
Derive \[{v^2} - {u^2} = 2as?\]
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Concept of the area under speed and time graph gives distance and area covered under velocity-time graph gives the displacement.
Complete step by step solution: There are three equations of motion out of which this is the third one which is used to calculate initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration or displacement by the object. In order to derive the equation let us consider the velocity-time graph for a body having some non-zero initial velocity at time \[t{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0\]
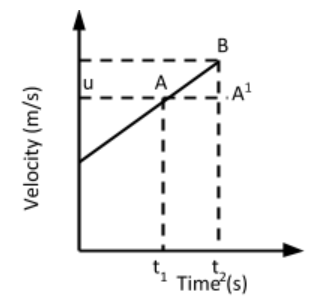
u is velocity at time $t_1$
v is velocity at time $t_2$
a is acceleration of the body along the straight line.
Displacement covered during the time interval \[{t_2} - {t_2} = {\text{ }}Area\]under AB i.e. $AB{t_1}{t_2} = s$
$s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times ({\text{sum of parallel sides)}} \times \,perpendicular\,dis\tan ce$
$S = \dfrac{1}{2}(v + u)t\,.....(i)$
There will be some situations when we don’t have any information about time and so it would be a good idea to derive an equation that does not have a t term. To do this we rearrange our first equation of motion $v = u + at$ to get
$t = \dfrac{{y - u}}{a}\,....(ii)$
And use this in equation (i) to replace t from equation (i), we get
$
s = \dfrac{1}{2}(v + u)\dfrac{{(v - u)}}{a} \\
as = \dfrac{1}{2}({v^2} - {u^2}) \\
\Rightarrow {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as \\
{v^2} = {u^2} + 2as \\
$
Which is the desired equation of motion.
Additional information: To solve problems using equations of motion, we should remember that
(1) If body starts from rest, it initial velocity = u = 0
(2) If we drop a body from some height, its Initial velocity = u = 0
(3) If body stops, its Final velocity = v = 0
(4) If body moves with uniform velocity, its Acceleration = a = 0
Note: Before applying the concept of the area under velocity and time graph, we will check if the v-t graph is linear or not and start with a non-zero value of velocity to derive the above expression.
Complete step by step solution: There are three equations of motion out of which this is the third one which is used to calculate initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration or displacement by the object. In order to derive the equation let us consider the velocity-time graph for a body having some non-zero initial velocity at time \[t{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0\]

u is velocity at time $t_1$
v is velocity at time $t_2$
a is acceleration of the body along the straight line.
Displacement covered during the time interval \[{t_2} - {t_2} = {\text{ }}Area\]under AB i.e. $AB{t_1}{t_2} = s$
$s = \dfrac{1}{2} \times ({\text{sum of parallel sides)}} \times \,perpendicular\,dis\tan ce$
$S = \dfrac{1}{2}(v + u)t\,.....(i)$
There will be some situations when we don’t have any information about time and so it would be a good idea to derive an equation that does not have a t term. To do this we rearrange our first equation of motion $v = u + at$ to get
$t = \dfrac{{y - u}}{a}\,....(ii)$
And use this in equation (i) to replace t from equation (i), we get
$
s = \dfrac{1}{2}(v + u)\dfrac{{(v - u)}}{a} \\
as = \dfrac{1}{2}({v^2} - {u^2}) \\
\Rightarrow {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as \\
{v^2} = {u^2} + 2as \\
$
Which is the desired equation of motion.
Additional information: To solve problems using equations of motion, we should remember that
(1) If body starts from rest, it initial velocity = u = 0
(2) If we drop a body from some height, its Initial velocity = u = 0
(3) If body stops, its Final velocity = v = 0
(4) If body moves with uniform velocity, its Acceleration = a = 0
Note: Before applying the concept of the area under velocity and time graph, we will check if the v-t graph is linear or not and start with a non-zero value of velocity to derive the above expression.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




