
Cell to cell contact in a plant cell is maintained through
(a) Tight junctions
(b) Desmosomes
(c) Interdigitations
(d) Plasmodesmata
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: In plants cell to cell contact is maintained through narrow threads of cytoplasm that pass through the cell walls of adjacent cells. Such junctions are seen only in plants and algae. They were named by Strasburger.
Complete answer:
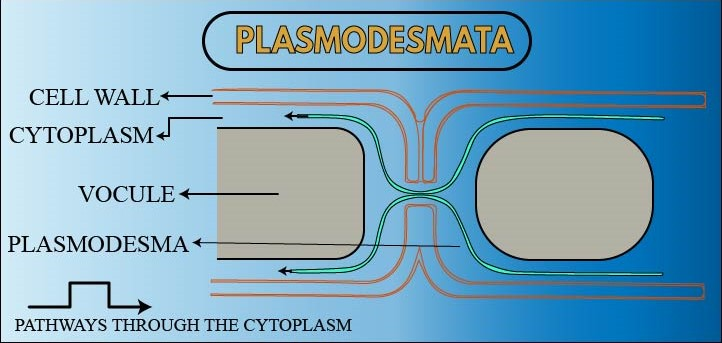
Cell to cell contact is important to maintain cytoplasmic continuity and structural integrity of an organism. This contact can be achieved using different mechanisms like desmosomes, gap junctions, etc. In plants and algae, this contact is maintained by narrow threads of cytoplasm which act as minute cytoplasmic bridges between adjacent cells. They pass through the cell walls of adjacent cells thus creating a communication.
These junctions are called plasmodesmata.
Plasmodesmata are fine cytoplasmic canals which are lined by a plasma membrane.
So, the answer is, ‘ Plasmodesmata.’
Additional Information:
Plasmodesmata form a continuum called symplast. This symplast provides a pathway for controlled passage of small particles between adjacent cells.
Molecules under a certain size called ‘size exclusion limit’, move freely through the plasmodesmal pathways by passive diffusion. This size-exclusion limit varies from plant to plant, and even among cell types within the same plant. Plasmodesmata may sometimes selectively dilate, allowing the passage of certain large molecules, such as proteins, although this process is still poorly understood.
Note: There are other types of cell connections too. Plasmodesmata are unique to plants and algal species. In animal cells, gap junctions are seen for the cell to cell contact which is a lot like the plasmodesmata. Invertebrates, these gap junctions develop when a set of six membrane proteins called connexins elongate to form a donut-like structure called a connexon. When these pores, or “doughnut holes,” of connexons are aligned a channel is formed between the cells.
Complete answer:
Cell to cell contact is important to maintain cytoplasmic continuity and structural integrity of an organism. This contact can be achieved using different mechanisms like desmosomes, gap junctions, etc. In plants and algae, this contact is maintained by narrow threads of cytoplasm which act as minute cytoplasmic bridges between adjacent cells. They pass through the cell walls of adjacent cells thus creating a communication.
These junctions are called plasmodesmata.
Plasmodesmata are fine cytoplasmic canals which are lined by a plasma membrane.

So, the answer is, ‘ Plasmodesmata.’
Additional Information:
Plasmodesmata form a continuum called symplast. This symplast provides a pathway for controlled passage of small particles between adjacent cells.
Molecules under a certain size called ‘size exclusion limit’, move freely through the plasmodesmal pathways by passive diffusion. This size-exclusion limit varies from plant to plant, and even among cell types within the same plant. Plasmodesmata may sometimes selectively dilate, allowing the passage of certain large molecules, such as proteins, although this process is still poorly understood.
Note: There are other types of cell connections too. Plasmodesmata are unique to plants and algal species. In animal cells, gap junctions are seen for the cell to cell contact which is a lot like the plasmodesmata. Invertebrates, these gap junctions develop when a set of six membrane proteins called connexins elongate to form a donut-like structure called a connexon. When these pores, or “doughnut holes,” of connexons are aligned a channel is formed between the cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




