
When benzaldehyde is oxidized to give benzoic acid then the oxidation state of carbon of aldehydic group is changed from:
A. $ + 2$ to $ + 3$
B. $ + 1$ to $ + 3$
C. Zero to $ + 2$
D. No change
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Oxidation is the process that occurs in an atom, ion, or molecule when there is a loss of electrons.Oxidation number in an atom of a molecule is defined as the residual charge which an atom has or appears to have when all other atoms in a molecule or ion are removed as ions. The oxidation number in an atom may be negative, positive or zero.A substance which gives oxygen or removes hydrogen is called oxidizing agent.According to the electron concept, a chemical reaction in which there is a transference of electrons from one substance (atom, ion or molecule) to another substances is called an oxidation- reduction reaction or redox reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The two bonds between the same atoms do not affect the oxidation state and are taken as zero. So we will consider the functional group for the calculation of the oxidation state of the carbon.
In benzaldehyde, the functional group is –CHO
The oxidation state of the carbon in the –CHO
$ \Rightarrow x + 1 - 2 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x = + 1$
The oxidation state of the carbon in –CHO is $ + 1$
Similarly,
In benzoic acid, the functional group is –COOH
The oxidation state of the carbon in the –COOH
$ \Rightarrow x - 2 - 2 + 1 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x - 4 + 1 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x - 3 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x = + 3$
The oxidation state of the carbon in –COOH is $ + 3$.
Therefore when benzaldehyde is oxidized to benzoic acid the oxidation state of the aldehydic carbon changes from $ + 1$ to $ + 3$.
So, the correct answer is Option B .
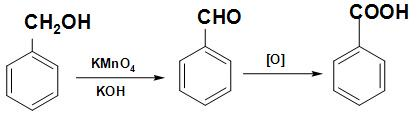
Note: The given reaction in the question is one of the methods of preparation of benzoic acid. When benzyl alcohol is heated with potassium dichromate and concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ or aqueous KOH, acids with the same number of carbon atoms result. The reaction involved in this process is written below:
Complete step by step answer:
The two bonds between the same atoms do not affect the oxidation state and are taken as zero. So we will consider the functional group for the calculation of the oxidation state of the carbon.
In benzaldehyde, the functional group is –CHO
The oxidation state of the carbon in the –CHO
$ \Rightarrow x + 1 - 2 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x = + 1$
The oxidation state of the carbon in –CHO is $ + 1$
Similarly,
In benzoic acid, the functional group is –COOH
The oxidation state of the carbon in the –COOH
$ \Rightarrow x - 2 - 2 + 1 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x - 4 + 1 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x - 3 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x = + 3$
The oxidation state of the carbon in –COOH is $ + 3$.
Therefore when benzaldehyde is oxidized to benzoic acid the oxidation state of the aldehydic carbon changes from $ + 1$ to $ + 3$.
So, the correct answer is Option B .
Note: The given reaction in the question is one of the methods of preparation of benzoic acid. When benzyl alcohol is heated with potassium dichromate and concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ or aqueous KOH, acids with the same number of carbon atoms result. The reaction involved in this process is written below:

Benzyl Benzaldehyde Benzoic acid
Alcohol
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




