
How to convert toluene to p-methyl benzoic acid?
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: The answer is based on the two step reaction where the first reaction is the Friedel – Crafts halogenations and this is followed by carboxylation of a Grignard reagent. Write the reactions to get the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
The concept of mechanism of the organic reactions and also some of the named reactions as well are familiar to us from the lower classes of organic chemistry.
Let us now see in detail about this reaction given and write its mechanism of reaction.
- Since toluene cannot be directly converted into acid, in the first step it is made to undergo the halogenation reaction particularly Friedel – Crafts halogenation where the compound is treated with bromine in the presence of alkyl bromide. The reaction is shown below:
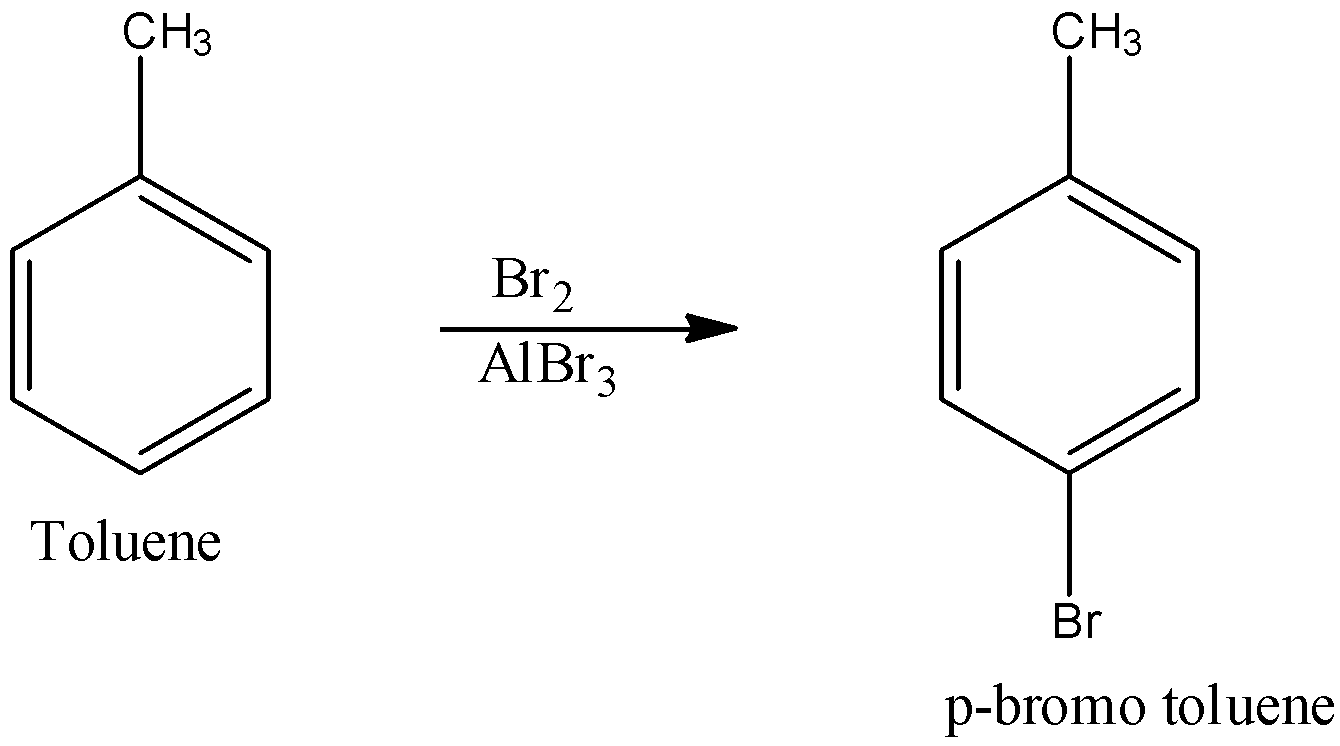
This reaction produces para bromo toluene.
