
\[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\] and \[\text{HCONHC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\] are called:
A. Position isomers
B. Chain isomers
C. Tautomers
D. Functional isomers
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: The compounds have the same molecular formula but different arrangements of the atoms in space are called isomers.
In this case, the compounds have the same molecular formula but they differ in the functional group attached to the main chain of carbon atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
- The compounds which have the same molecular formula but different functional groups attached to it are called functional isomers.
- \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\] and \[\text{HCONHC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\] are called functional isomers.
- They have the same molecular formula that is \[{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{NO}\].
- They differ in the functional groups attached.
- \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\], acetamide has the following structure:
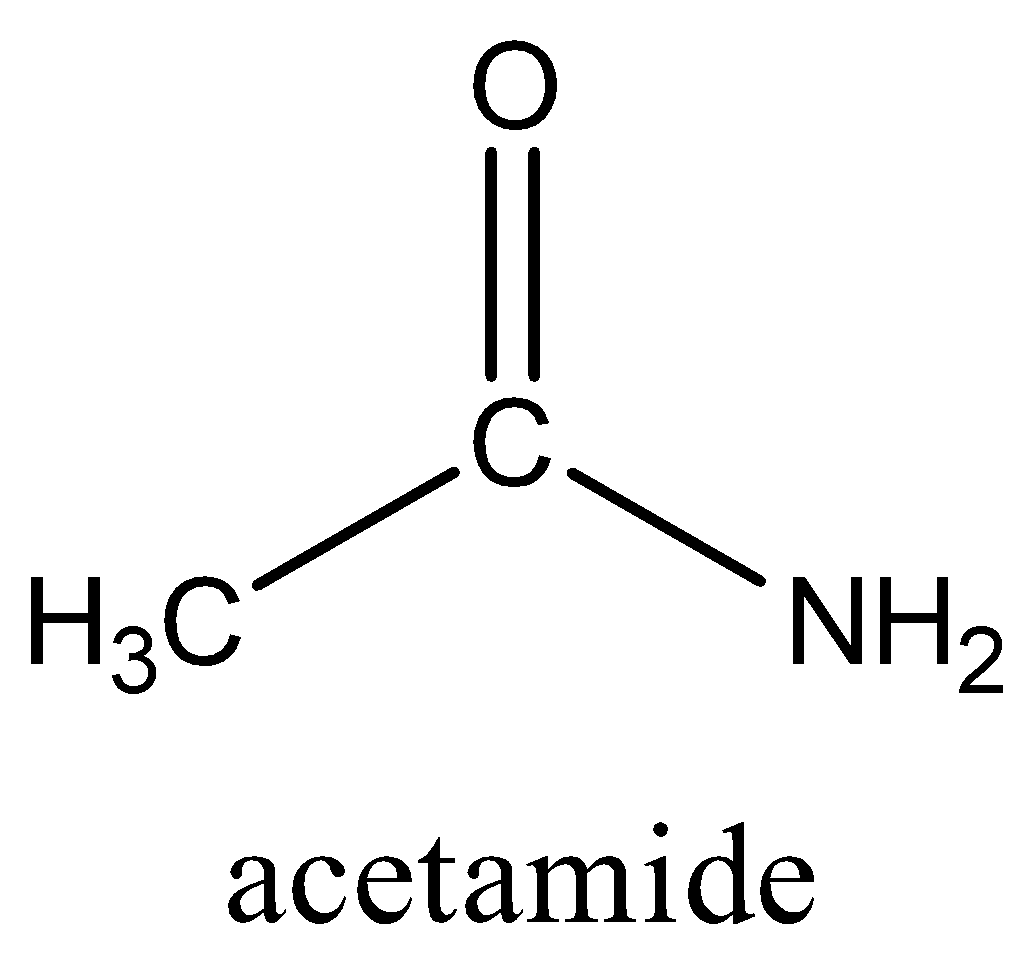
The functional group is the primary amide (\[\text{-CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\]). If it is broken down, the functional groups are ketone and primary amine.
