
Define osmosis.
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: Osmosis is a type of movement of solvent molecules. Osmosis tends to maintain equilibrium between both sides of the region. The solvent molecules move from a low solute concentration area to a high concentration solute area to equalize the solute and solvent molecules in that region.
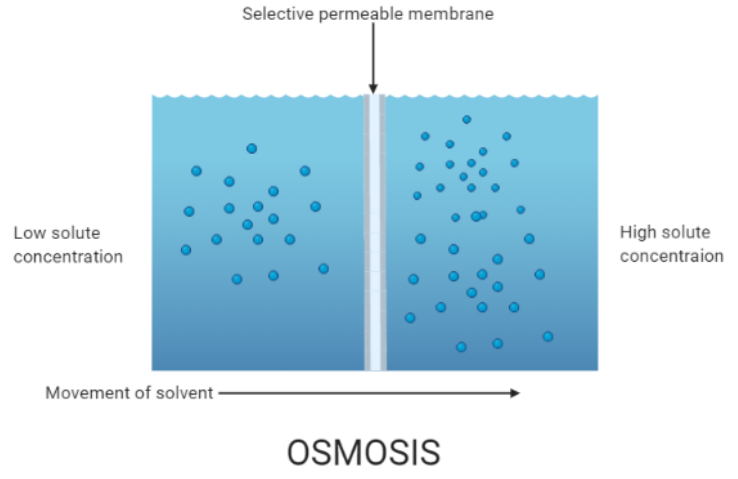
Complete step by step answer: The spontaneous net movement which involves the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration is called osmosis. It tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides inducing equilibrium on both sides. As biological membranes are semi-permeable osmosis is a vital process in biological systems. Semipermeable membranes are not permeable to large and polar molecules which include ions, proteins, and polysaccharides. When a cell is allowed to submerge in water, the movement of water molecules occurs from a low solute concentration area to a high solute concentration area across the cell membrane. For example, if a cell is submerged in saltwater, water molecules move out of the cell through the cell membrane as the solute concentration is higher outside the cell whereas if the cell is submerged in freshwater the water molecules will tend to move inside the cell. Water is the typical solvent in biological systems but osmosis can also occur through other liquids, gases, and supercritical liquids.
Note: Osmosis can also be defined as a simple physical process in which the solvent moves across the selectively permeable membrane in order to separate the two solutions having different concentrations. Osmosis and diffusion are totally different processes. Diffusion can be defined as a physical process in which the net movement of anything takes place from a high concentration area to a lower concentration area.
Complete step by step answer: The spontaneous net movement which involves the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration is called osmosis. It tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides inducing equilibrium on both sides. As biological membranes are semi-permeable osmosis is a vital process in biological systems. Semipermeable membranes are not permeable to large and polar molecules which include ions, proteins, and polysaccharides. When a cell is allowed to submerge in water, the movement of water molecules occurs from a low solute concentration area to a high solute concentration area across the cell membrane. For example, if a cell is submerged in saltwater, water molecules move out of the cell through the cell membrane as the solute concentration is higher outside the cell whereas if the cell is submerged in freshwater the water molecules will tend to move inside the cell. Water is the typical solvent in biological systems but osmosis can also occur through other liquids, gases, and supercritical liquids.

Note: Osmosis can also be defined as a simple physical process in which the solvent moves across the selectively permeable membrane in order to separate the two solutions having different concentrations. Osmosis and diffusion are totally different processes. Diffusion can be defined as a physical process in which the net movement of anything takes place from a high concentration area to a lower concentration area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




