
When benzene in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride reacts with ethyl chloride the compound formed is:
A.
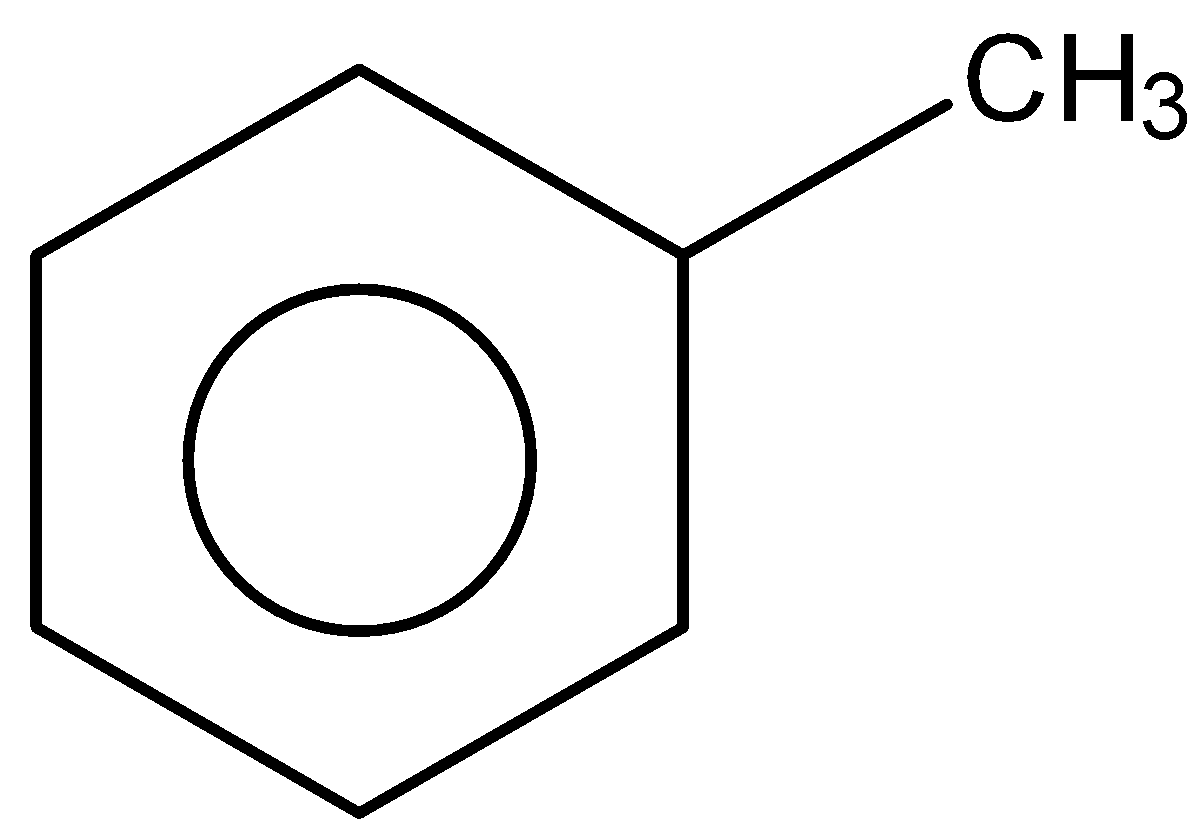
B.
