
Classroom activity (Constructing the ‘square root spiral’): Take a large sheet of paper and construct the ‘square root spiral’ in the following fashion. Start with a point O and draw a line segment \[O{P_1}\] of unit length. Draw a line segment \[{P_1}{P_2}\] perpendicular to \[O{P_1}\] of unit length. Now draw a line segment \[{P_2}{P_3}\] perpendicular to \[O{P_2}\]. Then draw the line segment \[{P_3}{P_4}\] perpendicular to \[O{P_3}\]. Continuing in this manner, you can get the line segment \[{P_{n - 1}}{P_n}\] by drawing a line segment of unit length perpendicular to \[O{P_{n - 1}}\]. In this manner you will have created the points \[{P_2},{P_3},.....,{P_n},.....,\] and joined them to create a beautiful spiral depicting \[\sqrt 2 ,\sqrt 3 ,\sqrt 4 ,......\]
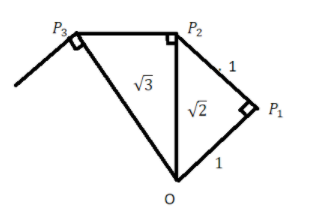

Answer
603k+ views
Hint: In this particular question first, draw perpendicular lines of unit (i.e. 1) length and then join their end point with O. And will apply Pythagoras Theorem (i.e. \[{\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}\] ) to find the length of that segment formed by joining the end point with O. Repeat this process again and again to draw the square root spiral.
Complete step-by-step answer:
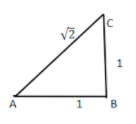
So, let us first draw a line segment AB of unit length.
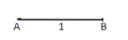
Then draw a line BC that is perpendicular to the line AB and is of unit length.
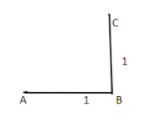
Now we had to join point A with point C.
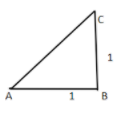
Now as we know that \[\angle B = 90^\circ \]. So, we can apply Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABC.
So, according to Pythagoras theorem \[{\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2}\]
So, in triangle ABC \[{\left( {{\text{AC}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{BC}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\text{BC}}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 1} = \sqrt 2 \]
Now draw a line CD that is perpendicular to the line CA and is of unit length.
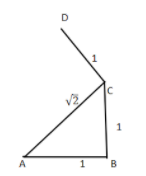
Join point D with point A.
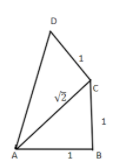
Now again applying Pythagoras theorem in triangle ACD.
\[ \Rightarrow AD = \sqrt {{{\left( {{\text{AC}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\text{CD}}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {2 + 1} = \sqrt 3 \]
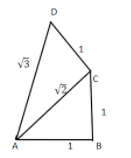
Similarly, proceeding further each time we will get a line having length equal to the square root of a next natural number.
So, the square root spiral will be as follows \[\sqrt 2 ,\sqrt 3 ,\sqrt 4 ,\sqrt 5 ,.......\]
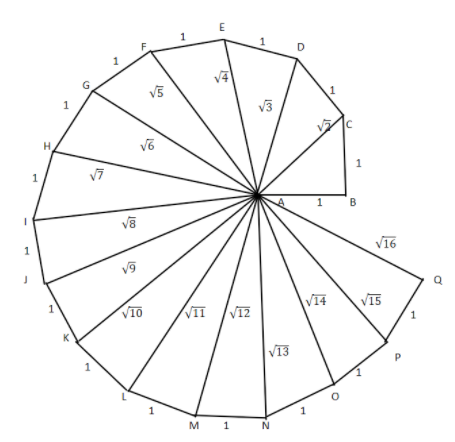
Note:Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that each time the length of the new line formed is the square root of the next natural number than the previous one because the new line formed is the hypotenuse of the new triangle. And the base the previous line while the perpendicular is always of unit length. So, by Pythagoras theorem \[{\left( {{\text{Length of new line}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Length of the previous line}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2}\]. So, if the length of the previous line is the square root of natural number x. Then, \[{\left( {{\text{Length of new line}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\sqrt x } \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{1}} \right)^2}\]. So, \[{\text{Length of new line}} = \sqrt {x + 1} \]. Hence we will get the spiral of the square root of numbers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, let us first draw a line segment AB of unit length.
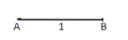
Then draw a line BC that is perpendicular to the line AB and is of unit length.

Now we had to join point A with point C.

Now as we know that \[\angle B = 90^\circ \]. So, we can apply Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABC.
So, according to Pythagoras theorem \[{\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2}\]
So, in triangle ABC \[{\left( {{\text{AC}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{BC}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\text{BC}}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 1} = \sqrt 2 \]

Now draw a line CD that is perpendicular to the line CA and is of unit length.

Join point D with point A.

Now again applying Pythagoras theorem in triangle ACD.
\[ \Rightarrow AD = \sqrt {{{\left( {{\text{AC}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\text{CD}}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {2 + 1} = \sqrt 3 \]

Similarly, proceeding further each time we will get a line having length equal to the square root of a next natural number.
So, the square root spiral will be as follows \[\sqrt 2 ,\sqrt 3 ,\sqrt 4 ,\sqrt 5 ,.......\]

Note:Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that each time the length of the new line formed is the square root of the next natural number than the previous one because the new line formed is the hypotenuse of the new triangle. And the base the previous line while the perpendicular is always of unit length. So, by Pythagoras theorem \[{\left( {{\text{Length of new line}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Length of the previous line}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2}\]. So, if the length of the previous line is the square root of natural number x. Then, \[{\left( {{\text{Length of new line}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\sqrt x } \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{1}} \right)^2}\]. So, \[{\text{Length of new line}} = \sqrt {x + 1} \]. Hence we will get the spiral of the square root of numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion class 8 biology CBSE

What are the methods of reducing friction. Explain




