
Calculate the formal charge of atoms $HCl{O_4},\,CO_3^{2 - }.$
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: The formal charge of $HCl{O_4}$ and $CO_3^{2 - }$ can be calculated using this formula: \[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\]
Formula used:
\[
Formal\,\,ch\arg e = [\,Tota\operatorname{l} \,\,no.\,\,of\,\,valence\,\,electrons] - [Tota\operatorname{l} \,\,no.\,\,of\,\,electrons\,\,of\,\,lone\,\,pairs] \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, - \dfrac{1}{2}[Tota\,\operatorname{l} \,\,no.\,\,of\,\,shared\,\,electrons] \\
\]
Complete step by step answer:
The formal charge on an atom in a molecule or ion is defined as the difference between the number of valence electrons of that atom in the free state and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in the Lewis structure, assuming that in each shared pair of electrons the atom has one electron of its own and the lone pair on it belongs to it completely. Thus, it can be calculated as follows
\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\]
where, $FC$ = Formal charge on an atom in a molecule
$V$= Total number of valence electrons in free atom
$L$ = Total number of electrons of lone pair (non-bonding electrons)
\[S\]= Total number of shared electrons (bonding electrons)
The Lewis structure of $HCl{O_4}$ is:
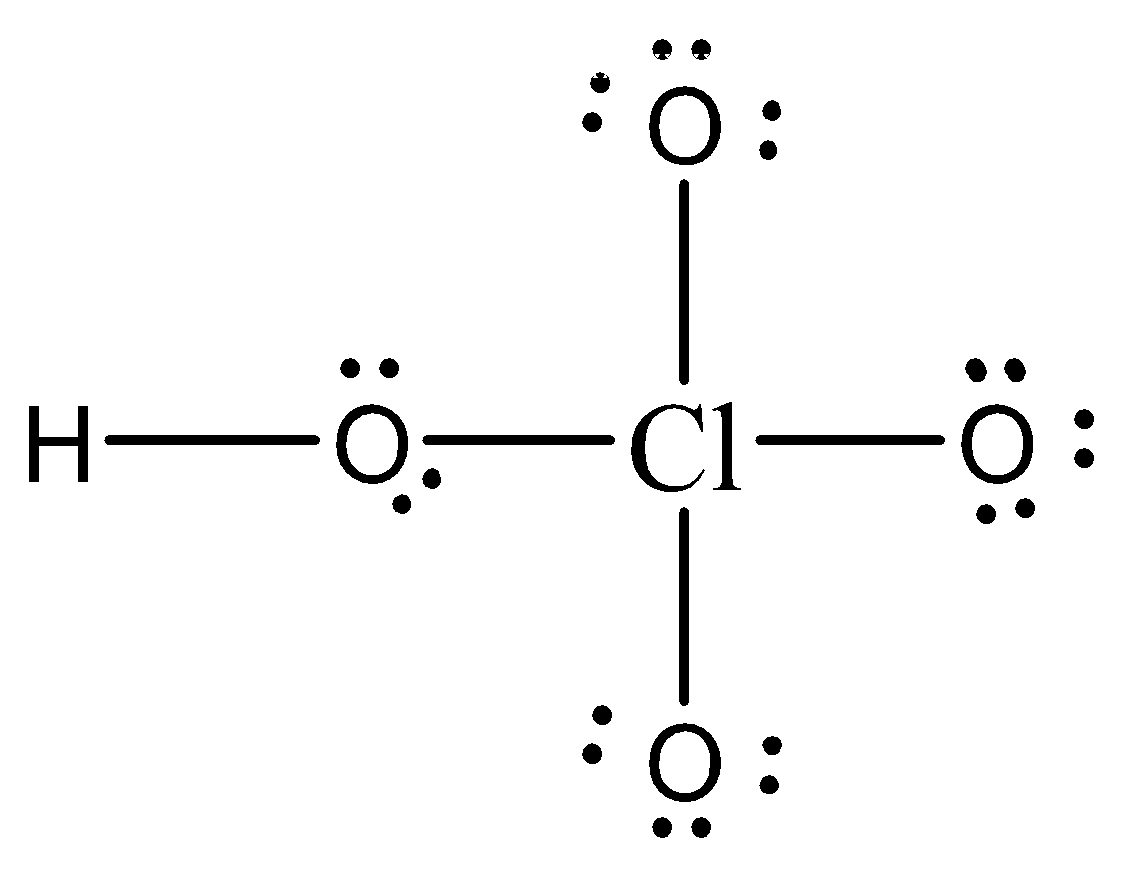
Thus, Formal charge on $Cl$ $ = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 7 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}(8)\,\,\, = 3\]
Formal charge on single bonded O atom $ = $ \[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{1}{2}(2)\,\,\, = - 1\]
Formal charge on O atom bonded to H$ = $ \[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{1}{2}(4)\,\,\, = 0\]
Formal charge on H$ = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 1 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}(2)\,\,\, = 0\]
The Lewis structure of $\,CO_3^{2 - }.$is:
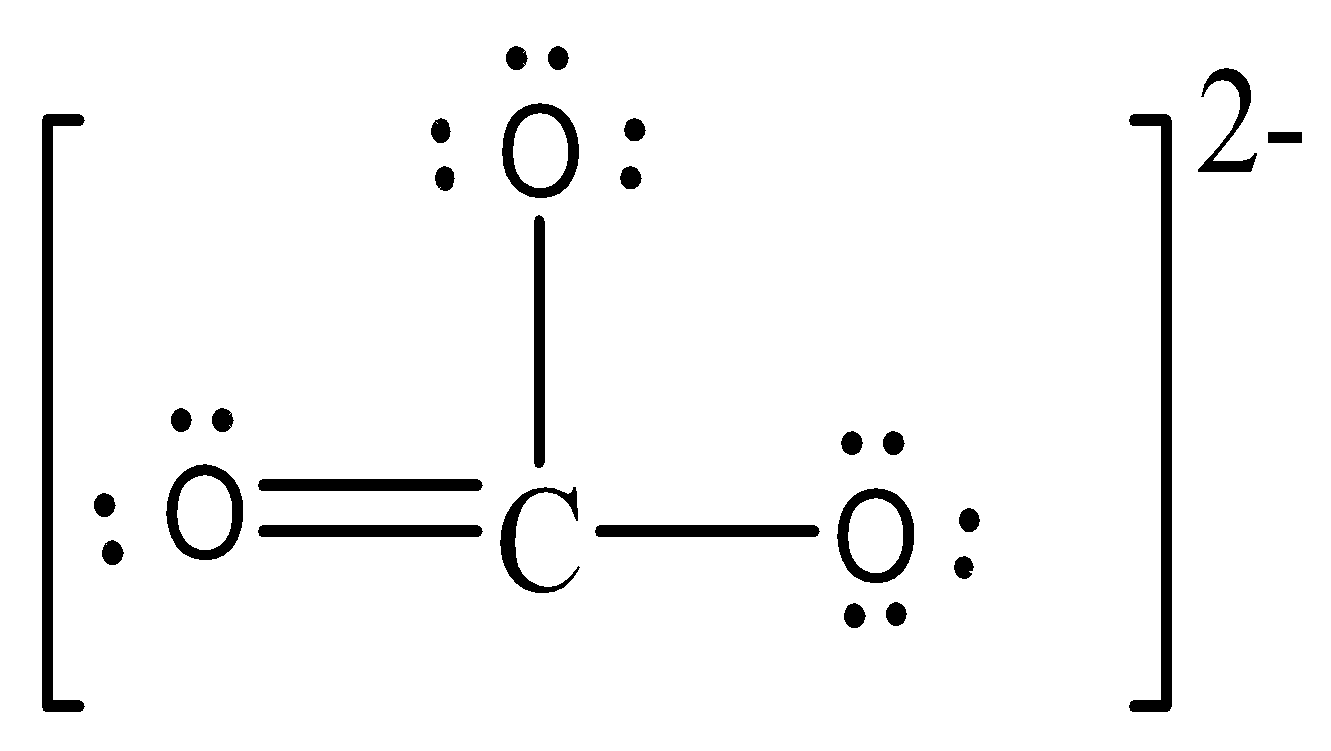
Formal charge on $C = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 4 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}(8)\,\,\, = 0\]
Formal charge on double bonded O atom$ = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{1}{2}(4)\,\,\, = 0\]
Formal charge on single bonded O atom$ = $ \[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{1}{2}(2)\,\,\, = - 1\]
Note:
To calculate formal charge it is necessary to draw a Lewis structure. In a molecule, there is no charge on the molecule as a whole or in a polyatomic ion, although the charge present on the ion is the charge on the ion as a whole and not on the individual atoms, yet for some purposes. It is useful to assign a formal charge to each atom in a molecule or ion. The main advantage of the calculation of formal charges is that it helps to select the most stable structure, the one with least energy out of the different possible Lewis structures. The most stable is the one which has the smallest formal charges on the atoms.
