
$C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HBr\to $
The major product formed is:
[A] $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Br$
[B] $C{{H}_{3}}-CH(Br)-C{{H}_{3}}$
[C] $C{{H}_{2}}Br-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$
[D] $C{{H}_{2}}=C=C{{H}_{2}}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
HINT: To answer this, you need to remember Markonikov’s addition. Here, the reaction will be an additional reaction. Two carbocations might be formed here but the secondary carbocation will be more stable and will give you the major product.
Complete step by step solution: Here, we can see that the compound given to us is an alkene named propene. It will react readily with hydrogen bromide and it will give us an alkyl bromide compound. Now, let us see the reaction to find out the major product.
Here, when we add HBr, it undergoes Markonikov’s addition giving us the product.
According to the Markovnikov’s Rule, bromine will be added to the most substituted carbon, giving us the major product by undergoing an additional reaction.
Now, let us see the mechanism of the addition.
We know that the H – Br bond is polarised due the electronegativity difference between them. Also, in the alkene the electron density is higher on the double bond.
The ${{H}^{+}}$ ion will attack on the propene carbocation and there is a possibility of formation of two carbocation - one primary, the other secondary. However, secondary carbocation is more stable so it will give us the major product. Then, the bromide ion reacts with the secondary carbocation formed and gives us an alkyl bromide.
We can show the mechanism as-
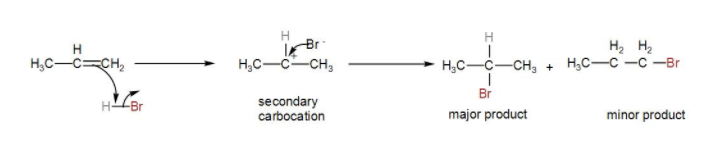
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] $C{{H}_{3}}-CH(Br)-C{{H}_{3}}$
NOTE: It is important for us to remember that HBr shows peroxide effect i.e.in presence of HBr and peroxide, it changes the region selectivity and gives the opposite of the expected product. The product thus obtained is the Anti-Markovnikov product. However, hydrogen chloride and hydrogen iodide do not show a peroxide effect.
Complete step by step solution: Here, we can see that the compound given to us is an alkene named propene. It will react readily with hydrogen bromide and it will give us an alkyl bromide compound. Now, let us see the reaction to find out the major product.
Here, when we add HBr, it undergoes Markonikov’s addition giving us the product.
According to the Markovnikov’s Rule, bromine will be added to the most substituted carbon, giving us the major product by undergoing an additional reaction.
Now, let us see the mechanism of the addition.
We know that the H – Br bond is polarised due the electronegativity difference between them. Also, in the alkene the electron density is higher on the double bond.
The ${{H}^{+}}$ ion will attack on the propene carbocation and there is a possibility of formation of two carbocation - one primary, the other secondary. However, secondary carbocation is more stable so it will give us the major product. Then, the bromide ion reacts with the secondary carbocation formed and gives us an alkyl bromide.
We can show the mechanism as-

Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] $C{{H}_{3}}-CH(Br)-C{{H}_{3}}$
NOTE: It is important for us to remember that HBr shows peroxide effect i.e.in presence of HBr and peroxide, it changes the region selectivity and gives the opposite of the expected product. The product thus obtained is the Anti-Markovnikov product. However, hydrogen chloride and hydrogen iodide do not show a peroxide effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




