
Consider the isoelectronic ions:
${{K}^{+}}$, ${{S}^{2-}}$, $C{{l}^{-}}$, and $C{{a}^{2+}}$
The radii of these ionic species follow the order.
A. $C{{a}^{2+}}>{{K}^{+}}>C{{l}^{-}}>{{S}^{2-}}$
B. $C{{l}^{-}}> {{S}^{2-}}>{{K}^{+}}>C{{a}^{2+}}$
C. ${{S}^{2-}}>C{{l}^{-}}>{{K}^{+}}>C{{a}^{2+}}$
D. ${{K}^{+}}>C{{a}^{2+}}>{{S}^{2-}}>C{{l}^{-}}$
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: For the isoelectronic species, the radii of the atom depends upon their atomic number that is their atomic radii is inversely proportional to their atomic number.
Complete step by step answer:
As we move across a period, the size of the atom decreases while moving down the group, the size of the atom increases. But for the isoelectronic species (i.e. the atoms having the same electronic configuration and number of electrons), the size of the atom is inversely proportional to its atomic number. As per the question, the following are the elements:
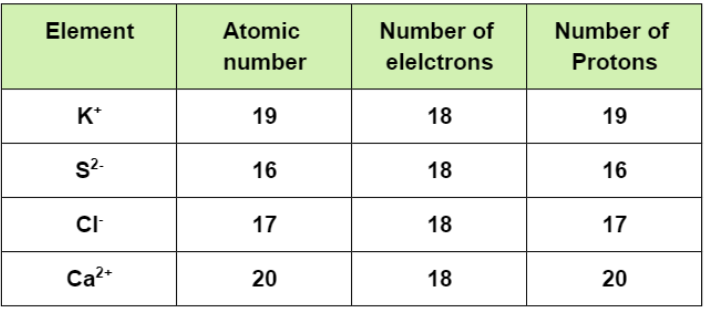
So, for the isoelectronic species, the atom having least effective nuclear charge that is lesser number of protons will exert less force on the valence electron and hence will possess larger atomic radii, while the atom having maximum effective nuclear charge that is a greater number of protons will ultimately have least atomic radii.
And here, as we can see that, Sulphur (S) has the least atomic number that means it will have the least number of protons and hence the largest radii. On the other hand, Calcium (Ca) having maximum number of protons will have the smallest size. So, Sulphur will be followed by Chlorine then Potassium and at last by Calcium i.e.
${{S}^{2-}}>C{{l}^{-}}>{{K}^{+}}>C{{a}^{2+}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: You may get confused with option A considering that atoms having greater number of protons will have larger atomic radii. But it should be kept in mind that, the atom having lesser number of protons will exert less effective nuclear charge thus possessing larger atomic radii.
Complete step by step answer:
As we move across a period, the size of the atom decreases while moving down the group, the size of the atom increases. But for the isoelectronic species (i.e. the atoms having the same electronic configuration and number of electrons), the size of the atom is inversely proportional to its atomic number. As per the question, the following are the elements:

So, for the isoelectronic species, the atom having least effective nuclear charge that is lesser number of protons will exert less force on the valence electron and hence will possess larger atomic radii, while the atom having maximum effective nuclear charge that is a greater number of protons will ultimately have least atomic radii.
And here, as we can see that, Sulphur (S) has the least atomic number that means it will have the least number of protons and hence the largest radii. On the other hand, Calcium (Ca) having maximum number of protons will have the smallest size. So, Sulphur will be followed by Chlorine then Potassium and at last by Calcium i.e.
${{S}^{2-}}>C{{l}^{-}}>{{K}^{+}}>C{{a}^{2+}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: You may get confused with option A considering that atoms having greater number of protons will have larger atomic radii. But it should be kept in mind that, the atom having lesser number of protons will exert less effective nuclear charge thus possessing larger atomic radii.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




