
Consider the nitration of benzene using mixed con. $HN{{O}_{3}}$ and ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$. If a large amount of $KHS{{O}_{4}}$ is added to the mixture, the rate of nitration will be:
(A) Faster
(B) Slower
(C) Unchanged
(D) Doubled
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: As potassium hydrogen sulfate salt is added to the reaction mixture, it will dissociate in the reaction medium. Then we can use Le Chetelier’s principle to predict what will be the effect on the reaction rate.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s see how the nitration of benzene occurs in order to decide what will be the effect of $KHS{{O}_{4}}$ will be upon its addition.
- Nitric acid and sulphuric acid react to give a molecule of water and nitronium ion with hydrogen sulphate ion. So, basically it is a dehydration reaction. This reaction can be given as under.
\[HN{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons N{{O}_{2}}^{+}+HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
- Now, nitronium ion generated here will be attacked by benzene and as a result nitrobenzene will be obtained as a final product. The mechanism can be given as under.
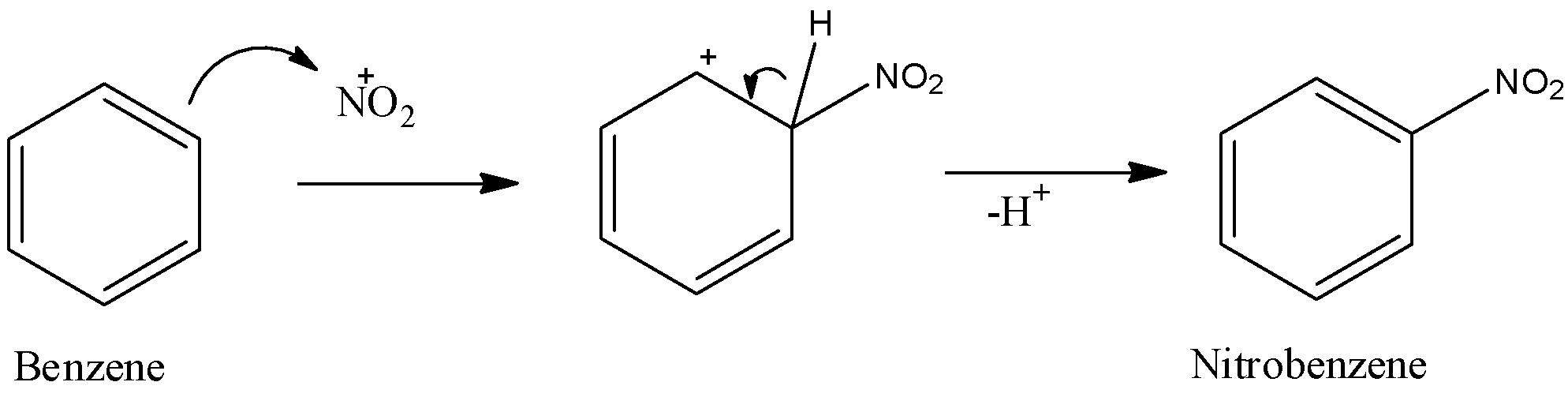
Now, we are given that we are adding a large amount of $KHS{{O}_{4}}$ to the reaction mixture. Now, potassium hydrogen sulphate is a salt and it will dissociate into its ionic form when dissolved in the solution. The dissociation can be given as,
\[KHS{{O}_{4(s)}}\to {{K}^{+}}_{(aq)}+HS{{O}_{4}}{{^{-}}_{(aq)}}\]
Now, addition of hydrogen sulphate and potassium ions will take place in the mixture. So, as we see the reaction of nitric acid and sulphuric acid, we can see that it is a reversible reaction.
- So, according to Le Chetelier’s principle. We can say that addition of hydrogen sulphate ions in the solution will take the reaction equilibrium towards the side of reactants. So, the amount of nitronium ions produced in the reaction mixture will be less.
- As the number of nitronium ions produced in the reaction is less, they will be less available for benzene to be attacked, so we can say that the rate of the reaction will decrease as we add potassium hydrogen sulfate to the mixture.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Remember that potassium hydrogen sulphate is not directly involved in the mechanism of nitration but its addition will decrease the concentration of nitronium ions. Here, the positively charged potassium ions cannot be attacked by benzene rings, so it will not alter the final product.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s see how the nitration of benzene occurs in order to decide what will be the effect of $KHS{{O}_{4}}$ will be upon its addition.
- Nitric acid and sulphuric acid react to give a molecule of water and nitronium ion with hydrogen sulphate ion. So, basically it is a dehydration reaction. This reaction can be given as under.
\[HN{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons N{{O}_{2}}^{+}+HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
- Now, nitronium ion generated here will be attacked by benzene and as a result nitrobenzene will be obtained as a final product. The mechanism can be given as under.

Now, we are given that we are adding a large amount of $KHS{{O}_{4}}$ to the reaction mixture. Now, potassium hydrogen sulphate is a salt and it will dissociate into its ionic form when dissolved in the solution. The dissociation can be given as,
\[KHS{{O}_{4(s)}}\to {{K}^{+}}_{(aq)}+HS{{O}_{4}}{{^{-}}_{(aq)}}\]
Now, addition of hydrogen sulphate and potassium ions will take place in the mixture. So, as we see the reaction of nitric acid and sulphuric acid, we can see that it is a reversible reaction.
- So, according to Le Chetelier’s principle. We can say that addition of hydrogen sulphate ions in the solution will take the reaction equilibrium towards the side of reactants. So, the amount of nitronium ions produced in the reaction mixture will be less.
- As the number of nitronium ions produced in the reaction is less, they will be less available for benzene to be attacked, so we can say that the rate of the reaction will decrease as we add potassium hydrogen sulfate to the mixture.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Remember that potassium hydrogen sulphate is not directly involved in the mechanism of nitration but its addition will decrease the concentration of nitronium ions. Here, the positively charged potassium ions cannot be attacked by benzene rings, so it will not alter the final product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




