
${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+N{{H}_{3}}\to $Addition compound (X)
$(X)\xrightarrow{450k}Y+Z(g)$
In the above sequence Y and Z are respectively:
(A)- borazine, ${{H}_{2}}O$
(B)- boron, ${{H}_{2}}$
(C)- boron nitride, ${{H}_{2}}$
(D)- borazine and hydrogen
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: The addition product formed by the action of ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$) on diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$) diammoniate of diborane., i.e. ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}$. It is ionic in nature. Reaction of ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ with $N{{H}_{3}}$ is one of the methods used for the synthesis of borazine.
Complete step by step answer:
The products of the reaction of diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$) with ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$) depends on the reaction conditions.
At low temperature, ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ reacts with $N{{H}_{3}}$ to form an addition product. The chemical reaction is given below:
\[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+2N{{H}_{3}}\to {{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}\]
${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}$ is ionic in nature and exists as \[{{\left[ {{H}_{3}}N\to B{{H}_{2}}\leftarrow N{{H}_{3}} \right]}^{+}}{{\left[ B{{H}_{4}} \right]}^{-}}\] .
When the reaction between ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ and $N{{H}_{3}}$ is carried out around 450 K temperature, the addition product formed gets converted into borazine and hydrogen. The sequence of chemical reactions taking place is given below:
\[\begin{align}
& {{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+2N{{H}_{3}}\to {{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}} \\
& 3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{450K}2{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}+12{{H}_{2}}(g) \\
\end{align}\]
Since ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}$ is unstable at 450 K and only appears as an intermediate in the reaction, we can also write the overall reaction as
\[3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+6N{{H}_{3}}\to 2{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}+12{{H}_{2}}\]
We can identify the compound Y and Z from the above sequence of reactions. Compound Y is borazine (${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$) and compound Z is hydrogen (${{H}_{2}}$) gas.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
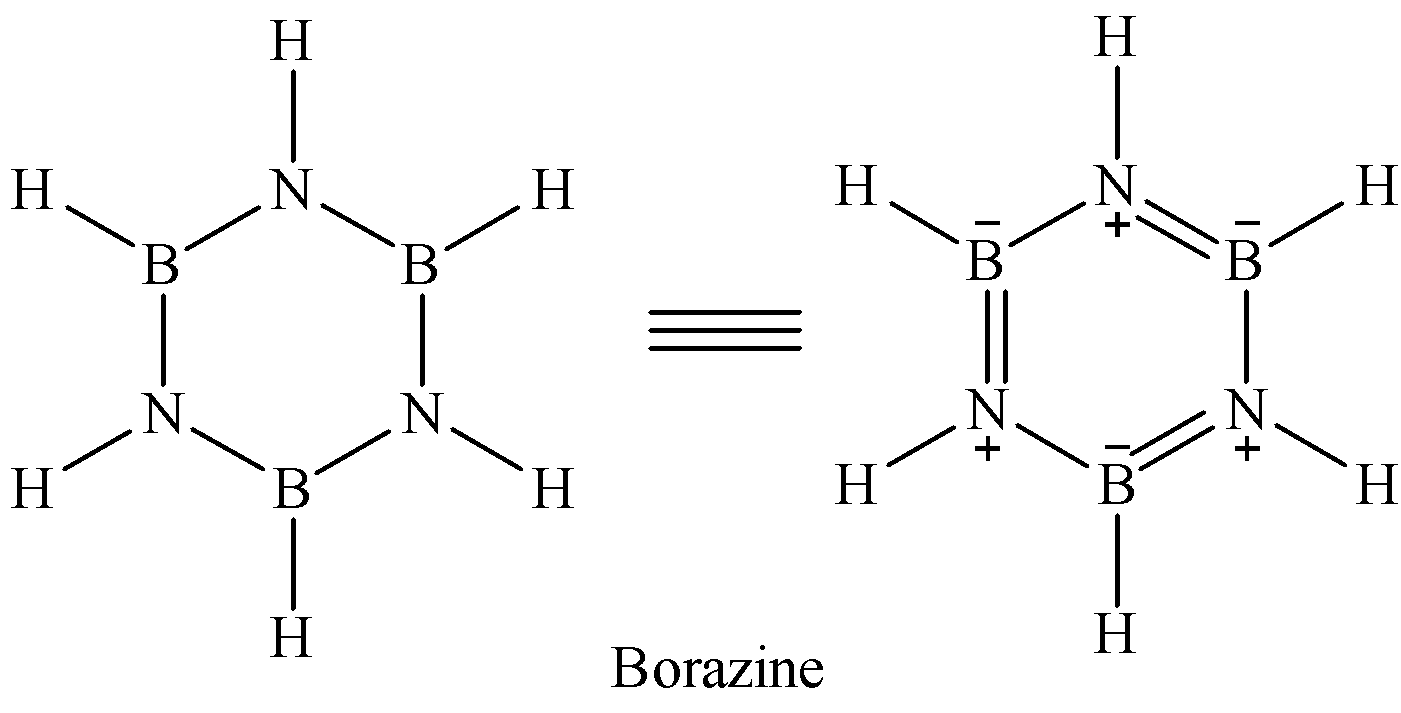
Borazine is known as inorganic benzene because its structure is similar to that of benzene.
Note: We might get confused between the options. So remember that diborane only forms boron nitride if it is treated with excess of ammonia at high temperature. Thus, here option C cannot be correct. And since there is no oxygen involved in the reaction, option A is also not correct.
Complete step by step answer:
The products of the reaction of diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$) with ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$) depends on the reaction conditions.
At low temperature, ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ reacts with $N{{H}_{3}}$ to form an addition product. The chemical reaction is given below:
\[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+2N{{H}_{3}}\to {{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}\]
${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}$ is ionic in nature and exists as \[{{\left[ {{H}_{3}}N\to B{{H}_{2}}\leftarrow N{{H}_{3}} \right]}^{+}}{{\left[ B{{H}_{4}} \right]}^{-}}\] .
When the reaction between ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ and $N{{H}_{3}}$ is carried out around 450 K temperature, the addition product formed gets converted into borazine and hydrogen. The sequence of chemical reactions taking place is given below:
\[\begin{align}
& {{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+2N{{H}_{3}}\to {{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}} \\
& 3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{450K}2{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}+12{{H}_{2}}(g) \\
\end{align}\]
Since ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}.2N{{H}_{3}}$ is unstable at 450 K and only appears as an intermediate in the reaction, we can also write the overall reaction as
\[3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+6N{{H}_{3}}\to 2{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}+12{{H}_{2}}\]
We can identify the compound Y and Z from the above sequence of reactions. Compound Y is borazine (${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$) and compound Z is hydrogen (${{H}_{2}}$) gas.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
Borazine is known as inorganic benzene because its structure is similar to that of benzene.

Note: We might get confused between the options. So remember that diborane only forms boron nitride if it is treated with excess of ammonia at high temperature. Thus, here option C cannot be correct. And since there is no oxygen involved in the reaction, option A is also not correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




