
Assertion: Positive catalyst lowers the activation energy of the reaction whereas the heat of the reaction remains the same.
Reason: The heat of reaction is equal to the difference between activation energies for forward and backward reactions.
A) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
C) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
D) Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: The positive catalyst alters the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy of reaction such that the heat of the reaction remains unaffected. This is because it provides a new path for the reaction. However, the heat of the reaction is the same. The reversible reactions are endothermic and exothermic reaction.Therefore the heat of reaction varies for a forward and backward reaction. But catalyst does not affect the heat of reaction associated with the reversible reaction.
Complete answer:
A substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any change in mass and chemical composition at the end of the reaction is called the catalyst.
It should be taken into consideration that the catalyst may increase or decrease the rate of reaction. The catalyst which increases the rate of reaction is called the positive catalyst. This phenomenon is named as the positive catalysis.
For example, the oxidation of sulphur dioxide $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ to sulphur trioxide $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$ in presence of vanadium pentoxide ${{\text{V}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$Catalyst in the contact process is an example of positive catalyst.The catalyst provide an entirely new path for the reaction in which reactant are converted into the product. It is believed that catalyst forms a new activated complex having the lower potential energy. This means that the catalyst lowers the activation energy of the reaction. This is as shown in the figure below:
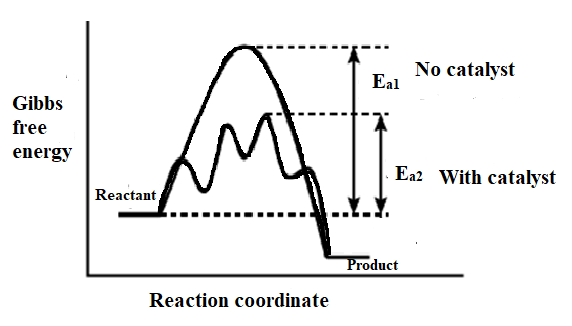
The catalyst may undergo the intermediate physical changes and it may even form temporary chemical bonds with the reactant but at the end of the reaction, it is recovered in its original chemical composition.
Although the catalyst speeds up the reaction it does not shift the position of the equilibrium for the reversible reactions. This is because the catalyst reduces the energy barrier by providing an alternative pathway. However, the lowering of activation energy is found to be the same for forward and backward reactions.
As a result, one can say that the catalyst increases the rate of reaction for the forward, and the backward reaction is reversible reactions. However, the position of equilibrium between the reaction remains affected. The catalyst does not change the heat of the reaction. It is seen from the diagram above that the energies associated with the reactant and product for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions remain the same. So, the heat of the formation of the product remains constant.
The reversible reactions are forward and backward reactions. If forward reaction is exothermic then backward is endothermic therefore the plot of potential energy against the reaction coordinates differ as shown below. This causes the change in heat of reaction for forward and backward reaction. However the total heat of reaction is the difference between the activation energy of forward and backward reaction. This is independent of the catalyst.

Therefore, the assertion and reason both are correct but the reason given is not a proper explanation for the assertion.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note:
The equilibrium constant for the reaction is not affected by the catalyst. However the change in temperature condition affects the equilibrium attained by the reaction. Similarly, concentration and number of moles also have a significant effect on the equilibrium constant.
Complete answer:
A substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any change in mass and chemical composition at the end of the reaction is called the catalyst.
It should be taken into consideration that the catalyst may increase or decrease the rate of reaction. The catalyst which increases the rate of reaction is called the positive catalyst. This phenomenon is named as the positive catalysis.
For example, the oxidation of sulphur dioxide $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ to sulphur trioxide $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$ in presence of vanadium pentoxide ${{\text{V}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$Catalyst in the contact process is an example of positive catalyst.The catalyst provide an entirely new path for the reaction in which reactant are converted into the product. It is believed that catalyst forms a new activated complex having the lower potential energy. This means that the catalyst lowers the activation energy of the reaction. This is as shown in the figure below:

The catalyst may undergo the intermediate physical changes and it may even form temporary chemical bonds with the reactant but at the end of the reaction, it is recovered in its original chemical composition.
Although the catalyst speeds up the reaction it does not shift the position of the equilibrium for the reversible reactions. This is because the catalyst reduces the energy barrier by providing an alternative pathway. However, the lowering of activation energy is found to be the same for forward and backward reactions.
As a result, one can say that the catalyst increases the rate of reaction for the forward, and the backward reaction is reversible reactions. However, the position of equilibrium between the reaction remains affected. The catalyst does not change the heat of the reaction. It is seen from the diagram above that the energies associated with the reactant and product for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions remain the same. So, the heat of the formation of the product remains constant.
The reversible reactions are forward and backward reactions. If forward reaction is exothermic then backward is endothermic therefore the plot of potential energy against the reaction coordinates differ as shown below. This causes the change in heat of reaction for forward and backward reaction. However the total heat of reaction is the difference between the activation energy of forward and backward reaction. This is independent of the catalyst.

Therefore, the assertion and reason both are correct but the reason given is not a proper explanation for the assertion.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note:
The equilibrium constant for the reaction is not affected by the catalyst. However the change in temperature condition affects the equilibrium attained by the reaction. Similarly, concentration and number of moles also have a significant effect on the equilibrium constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