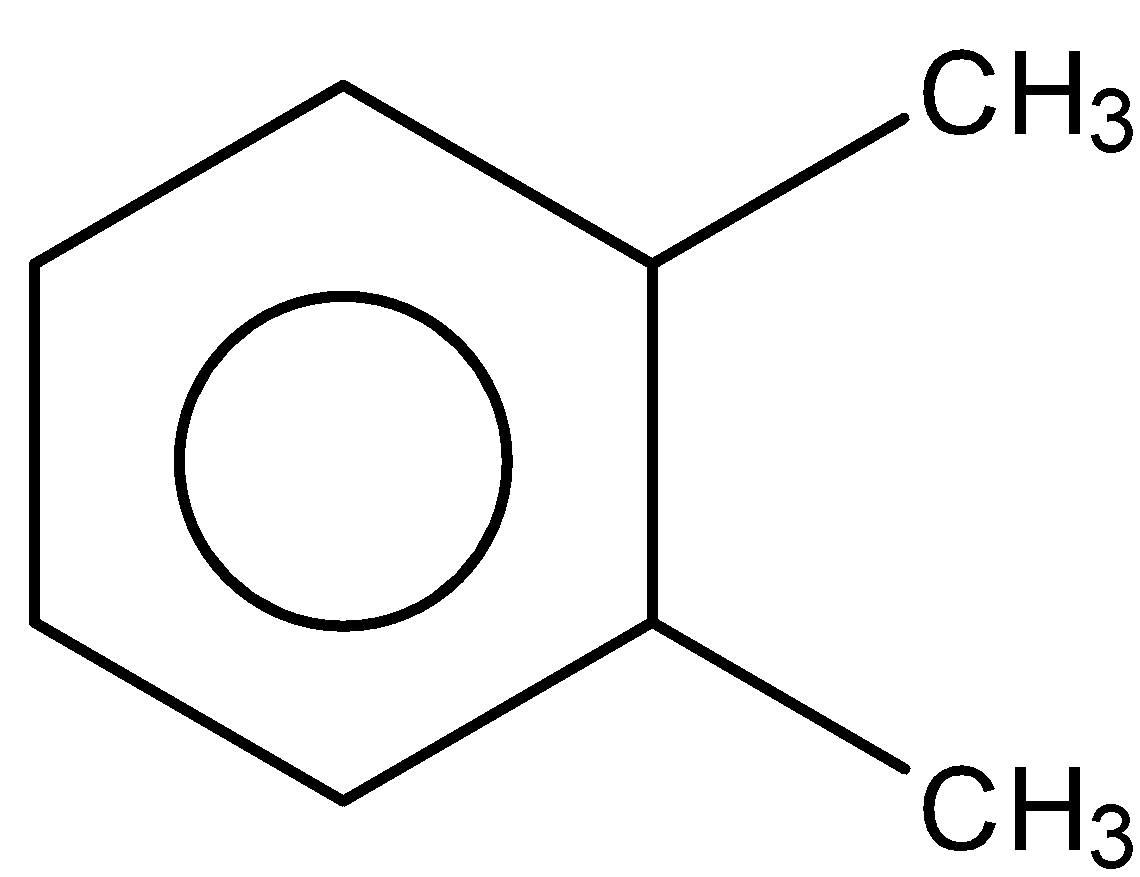
C.
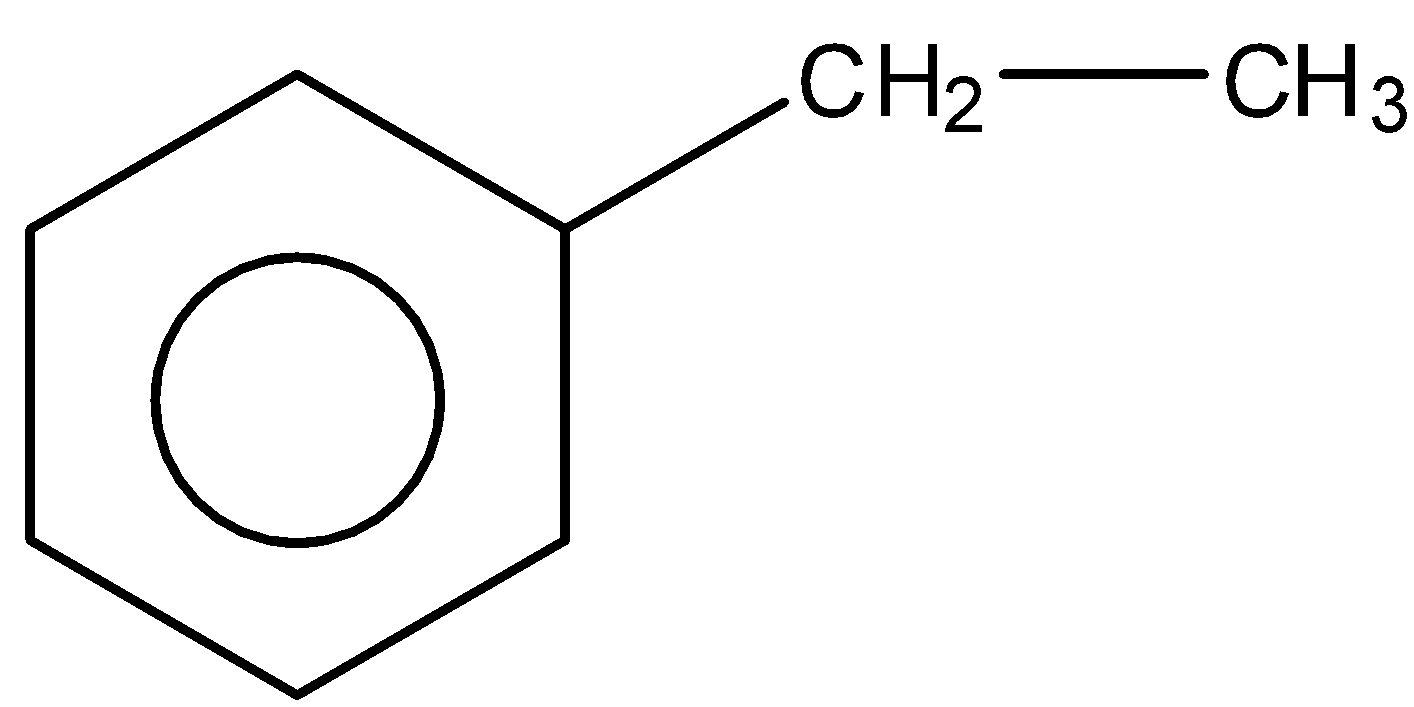
D.
