
By what acceleration, the wedge should move so that the block moves upwards along the surface of the wedge with an acceleration of $g\sin \theta $.
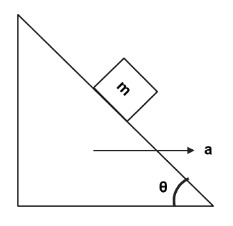
A. $2g\cos \theta $
B. $g\sin \theta $
C. $2g\tan \theta $
D. $g\cos \theta $

Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint:To construct a free-body diagram, we draw the point of concern, all forces acting on it, and resolve all force vectors into x– and y–components. A separate free-body diagram is required for each object in the question.
Complete step by step answer:
After drawing a free body diagram, we will get the following figure,

In the following question, we observe with respect to wedge. Hence, we apply pseudo force on the block. After substituting the values from free body diagram we will get,
$ma\cos \theta - mg\sin \theta = ma' \\
\Rightarrow ma\cos \theta - mg\sin \theta = mg\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow a\cos \theta = 2g\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{2g\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} \\
\therefore a = 2g\tan \theta \\ $
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Four forces are not often applied to objects. In certain cases, the number of forces described by a free-body diagram may be one, two, or three. In a free-body diagram, the number of forces that must be drawn is not a hard and fast rule. There is only one guideline to drawing free-body diagrams: reflect all of the forces that exist with that object in the given situation.
Complete step by step answer:
After drawing a free body diagram, we will get the following figure,

In the following question, we observe with respect to wedge. Hence, we apply pseudo force on the block. After substituting the values from free body diagram we will get,
$ma\cos \theta - mg\sin \theta = ma' \\
\Rightarrow ma\cos \theta - mg\sin \theta = mg\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow a\cos \theta = 2g\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{2g\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} \\
\therefore a = 2g\tan \theta \\ $
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Four forces are not often applied to objects. In certain cases, the number of forces described by a free-body diagram may be one, two, or three. In a free-body diagram, the number of forces that must be drawn is not a hard and fast rule. There is only one guideline to drawing free-body diagrams: reflect all of the forces that exist with that object in the given situation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




