
Average voltage for the given source is
A) ${V_0}$
B) $2{V_0}$
C) $\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2}$
D) $\dfrac{{3{V_0}}}{2}$

Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The average voltage of a periodic waveform like this triangular one can be defined as the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time. To calculate you need to average out all the instantaneous values along the time axis with time being one full period which for such a continuous waveform is calculated by calculating the area under the curve.
Formula used:
If a triangle has a base $b$ and height $h$, then the area of the triangle can be expressed as
$\Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {b \times h} \right)$ ……………(1)
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
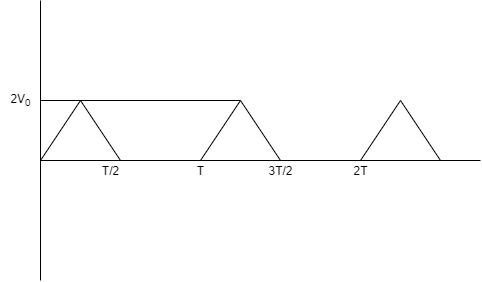
The peak of the voltage from the triangular waveforms shown in the graph is $2{V_0}$.
The period of the waveform from the graph is $T$.
To get: The average voltage ${V_{avg}}$ for the given source.
Step 1:
You can calculate the area under each periodic triangle from eq (1).
You can see for each triangle the base is $\dfrac{T}{2}$ and the height is $2{V_0}$.
So, the area under each triangle is
$ \Delta = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {base \times height} \right)$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {\dfrac{T}{2} \times 2{V_0}} \right) $
$ = \dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{2} $ ……..(2)
Step 2:
So, the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time period $T$ is the area you found just now.
Calculate the average voltage ${V_{avg}}$ from the definition
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{\Delta }{T}$
where $\Delta $ is the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time, $T$ is the period of the waveform.
$ \therefore {V_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{2}}}{T} $
$ = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2} $
The average voltage for the given source is $\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2}$. Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
Here you can approach to calculate the area under the curve through any method, but for the continuous waveform, you need to use this approach for the appropriate solution. One needs to be very careful in choosing the period. The symmetry of the wave form should be noticed for this type of regular waveform which can be easily computed.
Formula used:
If a triangle has a base $b$ and height $h$, then the area of the triangle can be expressed as
$\Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {b \times h} \right)$ ……………(1)
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The peak of the voltage from the triangular waveforms shown in the graph is $2{V_0}$.
The period of the waveform from the graph is $T$.
To get: The average voltage ${V_{avg}}$ for the given source.
Step 1:
You can calculate the area under each periodic triangle from eq (1).
You can see for each triangle the base is $\dfrac{T}{2}$ and the height is $2{V_0}$.
So, the area under each triangle is
$ \Delta = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {base \times height} \right)$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {\dfrac{T}{2} \times 2{V_0}} \right) $
$ = \dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{2} $ ……..(2)
Step 2:
So, the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time period $T$ is the area you found just now.
Calculate the average voltage ${V_{avg}}$ from the definition
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{\Delta }{T}$
where $\Delta $ is the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time, $T$ is the period of the waveform.
$ \therefore {V_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{V_0}T}}{2}}}{T} $
$ = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2} $
The average voltage for the given source is $\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2}$. Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
Here you can approach to calculate the area under the curve through any method, but for the continuous waveform, you need to use this approach for the appropriate solution. One needs to be very careful in choosing the period. The symmetry of the wave form should be noticed for this type of regular waveform which can be easily computed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




