
Describe in brief the structure and functions of human blood.
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Blood is a fluid connective tissue. Blood is composed of a fluid matrix, plasma, and formed elements. Plasma in the blood is a straw-colored, viscous fluid which accounts for 50-55% of blood. Plasma has 90-92% of water and 6-8% of proteins.
Complete answer:
Every living organism is either unicellular or multicellular. The body organization in different individuals describes their complexity. Unicellular organisms are made of only a single cell whereas multicellular organisms are made of multiple cells. Multicellular organisms exhibit complexity in their body organization in which they are either loose cell aggregates or cells are grouped into tissues and tissues form organs and organs form an organ system.
Blood is a connective tissue that consists of a matrix, plasma, and elements and proteins. Fibrinogen, albumins, and globulins are the main proteins. Globulins are involved in defense, albumins are involved in osmotic balance, and fibrinogens are involved in blood clotting. Formed elements of blood include RBCs, WBCs, and platelets. Blood has the function of transport of nutrients, exchange of gases, transport of hormones, regulation of body temperature, protection against foreign agents, maintenance of pH, and regulation of osmosis.
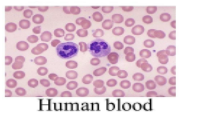
- Blood has RBCs, WBCs, and platelets as formed elements. RBCs are red blood cells or erythrocytes and are most abundant in human blood and involved in the transport of oxygen. RBCs of humans don't possess nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria. This frees up space and makes them efficient to carry hemoglobin molecules and without using energy for themselves. They are biconcave in shape.
- WBCs are white blood cells or leukocytes are involved in the defense mechanism of the body. They possess nuclei and have an ability to squeeze out (diapedesis) to engulf any foreign agent. They are of two types-granulocytes- (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes).
- Platelets are involved in blood clotting. They are formed by the division of megakaryocytes.
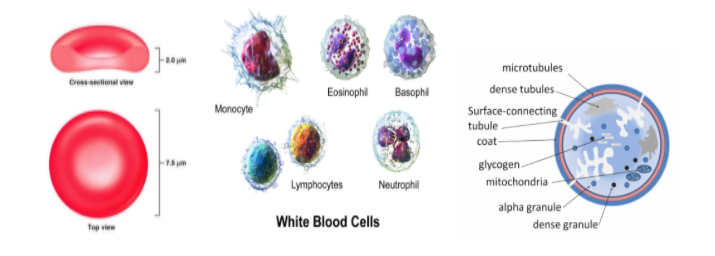
Note: Blood has a protective function as it has WBCs which are immune cells. Platelets (or thrombocytes) are involved in clot formation. Blood is also involved in the transport of waste materials, hormones, and enzymes. RBCs are also responsible to maintain the viscosity and pH of the blood. The pH of human blood is 7.35 to 7.45 indicating a slightly basic nature.
Complete answer:
Every living organism is either unicellular or multicellular. The body organization in different individuals describes their complexity. Unicellular organisms are made of only a single cell whereas multicellular organisms are made of multiple cells. Multicellular organisms exhibit complexity in their body organization in which they are either loose cell aggregates or cells are grouped into tissues and tissues form organs and organs form an organ system.
Blood is a connective tissue that consists of a matrix, plasma, and elements and proteins. Fibrinogen, albumins, and globulins are the main proteins. Globulins are involved in defense, albumins are involved in osmotic balance, and fibrinogens are involved in blood clotting. Formed elements of blood include RBCs, WBCs, and platelets. Blood has the function of transport of nutrients, exchange of gases, transport of hormones, regulation of body temperature, protection against foreign agents, maintenance of pH, and regulation of osmosis.

- Blood has RBCs, WBCs, and platelets as formed elements. RBCs are red blood cells or erythrocytes and are most abundant in human blood and involved in the transport of oxygen. RBCs of humans don't possess nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria. This frees up space and makes them efficient to carry hemoglobin molecules and without using energy for themselves. They are biconcave in shape.
- WBCs are white blood cells or leukocytes are involved in the defense mechanism of the body. They possess nuclei and have an ability to squeeze out (diapedesis) to engulf any foreign agent. They are of two types-granulocytes- (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes).
- Platelets are involved in blood clotting. They are formed by the division of megakaryocytes.

Note: Blood has a protective function as it has WBCs which are immune cells. Platelets (or thrombocytes) are involved in clot formation. Blood is also involved in the transport of waste materials, hormones, and enzymes. RBCs are also responsible to maintain the viscosity and pH of the blood. The pH of human blood is 7.35 to 7.45 indicating a slightly basic nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