- \[\text{HCONHC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\], n-methyl formamide has the following structure:
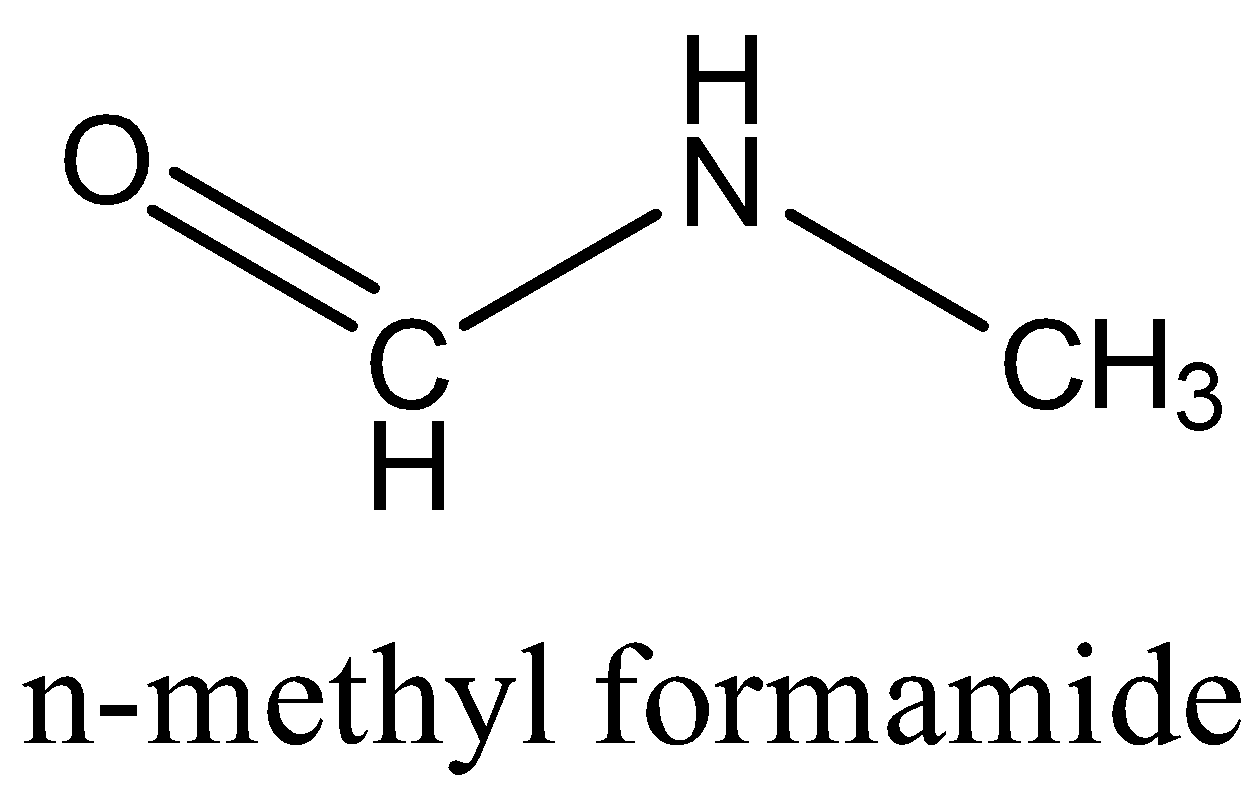
The functional group is the secondary amide. If it is broken down, the functional groups are aldehyde and secondary amine.
So, the correct option is D.
Additional information:
Isomers can be divided into two types:
Constitutional isomers
Stereoisomers
Note: Chain isomers and isomers with the same molecular formula but different arrangement of branches of carbon.
Positional isomers are the isomers with the same molecular formula but attachment the functional groups in the different locations in the carbon chain.
Tautomers are the isomers of a compound that exist in equilibrium. The most common example of tautomer is keto-enol formation.
Keto-enol formation is one of the important basic mechanisms of organic chemistry.
In this case, the compounds have the same molecular formula but they differ in the functional group attached to the main chain of carbon atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
- The compounds which have the same molecular formula but different functional groups attached to it are called functional isomers.
- \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\] and \[\text{HCONHC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\] are called functional isomers.
- They have the same molecular formula that is \[{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{NO}\].
- They differ in the functional groups attached.
- \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\], acetamide has the following structure:

The functional group is the primary amide (\[\text{-CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\]). If it is broken down, the functional groups are ketone and primary amine.
- \[\text{HCONHC}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\], n-methyl formamide has the following structure:

The functional group is the secondary amide. If it is broken down, the functional groups are aldehyde and secondary amine.
So, the correct option is D.
Additional information:
Isomers can be divided into two types:
Constitutional isomers
Stereoisomers
Note: Chain isomers and isomers with the same molecular formula but different arrangement of branches of carbon.
Positional isomers are the isomers with the same molecular formula but attachment the functional groups in the different locations in the carbon chain.
Tautomers are the isomers of a compound that exist in equilibrium. The most common example of tautomer is keto-enol formation.
Keto-enol formation is one of the important basic mechanisms of organic chemistry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




