
How many constitutional isomers are there for $ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}} $ ?
Answer
561k+ views
Hint The answer lies in the fact that constitutional isomers are those isomers which have the same number of atoms of each of the elements but differ in the presence of bonds between them that is which is having the distinct bond between them.
Complete step – by – step answer:
We are familiar with the concepts of organic chemistry which tells us about the types of isomers that can be formed by one molecule and also the variation in their structures or geometries from the lower classes of chemistry.
Now, let us see the detailed study about the isomers and its types which also include the constitutional isomers.
- Isomers are the molecules with the same molecular formula but have the distinct arrangement of atoms in space.
- There are many types of isomers among which a constitutional isomer is one of them which is defined as isomers that have the same number of atoms of each of the elements but are having the distinct bond between them.
- In the given formula $ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}} $ , the isomers which we can think of makes it to become 25 possible isomers because it can be taken as open chain as well as cyclic structure.
- Since, there are 25 constitutional isomers according to the study but it is also said that there are more than 30 isomers.
- Let us list out some possible isomers which are classified as acyclic and cyclic.
- Acyclic isomers:
1-hexene, 2-hexene, 3-hexene, 2-methyl -1-pentene, 3-methyl-1-pentene, 4-methyl-1-pentene, 2-methyl-2-pentene, 3-methyl-2-pentene, 4-methyl-2-pentene, 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene, 3,3-dimethyl-butene, 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
- Cyclic isomers:
Cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, 1,1-dimethylcyclobutane, 1,2-dimethylcyclobutane, 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane, 1,1,2-trimethylcyclopropane, 1,2,3-trimethylcyclopropane, 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclopropane, 1-ethyl-2-methylcyclopropane, Isopropylcyclopropane, Propylcyclopropane.
Apart from this there can also be cic-trans isomers and enantiomers.
- Let us draw the structures of two simple molecules each from acyclic and cyclic isomers.
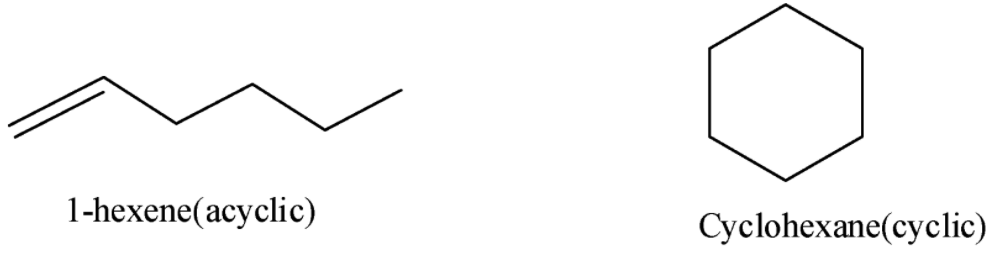
Note: Note that the constitutional isomers were also called as metamers formerly which have the same meaning and this concept also applies to the polyatomic ions with the same total charge and the example which can be cited is the cyanate ion.
Complete step – by – step answer:
We are familiar with the concepts of organic chemistry which tells us about the types of isomers that can be formed by one molecule and also the variation in their structures or geometries from the lower classes of chemistry.
Now, let us see the detailed study about the isomers and its types which also include the constitutional isomers.
- Isomers are the molecules with the same molecular formula but have the distinct arrangement of atoms in space.
- There are many types of isomers among which a constitutional isomer is one of them which is defined as isomers that have the same number of atoms of each of the elements but are having the distinct bond between them.
- In the given formula $ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}} $ , the isomers which we can think of makes it to become 25 possible isomers because it can be taken as open chain as well as cyclic structure.
- Since, there are 25 constitutional isomers according to the study but it is also said that there are more than 30 isomers.
- Let us list out some possible isomers which are classified as acyclic and cyclic.
- Acyclic isomers:
1-hexene, 2-hexene, 3-hexene, 2-methyl -1-pentene, 3-methyl-1-pentene, 4-methyl-1-pentene, 2-methyl-2-pentene, 3-methyl-2-pentene, 4-methyl-2-pentene, 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene, 3,3-dimethyl-butene, 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
- Cyclic isomers:
Cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, 1,1-dimethylcyclobutane, 1,2-dimethylcyclobutane, 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane, 1,1,2-trimethylcyclopropane, 1,2,3-trimethylcyclopropane, 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclopropane, 1-ethyl-2-methylcyclopropane, Isopropylcyclopropane, Propylcyclopropane.
Apart from this there can also be cic-trans isomers and enantiomers.
- Let us draw the structures of two simple molecules each from acyclic and cyclic isomers.
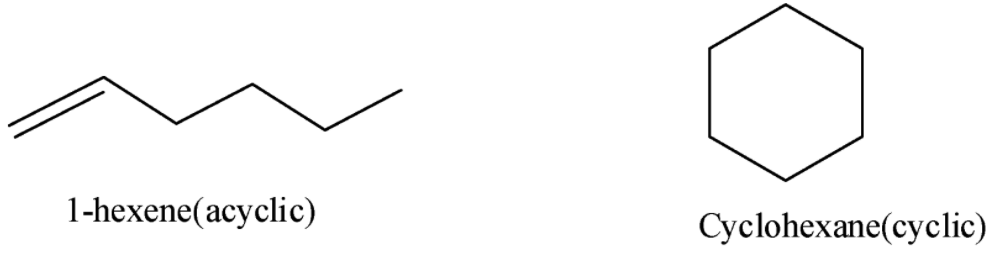
Note: Note that the constitutional isomers were also called as metamers formerly which have the same meaning and this concept also applies to the polyatomic ions with the same total charge and the example which can be cited is the cyanate ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




