
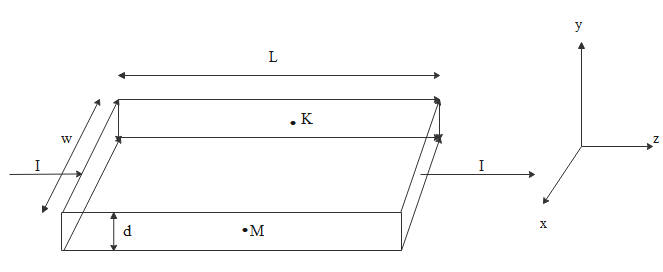
Consider two different metallic strips (1 and 2) of the same material. Their lengths are the same, widths are ${w_1}$ and ${w_2}$ and thicknesses are ${d_1}$ and ${d_2}$, respectively. Two points K and M are symmetrically located on the opposite faces parallel to the x-y plane. ${V_1}$ and ${V_2}$ are the potential differences between K and M in strips 1 and 2, respectively. Then, for a given current I flowing through them in a given magnetic field strength B, the correct statement(s) is (are)
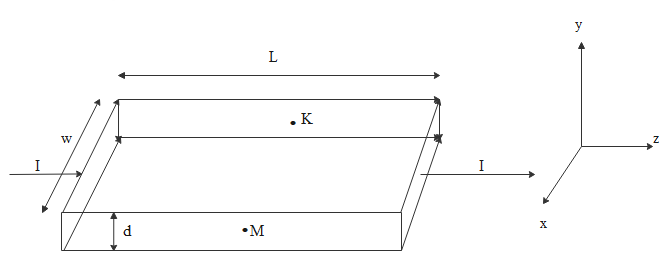
A. If ${w_1} = {w_2}$ and ${d_1} = 2{d_2}$, then ${V_2} = 2{V_1}$
B. If ${w_1} = {w_2}$ and ${d_1} = 2{d_2}$, then ${V_2} = {V_1}$
C. If ${w_1} = 2{w_2}$ and ${d_1} = {d_2}$, then ${V_2} = 2{V_1}$
D. If ${w_1} = 2{w_2}$ and ${d_1} = {d_2}$, then ${V_2} = {V_1}$

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: If there is a charge, an electric field and magnetic field is acting on that charge then force will be produced due to both electric and magnetic fields. The current passing through the cross section can be expressed in terms of area of cross section. By using the above information we will solve the question.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& {F_E} = Eq \cr
& {F_B} = qvB \cr
& I = vAne \cr} $
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that there is a magnetic field B and due to the potential difference generated, an electric field also will be produced. So if we consider the charge ‘q’ it will be acted upon the magnetic force and electric force. we will equate the both forces. We do this because the charge at the slab will be static. Static in the sense the forces should be balanced. Now the current is passing through the cross section. Hence we will apply the formula which will relate current with the drift velocity(v) and area of cross section(A) and charge density(n) and electron charge(e).
Due to the electric field the force acting on the charge ‘q’ will be
${F_E} = Eq$
Due to the magnetic field the force acting on the charge ‘q’ will be
${F_B} = qvB$
We have
$\eqalign{
& {V_M} - {V_K} = Ew \cr
& \Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{{V_M} - {V_K}}}{w} \cr} $
So the electric force will be
${F_E} = Eq = \dfrac{{{V_M} - {V_K}}}{w}q$
$ \Rightarrow {F_E} = {F_B}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_M} - {V_K}}}{w}q = qvB \cr
& \therefore {V_M} - {V_K} = wvB \cr} $
We have
$I = vAne$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow I = v(wd)ne \cr
& \therefore wv = \dfrac{I}{{ned}} \cr} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_M} - {V_K} = wvB$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {V_M} - {V_K} = \dfrac{I}{{ned}}B \cr
& \therefore {V_M} - {V_K}\alpha \dfrac{1}{d} \cr} $
If ${d_1} = 2{d_2}$ that means ${d_2}$ is half of the ${d_1}$ and as the potential difference is inversely proportional to the thickness ${V_2}$ will be twice the ${V_1}$
So if ${w_1} = {w_2}$ and ${d_1} = 2{d_2}$, then ${V_2} = 2{V_1}$
Since the potential difference is not dependant on width at all, if the thicknesses are equal then ${V_1}$ will be equal to ${V_2}$
Hence If ${w_1} = 2{w_2}$ and ${d_1} = {d_2}$, then ${V_2} = {V_1}$
So option A and option D will be correct.
Note: In this question, in case of current flowing we should consider the cross section area perpendicular to the flow of the current. That charges on the slab can’t move anywhere as it is not forming the closed circuit for the charges to flow. Hence we equated the forces so that charges will be at the rest.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& {F_E} = Eq \cr
& {F_B} = qvB \cr
& I = vAne \cr} $
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that there is a magnetic field B and due to the potential difference generated, an electric field also will be produced. So if we consider the charge ‘q’ it will be acted upon the magnetic force and electric force. we will equate the both forces. We do this because the charge at the slab will be static. Static in the sense the forces should be balanced. Now the current is passing through the cross section. Hence we will apply the formula which will relate current with the drift velocity(v) and area of cross section(A) and charge density(n) and electron charge(e).

Due to the electric field the force acting on the charge ‘q’ will be
${F_E} = Eq$
Due to the magnetic field the force acting on the charge ‘q’ will be
${F_B} = qvB$
We have
$\eqalign{
& {V_M} - {V_K} = Ew \cr
& \Rightarrow E = \dfrac{{{V_M} - {V_K}}}{w} \cr} $
So the electric force will be
${F_E} = Eq = \dfrac{{{V_M} - {V_K}}}{w}q$
$ \Rightarrow {F_E} = {F_B}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_M} - {V_K}}}{w}q = qvB \cr
& \therefore {V_M} - {V_K} = wvB \cr} $
We have
$I = vAne$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow I = v(wd)ne \cr
& \therefore wv = \dfrac{I}{{ned}} \cr} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_M} - {V_K} = wvB$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {V_M} - {V_K} = \dfrac{I}{{ned}}B \cr
& \therefore {V_M} - {V_K}\alpha \dfrac{1}{d} \cr} $
If ${d_1} = 2{d_2}$ that means ${d_2}$ is half of the ${d_1}$ and as the potential difference is inversely proportional to the thickness ${V_2}$ will be twice the ${V_1}$
So if ${w_1} = {w_2}$ and ${d_1} = 2{d_2}$, then ${V_2} = 2{V_1}$
Since the potential difference is not dependant on width at all, if the thicknesses are equal then ${V_1}$ will be equal to ${V_2}$
Hence If ${w_1} = 2{w_2}$ and ${d_1} = {d_2}$, then ${V_2} = {V_1}$
So option A and option D will be correct.
Note: In this question, in case of current flowing we should consider the cross section area perpendicular to the flow of the current. That charges on the slab can’t move anywhere as it is not forming the closed circuit for the charges to flow. Hence we equated the forces so that charges will be at the rest.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




