
Define resonance (mesomeric)effect.
Answer
512.1k+ views
Hint :The resonance or mesomeric effect is the withdrawal or releasing effect of electrons assigned to a specific substituent through delocalization of pi electrons, which may be demonstrated by sketching different canonical structures.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When components other than carbon atoms and hydrogen actively participate in the creation of molecular bonds, electron behaviour alters in Organic Chemistry. Furthermore, the electromeric effect, inductive effect, resonance effects, hyperconjugation, and other electronic variables influence organic processes. All of these components have different relationships with organic molecules. The six elements carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, sulphur, and phosphorus make up the majority of biological compounds. They do not, however, prohibit organic molecules from acquiring a wide range of chemical reactivity and physical attributes. A resonance effect or mesomeric effect is the withdrawal or release of electrons associated to a specific substituent through the delocalization of or pi-electrons, which may be demonstrated by sketching various canonical structures. The resonance effect is represented by the M or R symbols. The polarity created in a molecule by the interaction between a lone pair of electrons and a pi bond is described by the resonance effect. It can also happen when two pi bonds in nearby atoms engage. In its most basic form, resonance refers to molecules that have numerous Lewis structures. In chemistry, resonance aids in the study of a compound's stability as well as its energy states.
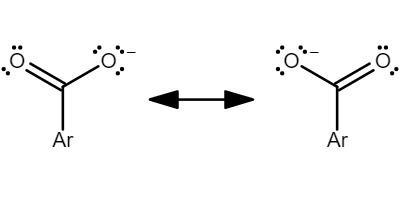
Note :
The resonance effect is a chemical phenomena that is found in organic molecules that contain double bonds. Organic molecules feature these double bonds in their structures, and the p-orbitals on the two opposite sides of carbon atoms are frequently overlapping.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When components other than carbon atoms and hydrogen actively participate in the creation of molecular bonds, electron behaviour alters in Organic Chemistry. Furthermore, the electromeric effect, inductive effect, resonance effects, hyperconjugation, and other electronic variables influence organic processes. All of these components have different relationships with organic molecules. The six elements carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, sulphur, and phosphorus make up the majority of biological compounds. They do not, however, prohibit organic molecules from acquiring a wide range of chemical reactivity and physical attributes. A resonance effect or mesomeric effect is the withdrawal or release of electrons associated to a specific substituent through the delocalization of or pi-electrons, which may be demonstrated by sketching various canonical structures. The resonance effect is represented by the M or R symbols. The polarity created in a molecule by the interaction between a lone pair of electrons and a pi bond is described by the resonance effect. It can also happen when two pi bonds in nearby atoms engage. In its most basic form, resonance refers to molecules that have numerous Lewis structures. In chemistry, resonance aids in the study of a compound's stability as well as its energy states.

Note :
The resonance effect is a chemical phenomena that is found in organic molecules that contain double bonds. Organic molecules feature these double bonds in their structures, and the p-orbitals on the two opposite sides of carbon atoms are frequently overlapping.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




