
Define optical centre of a spherical lens.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The light travelling through lens undergoes the refraction. Hence, the principle of refraction must be understood first, before understanding the concept of lens and image formation in the lens.
Complete step by step solution:
Refraction is the phenomenon in which the light ray travelling from one medium to another medium of different optical density, deviates from its usual path towards or away from the normal.
The refraction is governed by Snell’s law which gives the following equation:
${n_{12}} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
where, ${n_{12}}$ is the refractive index for the pair of media and i & r are the incident and refracted angles.
Lens is an optical device made of a transparent material, that focuses or diverges an incoming light beam by refraction. There are two major types of lens, namely, biconvex and biconcave lens.
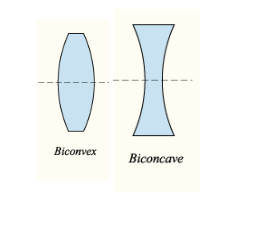
The biconvex lens is called converging lens because it converges the incoming ray to a point called principal focus and the biconcave lens is called diverging lens because it diverges the incoming ray in a direction, which is along the point called principal focus.
Let us understand the refraction in the lens by taking the example of a biconvex lens.
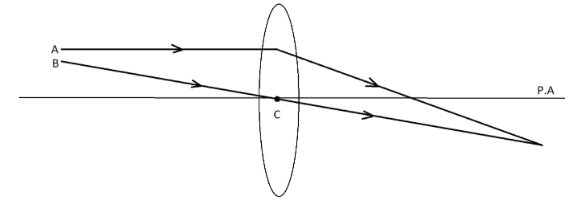
The line passing through the middle of the lens is called principal axis. The point at which the principal axis passes through the lens is called the optical centre of the lens, denoted by C in the figure above.
Consider 2 rays, A and B as shown the figure. The ray A after passing through the lens, refracts and bends towards the principal axis. The ray B, after passing through the optical centre, C goes undeviated.
The optical centre of the lens is the central point of the lens where the incoming ray goes undeviated.
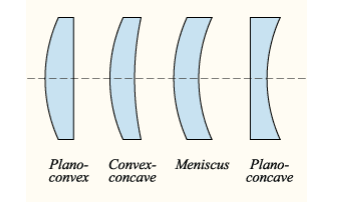
Note: The biconvex and biconcave are the most common types of lens used, commercially and scientifically. However, for special purposes, there are other kinds of lens used, such as plano-concave lens, plano-convex lens, concave-convex lens and meniscus.
Complete step by step solution:
Refraction is the phenomenon in which the light ray travelling from one medium to another medium of different optical density, deviates from its usual path towards or away from the normal.
The refraction is governed by Snell’s law which gives the following equation:
${n_{12}} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
where, ${n_{12}}$ is the refractive index for the pair of media and i & r are the incident and refracted angles.
Lens is an optical device made of a transparent material, that focuses or diverges an incoming light beam by refraction. There are two major types of lens, namely, biconvex and biconcave lens.

The biconvex lens is called converging lens because it converges the incoming ray to a point called principal focus and the biconcave lens is called diverging lens because it diverges the incoming ray in a direction, which is along the point called principal focus.
Let us understand the refraction in the lens by taking the example of a biconvex lens.

The line passing through the middle of the lens is called principal axis. The point at which the principal axis passes through the lens is called the optical centre of the lens, denoted by C in the figure above.
Consider 2 rays, A and B as shown the figure. The ray A after passing through the lens, refracts and bends towards the principal axis. The ray B, after passing through the optical centre, C goes undeviated.
The optical centre of the lens is the central point of the lens where the incoming ray goes undeviated.
Note: The biconvex and biconcave are the most common types of lens used, commercially and scientifically. However, for special purposes, there are other kinds of lens used, such as plano-concave lens, plano-convex lens, concave-convex lens and meniscus.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




