
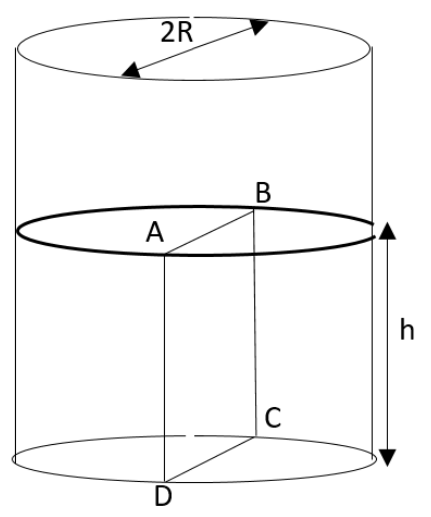
As shown in the diagram, water will be filled up to a height of $h$ in a beaker of radius $R$. The density of water is $\rho $, the surface tension of water is $T$ and the atmospheric pressure be ${{P}_{0}}$. Assume a vertical section ABCD of the water column through the diameter of the beaker. What will be the magnitude of the force on the water on one side of the section by water on the other side of this section?
$\begin{align}
& A.2{{P}_{0}}Rh+\pi {{R}^{2}}\rho gh-2RT \\
& B.2{{P}_{0}}Rh+R\rho g{{h}^{2}}-2RT \\
& C.{{P}_{0}}Rh+{{R}^{2}}\rho g{{h}^{2}}-2RT \\
& D.{{P}_{0}}Rh+{{R}^{2}}\rho g{{h}^{2}}+2RT \\
\end{align}$

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: First of all find the pressure at a depth from the surface of the water. This will be equivalent to the product of the density of water, acceleration due to gravity, and depth from the surface of the water. Therefore the resultant force on each surface of ABCD will be the integral of the product of the total pressure and the area. This will be helpful in answering this question.
Complete step by step solution:
let us find the pressure at the depth $x$ from the surface of the water. This can be written as,
$P=\rho gx$
Where $\rho $ be the density of water and $g$ be acceleration due to gravity.
Therefore the resultant force on each surface of ABCD will be the integral of the product of the total pressure and the area. This can be written as,
$\int\limits_{0}^{h}{\left( {{P}_{0}}+\rho gx \right)}\left( 2Rdx \right)$
Let us perform the integration,
$\begin{align}
&\int\limits_{0}^{h}{\left({{P}_{0}}+\rho gx \right)}\left( 2Rdx \right)=2R\int\limits_{0}^{h}{{{P}_{0}}dx}+\int\limits_{0}^{h}{\rho gx}dx \\
& \Rightarrow 2R\left[ \left[ {{P}_{0}}x \right]_{0}^{h}+\left[ \rho g{{x}^{2}} \right]_{0}^{h} \right] \\
& \therefore F=2R{{P}_{0}}h+R\rho g{{h}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
However the side will attract the segment because the surface tension experiencing along AB will be equal to,
$AB=T\left( 2R \right)$
Hence the net force will be obtained by subtracting this opposite attractive force occurring.
Therefore the resultant force experiencing on each of the side will be given as,
\[F=2{{P}_{0}}Rh+R\rho g{{h}^{2}}-2RT\]
Therefore the answer has been obtained. It has been given as option B.
Note: Pressure is the force, which can be experienced perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which this force is. The unit of pressure is given as Pascals. Kinds of Pressure are given as Absolute, Differential, atmosphere, and Gauge Pressure.
Complete step by step solution:
let us find the pressure at the depth $x$ from the surface of the water. This can be written as,
$P=\rho gx$
Where $\rho $ be the density of water and $g$ be acceleration due to gravity.
Therefore the resultant force on each surface of ABCD will be the integral of the product of the total pressure and the area. This can be written as,
$\int\limits_{0}^{h}{\left( {{P}_{0}}+\rho gx \right)}\left( 2Rdx \right)$
Let us perform the integration,
$\begin{align}
&\int\limits_{0}^{h}{\left({{P}_{0}}+\rho gx \right)}\left( 2Rdx \right)=2R\int\limits_{0}^{h}{{{P}_{0}}dx}+\int\limits_{0}^{h}{\rho gx}dx \\
& \Rightarrow 2R\left[ \left[ {{P}_{0}}x \right]_{0}^{h}+\left[ \rho g{{x}^{2}} \right]_{0}^{h} \right] \\
& \therefore F=2R{{P}_{0}}h+R\rho g{{h}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
However the side will attract the segment because the surface tension experiencing along AB will be equal to,
$AB=T\left( 2R \right)$
Hence the net force will be obtained by subtracting this opposite attractive force occurring.
Therefore the resultant force experiencing on each of the side will be given as,
\[F=2{{P}_{0}}Rh+R\rho g{{h}^{2}}-2RT\]
Therefore the answer has been obtained. It has been given as option B.
Note: Pressure is the force, which can be experienced perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which this force is. The unit of pressure is given as Pascals. Kinds of Pressure are given as Absolute, Differential, atmosphere, and Gauge Pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