- In the next step, this compound will undergo carboxylation reaction in the presence of Grignard reagent that is magnesium in dry ether which further reacts with carbon dioxide to yield p-methyl benzoic acid. The reaction is:
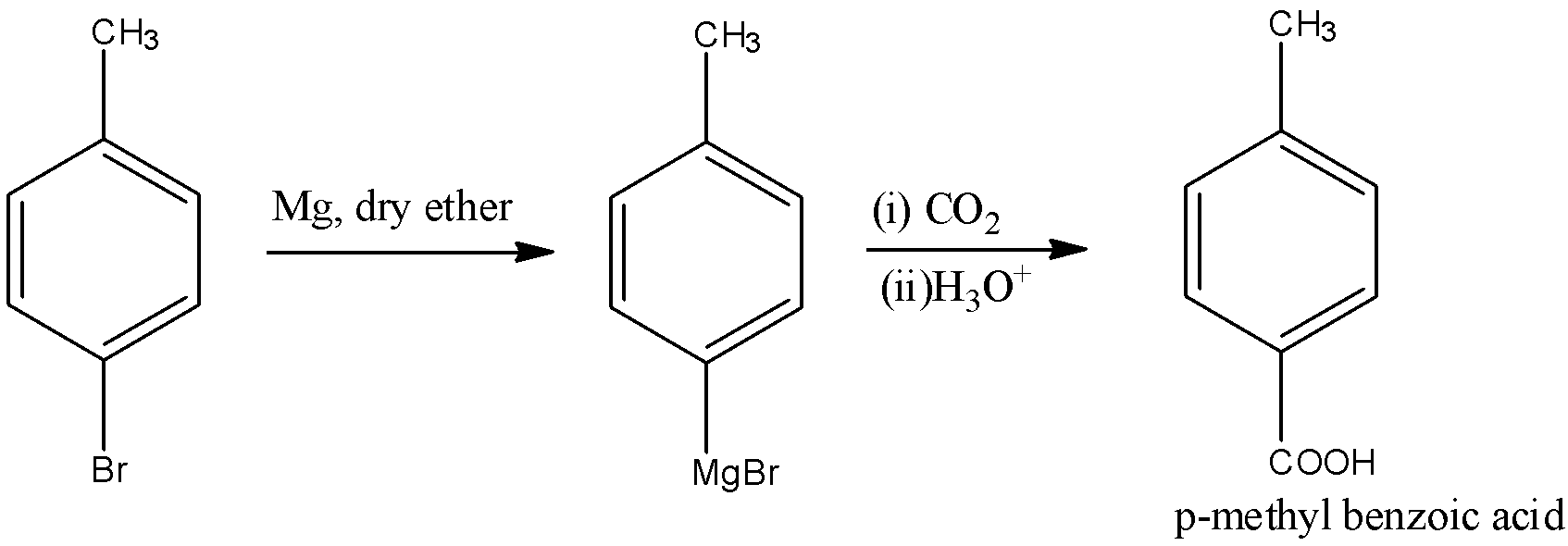
Here, magnesium in dry ether is nothing but the synthesis procedure for the Grignard reagent where organic halide reacts with magnesium metal and the cyclic or acyclic ethers stabilize the organomagnesium compounds.
Note: Note that aluminium bromide is the Lewis acid which acts as a catalyst to activate it to become a very strong electrophile and therefore bromine acts as an electrophile which will be substituted in para position of toluene where bromine alone cannot be good electrophile.
Complete step by step answer:
The concept of mechanism of the organic reactions and also some of the named reactions as well are familiar to us from the lower classes of organic chemistry.
Let us now see in detail about this reaction given and write its mechanism of reaction.
- Since toluene cannot be directly converted into acid, in the first step it is made to undergo the halogenation reaction particularly Friedel – Crafts halogenation where the compound is treated with bromine in the presence of alkyl bromide. The reaction is shown below:

This reaction produces para bromo toluene.
- In the next step, this compound will undergo carboxylation reaction in the presence of Grignard reagent that is magnesium in dry ether which further reacts with carbon dioxide to yield p-methyl benzoic acid. The reaction is:

Here, magnesium in dry ether is nothing but the synthesis procedure for the Grignard reagent where organic halide reacts with magnesium metal and the cyclic or acyclic ethers stabilize the organomagnesium compounds.
Note: Note that aluminium bromide is the Lewis acid which acts as a catalyst to activate it to become a very strong electrophile and therefore bromine acts as an electrophile which will be substituted in para position of toluene where bromine alone cannot be good electrophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




