
But-1-ene in reaction with HCl in the presence of sodium peroxide yields.
(A) n-butyl chloride
(B) Isobutyl chloride
(C) Secondary butyl chloride
(D) none of these
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: This reaction follows the Markovnikov rule in alkenes. This rule is one of the important rules for the prediction of the electrophilic addition reaction of unsymmetrical alkenes in organic chemistry. This rule mechanism mainly depends on the stability of carbocation and its structure also predicts the product conformational structure.
Complete step by step answer:
The given compound is But-1-ene. $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$
According to Markovnikov’s rule, the given alkene reacts with HCl in the presence of sodium peroxide follows,
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HCl\to C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C(Cl)H-C{{H}_{3}}$
The mechanism of the above reaction with electrophilic addition and obeying Markovnikov’s rule
Step-1: HCl dissociate into ions in the presence of sodium peroxide
\[HCl\to \underset{electrophile}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,+\underset{nucleophile}{\mathop{C{{l}^{-}}}}\,\]
Step-2: the electrophile involves addition reaction with But-1-ene,
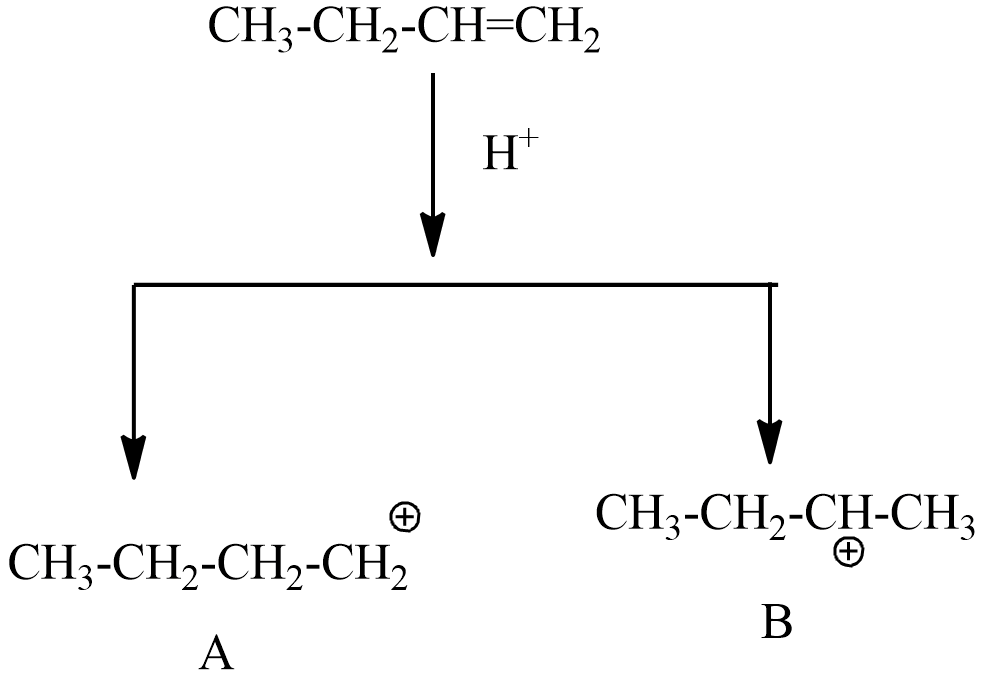
In this step, A=primary carbocation, B= secondary carbocation
Hence the stability of secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation. So, the intermediate B, will continue the reaction by obeying markovnikov’s rule.
Step-3: intermediate B carbocation reacts with chloride ion and forms the product 2-chloro butane.
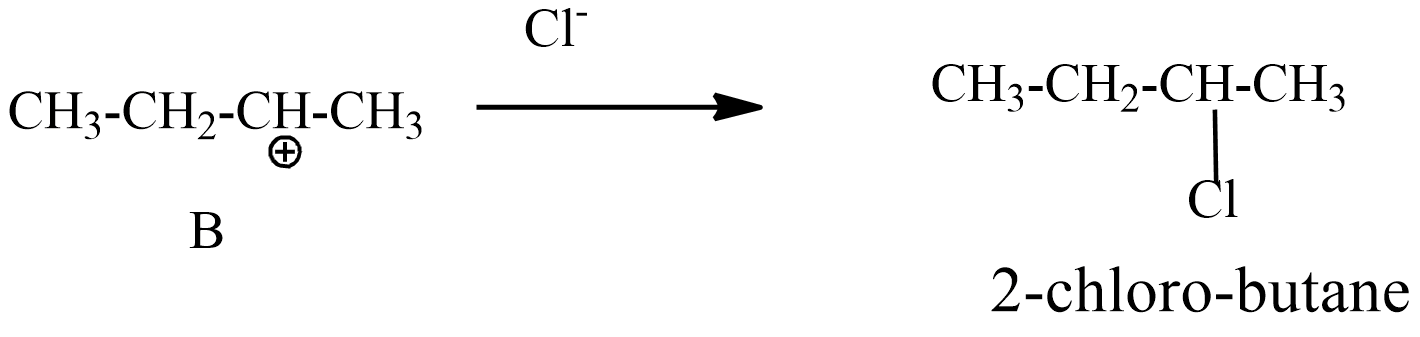
This 2-chloro butane is also known as secondary butyl chloride.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Markovnikov’s rule does not apply to symmetrical alkenes. Especially ethene is symmetrical alkene, this rule does not apply. Because, there is only one product from the electrophilic addition of HX to ethene. There is an AntiMarkovnikov's rule which includes that hydrogen atoms are attached to the carbon atom with the least hydrogen substituents. This rule explains the opposite of Markovnikov’s rule.
Complete step by step answer:
The given compound is But-1-ene. $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$
According to Markovnikov’s rule, the given alkene reacts with HCl in the presence of sodium peroxide follows,
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HCl\to C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C(Cl)H-C{{H}_{3}}$
The mechanism of the above reaction with electrophilic addition and obeying Markovnikov’s rule
Step-1: HCl dissociate into ions in the presence of sodium peroxide
\[HCl\to \underset{electrophile}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,+\underset{nucleophile}{\mathop{C{{l}^{-}}}}\,\]
Step-2: the electrophile involves addition reaction with But-1-ene,

In this step, A=primary carbocation, B= secondary carbocation
Hence the stability of secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation. So, the intermediate B, will continue the reaction by obeying markovnikov’s rule.
Step-3: intermediate B carbocation reacts with chloride ion and forms the product 2-chloro butane.

This 2-chloro butane is also known as secondary butyl chloride.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Markovnikov’s rule does not apply to symmetrical alkenes. Especially ethene is symmetrical alkene, this rule does not apply. Because, there is only one product from the electrophilic addition of HX to ethene. There is an AntiMarkovnikov's rule which includes that hydrogen atoms are attached to the carbon atom with the least hydrogen substituents. This rule explains the opposite of Markovnikov’s rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