Formula used:
\[
Formal\,\,ch\arg e = [\,Tota\operatorname{l} \,\,no.\,\,of\,\,valence\,\,electrons] - [Tota\operatorname{l} \,\,no.\,\,of\,\,electrons\,\,of\,\,lone\,\,pairs] \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, - \dfrac{1}{2}[Tota\,\operatorname{l} \,\,no.\,\,of\,\,shared\,\,electrons] \\
\]
Complete step by step answer:
The formal charge on an atom in a molecule or ion is defined as the difference between the number of valence electrons of that atom in the free state and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in the Lewis structure, assuming that in each shared pair of electrons the atom has one electron of its own and the lone pair on it belongs to it completely. Thus, it can be calculated as follows
\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\]
where, $FC$ = Formal charge on an atom in a molecule
$V$= Total number of valence electrons in free atom
$L$ = Total number of electrons of lone pair (non-bonding electrons)
\[S\]= Total number of shared electrons (bonding electrons)
The Lewis structure of $HCl{O_4}$ is:

Thus, Formal charge on $Cl$ $ = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 7 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}(8)\,\,\, = 3\]
Formal charge on single bonded O atom $ = $ \[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{1}{2}(2)\,\,\, = - 1\]
Formal charge on O atom bonded to H$ = $ \[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{1}{2}(4)\,\,\, = 0\]
Formal charge on H$ = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 1 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}(2)\,\,\, = 0\]
The Lewis structure of $\,CO_3^{2 - }.$is:

Formal charge on $C = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 4 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}(8)\,\,\, = 0\]
Formal charge on double bonded O atom$ = $\[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{1}{2}(4)\,\,\, = 0\]
Formal charge on single bonded O atom$ = $ \[FC = V - L - \dfrac{1}{2}S\,\, = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{1}{2}(2)\,\,\, = - 1\]
Note:
To calculate formal charge it is necessary to draw a Lewis structure. In a molecule, there is no charge on the molecule as a whole or in a polyatomic ion, although the charge present on the ion is the charge on the ion as a whole and not on the individual atoms, yet for some purposes. It is useful to assign a formal charge to each atom in a molecule or ion. The main advantage of the calculation of formal charges is that it helps to select the most stable structure, the one with least energy out of the different possible Lewis structures. The most stable is the one which has the smallest formal charges on the atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




