
What is the characteristic of a nuclear envelope?
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: The nuclear envelope is composed of lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane, and an outer nuclear membrane. The gap between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is lined with a fiber complex called the nuclear lamina which is 10-40nm thick and provides strength.
Complete answer:
The nuclear envelope is also known as the nuclear membrane, is a double membrane layer that divides the contents of the nucleus from the remaining part of the cell. It is a blockade that physically protects the cell’s DNA from the chemical reactions that are occurring somewhere else in the cell. The envelope also contains a complex of proteins that keep the genetic matter in place inside the nucleus.
Additional information:
The outer nuclear membrane also shares a familiar border with the endoplasmic reticulum. The outer nuclear membrane contains proteins that are physically joined found in extremely higher concentrations than the endoplasmic reticulum.
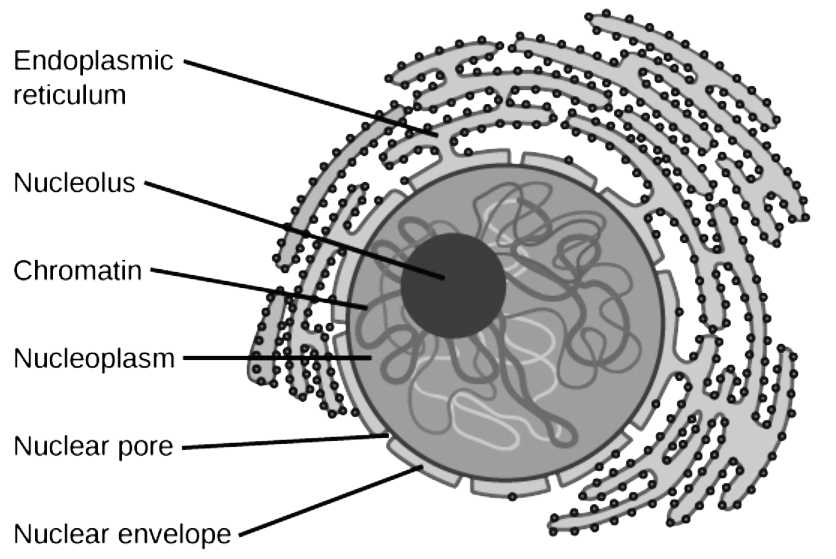
The inner nuclear membrane encompasses the nucleoplasm and is covered by the nuclear lamina, a network of intermediate filaments that stabilizes the nuclear membrane as well as being involved in chromatin purpose and complete expression. It is linked to the outer membrane by nuclear pores that penetrate the membranes.
Note: The nuclear Envelope is typically about 20–40nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is unremitting with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has numerous nuclear pores that allow materials to move amid the cytosol and the nucleus.
Intermediate filament proteins called lamina shape a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner portion of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus.
Complete answer:
The nuclear envelope is also known as the nuclear membrane, is a double membrane layer that divides the contents of the nucleus from the remaining part of the cell. It is a blockade that physically protects the cell’s DNA from the chemical reactions that are occurring somewhere else in the cell. The envelope also contains a complex of proteins that keep the genetic matter in place inside the nucleus.
Additional information:
The outer nuclear membrane also shares a familiar border with the endoplasmic reticulum. The outer nuclear membrane contains proteins that are physically joined found in extremely higher concentrations than the endoplasmic reticulum.

The inner nuclear membrane encompasses the nucleoplasm and is covered by the nuclear lamina, a network of intermediate filaments that stabilizes the nuclear membrane as well as being involved in chromatin purpose and complete expression. It is linked to the outer membrane by nuclear pores that penetrate the membranes.
Note: The nuclear Envelope is typically about 20–40nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is unremitting with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has numerous nuclear pores that allow materials to move amid the cytosol and the nucleus.
Intermediate filament proteins called lamina shape a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner portion of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




