
What is the cartesian form of complex numbers ?
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: The cartesian form of a complex number is represented in a two – dimensional plane . Let \[a + ib\] be a complex number , here \[a\] represents the real part of the complex number and \[b\] represents the imaginary part of the complex number .
Complete step-by-step answer:
A complex number system is a form of number system in which imaginary numbers are represented . The cartesian plane of the complex number has two axes - one is the imaginary axis and the other one is the real axis . For better understanding , let us take an example :
Let \[{z_1} = a + ib\] be a complex number . Let us plot it on a cartesian plane .
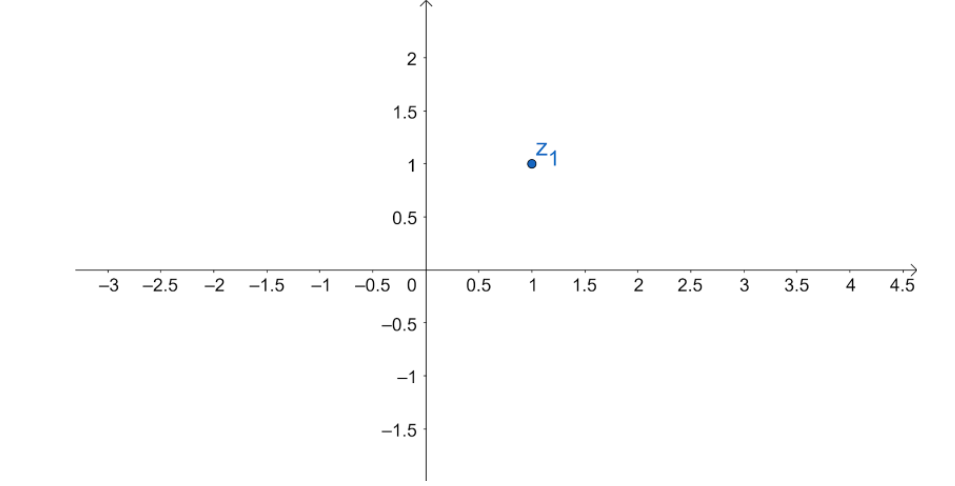
The real number is called the subset of the complex number as when we have \[b = 0\] . Also , the conjugate of a complex number can be represented on cartesian plane such as :
\[{z_2} = \overline {a + ib} \] can be represented as ,

Therefore , the imaginary part will become negative after taking the conjugate of a complex number . A complex number can be represented in a Cartesian axis diagram with a real and an imaginary axis - also known as the Argand diagram .
Note: The argument of a complex number can be calculated by taking \[\tan \] of slope of the point . The argument of \[\overline {{z_1}} \] depends upon the quadrant in which point \[{z_1}\] lies . The conjugate of a complex number is represented by \[\overline {{z_1}} \] which is equal to \[\overline {{z_1}} = a - ib\] . The plane on which a complex number is represented is also known as the Gaussian plane .
Complete step-by-step answer:
A complex number system is a form of number system in which imaginary numbers are represented . The cartesian plane of the complex number has two axes - one is the imaginary axis and the other one is the real axis . For better understanding , let us take an example :
Let \[{z_1} = a + ib\] be a complex number . Let us plot it on a cartesian plane .

The real number is called the subset of the complex number as when we have \[b = 0\] . Also , the conjugate of a complex number can be represented on cartesian plane such as :
\[{z_2} = \overline {a + ib} \] can be represented as ,

Therefore , the imaginary part will become negative after taking the conjugate of a complex number . A complex number can be represented in a Cartesian axis diagram with a real and an imaginary axis - also known as the Argand diagram .
Note: The argument of a complex number can be calculated by taking \[\tan \] of slope of the point . The argument of \[\overline {{z_1}} \] depends upon the quadrant in which point \[{z_1}\] lies . The conjugate of a complex number is represented by \[\overline {{z_1}} \] which is equal to \[\overline {{z_1}} = a - ib\] . The plane on which a complex number is represented is also known as the Gaussian plane .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




