
Binary fission in amoeba differs from budding a yeast as in the former:
A. Parent cell remains intact
B. Protuberance is present
C. Division of cytoplasm is equal
D. Meiotic division is involved
Answer
394.5k+ views
Hint: Reproduction is a biological process that ensures the survival of a race or species. As a result, this mechanism is essential for a species' survival. Depending on the organism, there are numerous methods of reproduction, ranging from the most basic asexual to the most complicated sexual.
Complete step by step answer:
To form new individuals and continue the species, unicellular organisms reproduce by cell division or fission, the most basic type of reproduction. Binary fission is a type of asexual cell division known as binary fission. bacterial cells have many straight rods like chromosomes surrounded in a membrane-bound nucleus, binary fission also takes various steps like a higher organism, as bacterial cells must copy their DNA. This mechanism is most likely to occur when the surrounding conditions are ideal.
Amoeba: Amoeba is a single-celled eukaryotic organism that gathers food and moves about by extending a protoplasmic finger. Amoebae are either parasitic or free-living in wet settings. The Amoeba's shape is irregular and can alter depending on the time and situation. Amoebae are incredibly diverse in nature; thus, they reproduce in a variety of ways, including binary fission, spore development, and even sexual reproduction.
Budding is another sort of asexual reproduction. Budding is a process in which an organism creates a protrusion or bud as a result of cell division under ideal conditions. The protrusion or bud gives rise to a new organism. Because this is a primitive sort of asexual reproduction, the genetic material in the daughter cells is identical to that of the parent cell. Yeast and hydra are the only organisms that reproduce by vegetative growth of budding. Yeast is a single-celled eukaryote from the fungal kingdom that is commonly used in the fermentation process. The most common way for yeast to proliferate is by budding.
Binary fission is an asexual reproduction method in which a fully developed parent cell divides into two halves, resulting in the formation of two new daughter cells. Bacteria, Amoeba, and Paramecium are among the organisms that have it. After duplicating its genetic information by mitotic division, the cell divides equal-sized daughter cells. First, nuclear division occurs, followed by cytoplasm cleavage into equal pieces. It is afterward associated with the division of the daughter nuclei into two daughter cells. Cell reproduction produces a pair of genetically identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
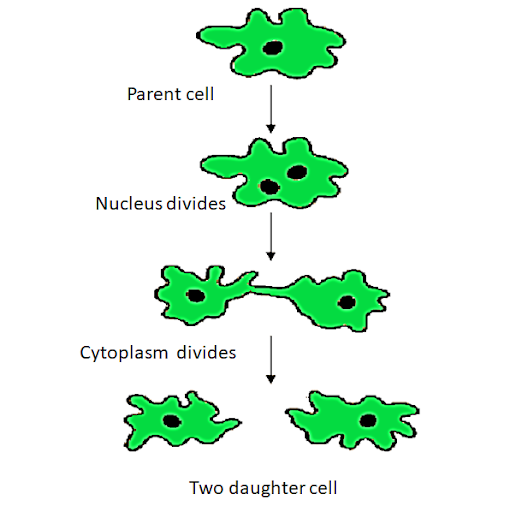
Image: Binary fission in Amoeba
Link: https://www.vedantu.com/question-sets/18abe145-75d2-4418-83e4-808aa4a4d3606435337058416686689.png
As a result, the correct answer is option C division of cytoplasm is equal.
Note: Budding is a type of vegetative asexual reproduction in which buds form on the parent cell and these buds produce new individuals. The parent nucleus divides into daughter nuclei, which then travel to the daughter cell.
Complete step by step answer:
To form new individuals and continue the species, unicellular organisms reproduce by cell division or fission, the most basic type of reproduction. Binary fission is a type of asexual cell division known as binary fission. bacterial cells have many straight rods like chromosomes surrounded in a membrane-bound nucleus, binary fission also takes various steps like a higher organism, as bacterial cells must copy their DNA. This mechanism is most likely to occur when the surrounding conditions are ideal.
Amoeba: Amoeba is a single-celled eukaryotic organism that gathers food and moves about by extending a protoplasmic finger. Amoebae are either parasitic or free-living in wet settings. The Amoeba's shape is irregular and can alter depending on the time and situation. Amoebae are incredibly diverse in nature; thus, they reproduce in a variety of ways, including binary fission, spore development, and even sexual reproduction.
Budding is another sort of asexual reproduction. Budding is a process in which an organism creates a protrusion or bud as a result of cell division under ideal conditions. The protrusion or bud gives rise to a new organism. Because this is a primitive sort of asexual reproduction, the genetic material in the daughter cells is identical to that of the parent cell. Yeast and hydra are the only organisms that reproduce by vegetative growth of budding. Yeast is a single-celled eukaryote from the fungal kingdom that is commonly used in the fermentation process. The most common way for yeast to proliferate is by budding.
Binary fission is an asexual reproduction method in which a fully developed parent cell divides into two halves, resulting in the formation of two new daughter cells. Bacteria, Amoeba, and Paramecium are among the organisms that have it. After duplicating its genetic information by mitotic division, the cell divides equal-sized daughter cells. First, nuclear division occurs, followed by cytoplasm cleavage into equal pieces. It is afterward associated with the division of the daughter nuclei into two daughter cells. Cell reproduction produces a pair of genetically identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.

Image: Binary fission in Amoeba
Link: https://www.vedantu.com/question-sets/18abe145-75d2-4418-83e4-808aa4a4d3606435337058416686689.png
As a result, the correct answer is option C division of cytoplasm is equal.
Note: Budding is a type of vegetative asexual reproduction in which buds form on the parent cell and these buds produce new individuals. The parent nucleus divides into daughter nuclei, which then travel to the daughter cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE




