
How will you convert the following: Benzene diazonium chloride to phenol.
Answer
517.8k+ views
Hint: Benzene diazonium chloride, $[{C_6}{H_5}{N_2}]Cl$ is an organic salt of diazonium cation and chloride anion. The positive charge is on the nitrogen atom while the negative charge is on the chlorine atom. It is a colorless, crystalline solid which is soluble in water and other polar solvents. It is prepared by diazotization of aniline in the presence of HCl.
Complete answer:
Benzene diazonium chloride, $[{C_6}{H_5}{N_2}]Cl$ is prepared from the reaction aniline, ${C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}$ with nitrous acid by diazotization reaction at very low temperature $(273K - 278K)$ .
Diazotisation: It is the processing of converting primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts.
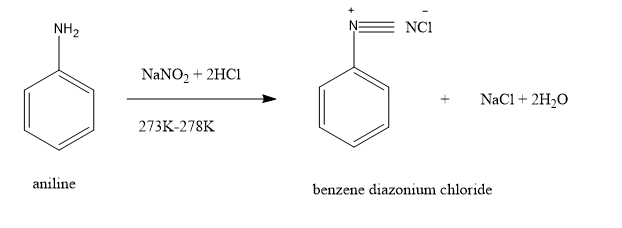
Here, nitrous acid is produced by reacting sodium nitrite with HCl.
Benzene diazonium chloride is stable only at cold conditions and therefore has to be immediately used after preparation due to its instability. These salts can undergo reaction by either displacing the nitrogen atom attached to the ring or by retaining the diazo group. Diazonium salts are water soluble salts that are stable only at low temperature. If the temperature is raised to $283\,K$ , the nitrogen group gets replaced by hydroxyl (OH) group. The above hydrolysis reaction results in the production of phenol.
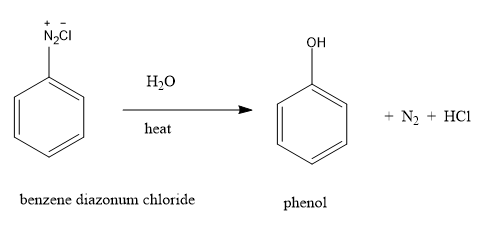
By the above hydrolysis reaction, we can convert benzene diazonium chloride to phenol.
Note:
Benzene diazonium salts are soluble in water. Phenol can be prepared only by heating the aqueous solution. These salts act as good intermediates for the introduction of various functional groups like $ - Cl, - F, - Br, - I, - OH, - CN, - N{O_2}$ on the benzene ring. Reactions involving retention of the diazo group include coupling reactions. Coupling of benzene diazonium salts with phenol and aryl amines gives azo dyes that have various applications in the field of chemistry.
Complete answer:
Benzene diazonium chloride, $[{C_6}{H_5}{N_2}]Cl$ is prepared from the reaction aniline, ${C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}$ with nitrous acid by diazotization reaction at very low temperature $(273K - 278K)$ .
Diazotisation: It is the processing of converting primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts.

Here, nitrous acid is produced by reacting sodium nitrite with HCl.
Benzene diazonium chloride is stable only at cold conditions and therefore has to be immediately used after preparation due to its instability. These salts can undergo reaction by either displacing the nitrogen atom attached to the ring or by retaining the diazo group. Diazonium salts are water soluble salts that are stable only at low temperature. If the temperature is raised to $283\,K$ , the nitrogen group gets replaced by hydroxyl (OH) group. The above hydrolysis reaction results in the production of phenol.

By the above hydrolysis reaction, we can convert benzene diazonium chloride to phenol.
Note:
Benzene diazonium salts are soluble in water. Phenol can be prepared only by heating the aqueous solution. These salts act as good intermediates for the introduction of various functional groups like $ - Cl, - F, - Br, - I, - OH, - CN, - N{O_2}$ on the benzene ring. Reactions involving retention of the diazo group include coupling reactions. Coupling of benzene diazonium salts with phenol and aryl amines gives azo dyes that have various applications in the field of chemistry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