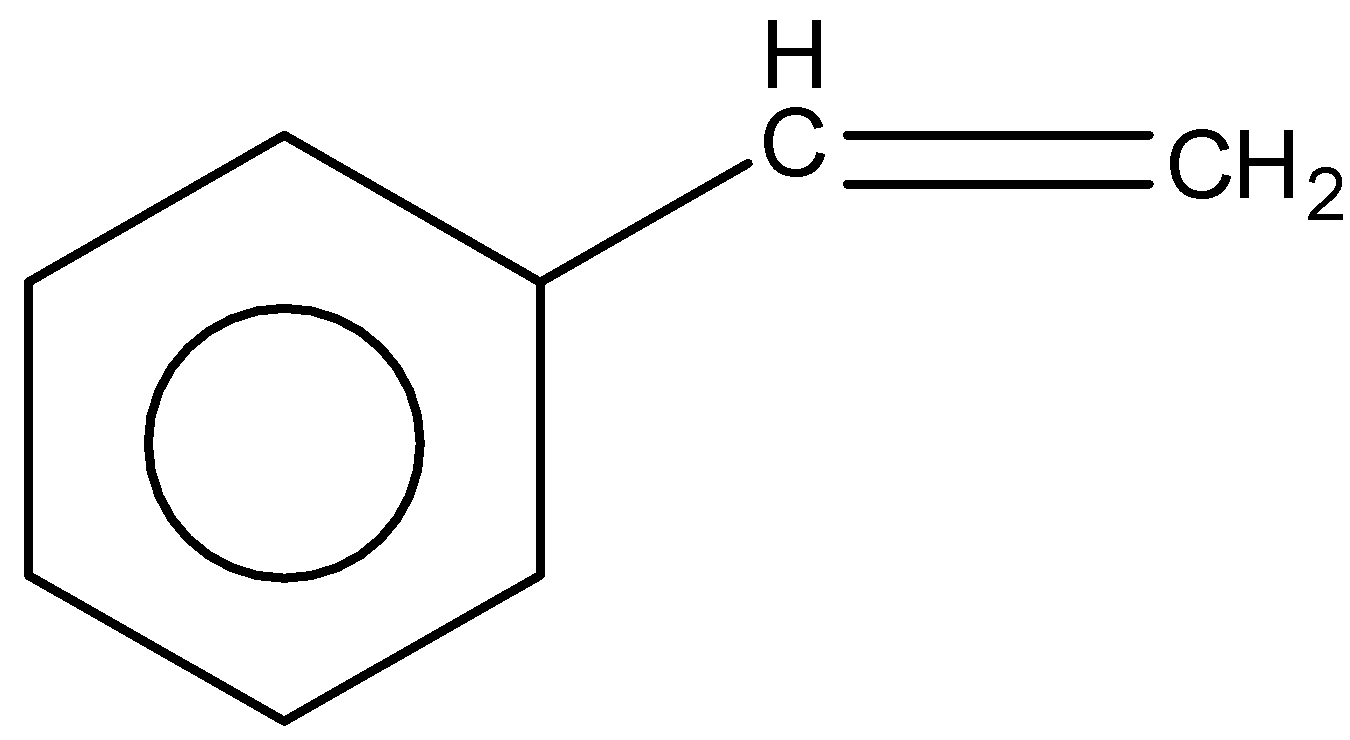




Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We know that haloarenes usually undergo electrophilic reactions of benzene rings. Some examples of electrophilic reactions of benzene are nitration, halogenations, Friedel Crafts reaction and halogenations reaction.Friedel Crafts reaction in detail. It is the reaction in which benzene undergoes reaction with alkyl halide (typically bromide, chloride or iodide) in presence of a Lewis acid namely aluminium chloride $\left( {{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$, ferric chloride $\left( {{\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Let se Friedel Crafts reaction
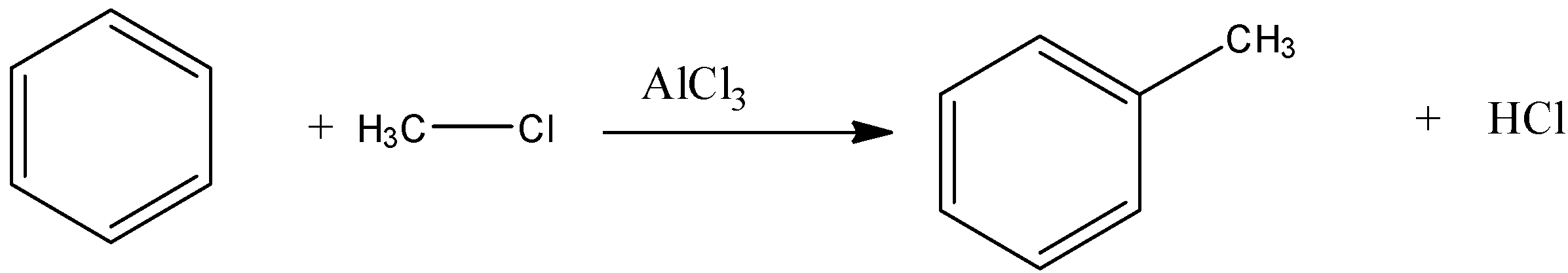
Now, come to the question. Here, benzene reacts with ethyl chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride. That means, the reaction is a Friedel Craft reaction.
