
Define ideal simple pendulum. Show that under certain conditions, a simple pendulum performs linear simple harmonic motion.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Whenever the force is directly proportional to the negative of displacement, then it means that the body will execute a simple harmonic motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Ideal simple pendulum: An ideal simple pendulum is one which consists of a point mass suspended by a weightless inextensible perfectly flexible thread and free to vibrate without any friction.
Simple pendulum executing simple harmonic motion:
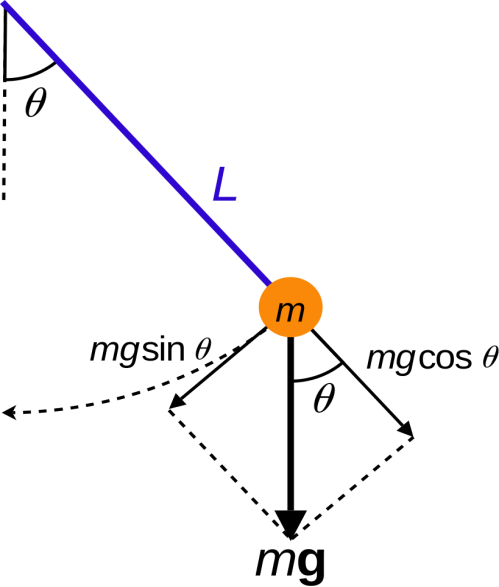
Let the mass of the bob is m, and L is the length to which it is suspended from a rigid support.
Let $\theta $ be the small angle in the vertical plane to which it is displaced, g is the acceleration due to gravity. Now resolves the weight components in vertical and horizontal components.
The two resolved components are $mg\sin \theta $ and$mg\cos \theta $.
Now the restoring force is given by-
$F = - mg\sin \theta $
Now as $\theta $ is very small therefore,$\sin \theta \approx \theta $
$F = - mg\theta $ …………..(1)
And $\theta = \dfrac{x}{L}$
Now substituting this in eq.(1) we get,
$F = - mg\left( {\dfrac{x}{L}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow F \propto \left( { - x} \right)$
Since the restoring force is directly proportional to the negative of the displacement, hence the motion of the simple pendulum is simple harmonic in nature (SHM).
Conditions for a simple pendulum: Followings are the conditions of a simple pendulum-
(i) Bob must be a point heavy mass.
(ii) It must be suspended with a thread of negligible weight.
(iii) It must be supported by rigid support.
(iv) The amplitude should be very small.
Note:
Also remember that the acceleration is given by-
$
ma = - mg\dfrac{x}{L} \\
\Rightarrow a = - \dfrac{x}{L}g \\
$
Magnitude of Acceleration per unit displacement $\left| {\dfrac{a}{x}} \right| = \dfrac{g}{L}$
Time period is given by-
$
T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{L}} }} \\
\Rightarrow T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{g}} \\
$
Complete step by step answer:
Ideal simple pendulum: An ideal simple pendulum is one which consists of a point mass suspended by a weightless inextensible perfectly flexible thread and free to vibrate without any friction.
Simple pendulum executing simple harmonic motion:
Let the mass of the bob is m, and L is the length to which it is suspended from a rigid support.
Let $\theta $ be the small angle in the vertical plane to which it is displaced, g is the acceleration due to gravity. Now resolves the weight components in vertical and horizontal components.
The two resolved components are $mg\sin \theta $ and$mg\cos \theta $.
Now the restoring force is given by-
$F = - mg\sin \theta $
Now as $\theta $ is very small therefore,$\sin \theta \approx \theta $
$F = - mg\theta $ …………..(1)
And $\theta = \dfrac{x}{L}$
Now substituting this in eq.(1) we get,
$F = - mg\left( {\dfrac{x}{L}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow F \propto \left( { - x} \right)$
Since the restoring force is directly proportional to the negative of the displacement, hence the motion of the simple pendulum is simple harmonic in nature (SHM).

Conditions for a simple pendulum: Followings are the conditions of a simple pendulum-
(i) Bob must be a point heavy mass.
(ii) It must be suspended with a thread of negligible weight.
(iii) It must be supported by rigid support.
(iv) The amplitude should be very small.
Note:
Also remember that the acceleration is given by-
$
ma = - mg\dfrac{x}{L} \\
\Rightarrow a = - \dfrac{x}{L}g \\
$
Magnitude of Acceleration per unit displacement $\left| {\dfrac{a}{x}} \right| = \dfrac{g}{L}$
Time period is given by-
$
T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{L}} }} \\
\Rightarrow T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{g}} \\
$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




