kept separated and a source of ions is placed at the centre in the gap between the Dees. They are placed between the pole pieces of a strong electromagnet. The magnetic field acts perpendicular to the plane of the Dees. The Dees are connected to a high frequency oscillator.
Working Theory
When a positive ion of charge q and mass m is emitted from the source, it is accelerated towards the Dee having a negative potential at that instant of time. Due to the normal magnetic field, the ion experiences magnetic lorentz force and moves in a circular path. By the time the ion arrives at the gap between the Dees, the polarity of the Dees gets reversed. Hence the particle is once again accelerated and moves into the other Dee with a greater velocity along a circle of greater radius. Thus the particle moves in a spiral path of increasing radius and when it comes near the edge, it is taken out with the help of a deflector plate (D.P). The particle with high energy is now allowed to hit the target T.
Note: According to the concept of magnetic lorentz force, when the particle moves along a circle of radius r with a velocity v then the magnetic lorentz force provides the necessary centripetal force which means that here the magnetic lorentz force will be equal to the centripetal force i.e., Bqv = $\dfrac{{{\text{m}}{{\text{v}}^2}}}{{\text{r}}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