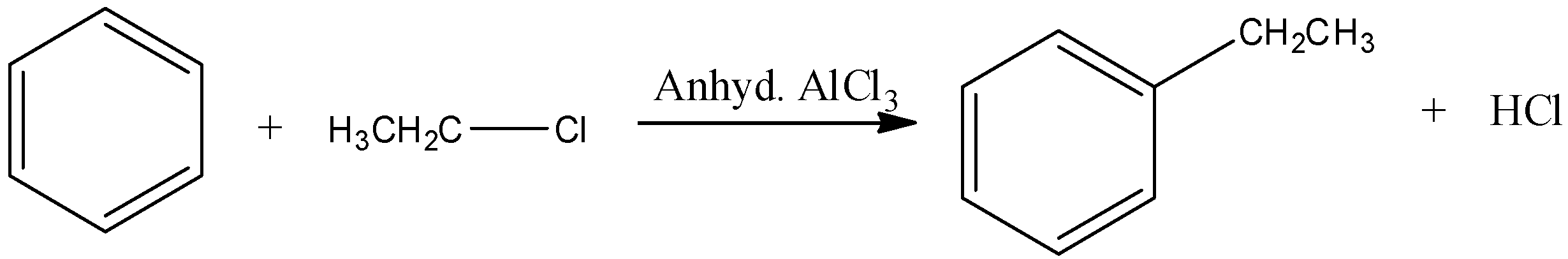
Let’s understand the electrophilic substitution of benzene rings. Halogen atom is o,p- directing besides being slightly deactivating. Therefore, substitution occurs at para and ortho position with respect to the halogen.
The o, p influence of halogen atoms is understood by the resonance structures of a halobenzene (chlorobenzene). The resonance structures of chlorobenzene are,
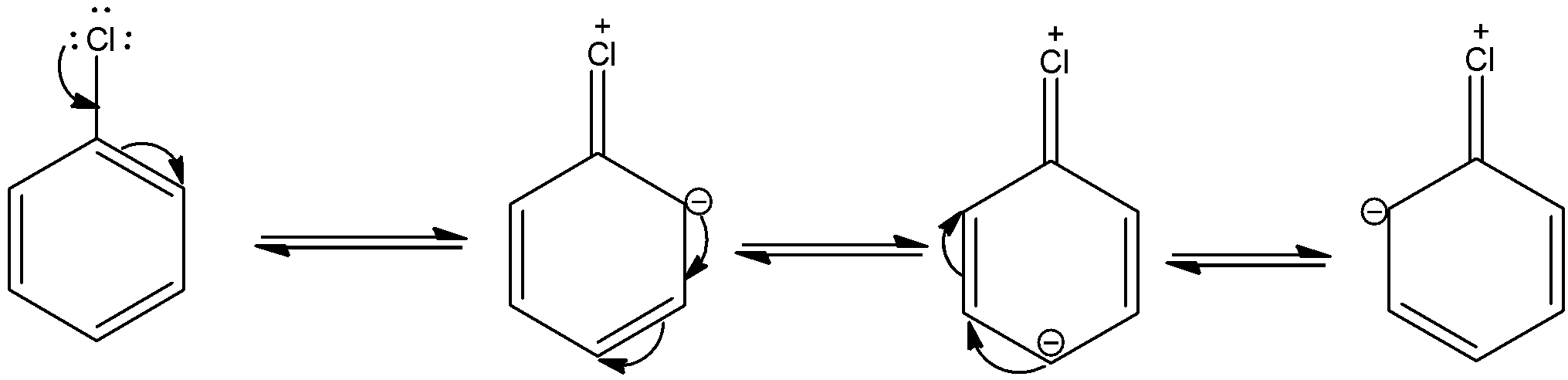
Due to resonance, electron density increases at ortho and para positions than at meta position. Also, the halogen atom shows –I effect due to which it has a tendency to withdraw electrons from the benzene ring. Because of this, the ring gets deactivated comparing the benzene ring. This is the reason due to which electrophilic substitution in haloarenes occurs slowly and needs drastic conditions compared to benzene.
