
Define Interconversion of matter.
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: The question will be easily understandable after knowing what is matter. In chemistry, Matter is any substance which has mass and taking up space means it has volume. Matter is something which can be touched and is composed of atoms and its sub-particles.
Complete answer:
All matter can change from one state to another. This is called interconversion of matter. Matter can move from one state to another when specific physical conditions change, the physical conditions such as temperature and pressure of the substance. There are three types of matter: solid, liquid and gases. The interconversion of state of matter occurs by different processes. The processes include-
(1) Vaporization: It is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapour. Boiling point is the temperature at which liquid changes to vapour. For example: Boiling of water. Water changes to vapours at 100$^\circ$C.
(2) Freezing also known as solidification: It is a state transition in which a liquid changes to solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. Freezing point is the temperature at which liquid changes to solid. Water turning to ice is one such example of freezing.
(3) Sublimation: The change from solid state to vapour state without passing through the liquid state and vice-versa is called sublimation and the substance is called sublime. Example: Dry ice ( solid $CO_2$ ) and iodine sublimes.
(4) Melting: The temperature at which a given substance changes from a solid to a liquid is called its melting point. Example: Ice melts at 0$^\circ$C.
Additional Information: Properties of matter:
> States of matter are interconvertible by applying heat and pressure to them.
> Liquids on further heating get converted into gases.
> When solids are heated, the intermolecular force of attraction between particles decreases and they get converted into liquids.
> Gases do not have any fixed shape and volume because intermolecular force of attraction is almost negligible or zero.
Note: The processes involved in the interconversion of matter can be simply remembered by a simple and catchy flowchart.
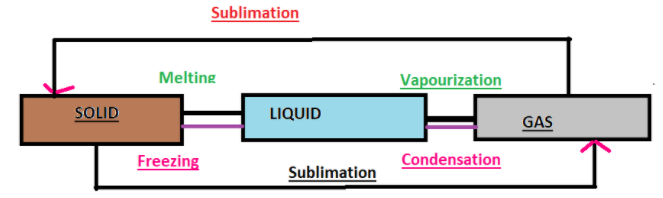
Complete answer:
All matter can change from one state to another. This is called interconversion of matter. Matter can move from one state to another when specific physical conditions change, the physical conditions such as temperature and pressure of the substance. There are three types of matter: solid, liquid and gases. The interconversion of state of matter occurs by different processes. The processes include-
(1) Vaporization: It is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapour. Boiling point is the temperature at which liquid changes to vapour. For example: Boiling of water. Water changes to vapours at 100$^\circ$C.
(2) Freezing also known as solidification: It is a state transition in which a liquid changes to solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. Freezing point is the temperature at which liquid changes to solid. Water turning to ice is one such example of freezing.
(3) Sublimation: The change from solid state to vapour state without passing through the liquid state and vice-versa is called sublimation and the substance is called sublime. Example: Dry ice ( solid $CO_2$ ) and iodine sublimes.
(4) Melting: The temperature at which a given substance changes from a solid to a liquid is called its melting point. Example: Ice melts at 0$^\circ$C.
Additional Information: Properties of matter:
> States of matter are interconvertible by applying heat and pressure to them.
> Liquids on further heating get converted into gases.
> When solids are heated, the intermolecular force of attraction between particles decreases and they get converted into liquids.
> Gases do not have any fixed shape and volume because intermolecular force of attraction is almost negligible or zero.
Note: The processes involved in the interconversion of matter can be simply remembered by a simple and catchy flowchart.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