So, the correct answer is Option c.
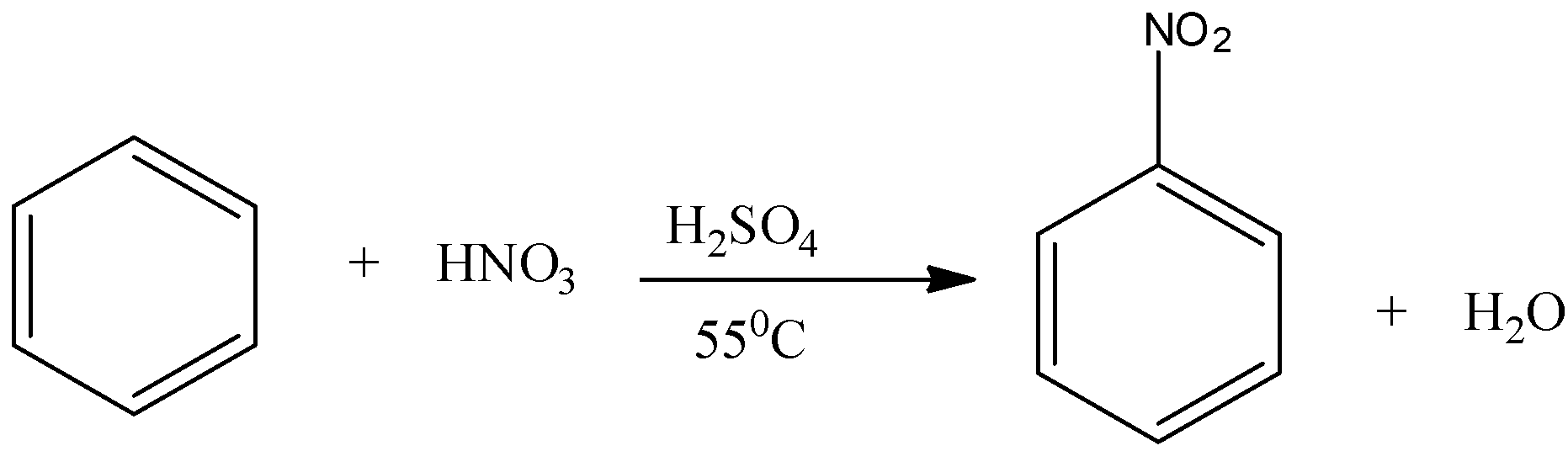
Note: Nitration is the reaction in which a nitrate group is introduced to the benzene ring. This can be done by reacting benzene with concentrated nitric acid at 55 degree Celsius in presence of the catalyst, that is, concentrated sulphuric acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Let se Friedel Crafts reaction

Now, come to the question. Here, benzene reacts with ethyl chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride. That means, the reaction is a Friedel Craft reaction.

Let’s understand the electrophilic substitution of benzene rings. Halogen atom is o,p- directing besides being slightly deactivating. Therefore, substitution occurs at para and ortho position with respect to the halogen.
The o, p influence of halogen atoms is understood by the resonance structures of a halobenzene (chlorobenzene). The resonance structures of chlorobenzene are,

Due to resonance, electron density increases at ortho and para positions than at meta position. Also, the halogen atom shows –I effect due to which it has a tendency to withdraw electrons from the benzene ring. Because of this, the ring gets deactivated comparing the benzene ring. This is the reason due to which electrophilic substitution in haloarenes occurs slowly and needs drastic conditions compared to benzene.
So, the correct answer is Option c.
Note: Nitration is the reaction in which a nitrate group is introduced to the benzene ring. This can be done by reacting benzene with concentrated nitric acid at 55 degree Celsius in presence of the catalyst, that is, concentrated sulphuric acid.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




