
Areolar connective tissues join
(a)Bone with bone
(b)fat body with muscles
(c)integument with muscles
(d)bone with muscles
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Loose connective tissue consists of cells and fibres loosely arranged in a semi-fluid ground substance (matrix). Examples of loose connective tissues are areolar tissue and adipose tissues.
Complete step-by-step answer:
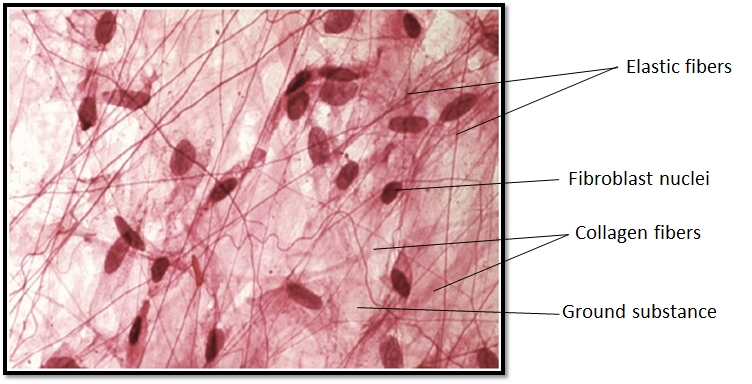
Areolar tissues are the most widely distributed connective tissue in the animal body. It is present beneath the skin. It serves as a support framework for epithelium. It joints skin to muscles; it fills space inside organs and is found around muscle blood vessels and nerves. The areolar tissue consists of ground substance, the matrix which is made up of modified polysaccharides (mucopolysaccharides) and proteins (glycoproteins).
Also scattered in the matrix are several kinds of irregular cells that perform different functions in the body. These cells are:
-Fibroblasts: These cells secrete fibres and matrix.
-Macrophages: Ingest cell debris, bacteria, and foreign matter.
-Mast cells: Produces histamine, heparin, and serotonin.
-Plasma cells: Produces antibodies.
Apart from these cells matrix also contains two types of protein fibres:
White collagen fibres: These fibres are made up of collagen proteins. These occur in bundles and are unbranched and inelastic.
Yellow elastic fibres: These fibres are made up of elastin proteins. These are branched and elastic.
The function of areolar tissue is:
- It acts as tissue that supports and packs between organs lying in the cavity of the body.
-It helps in the repair of tissues after an injury.
So, the correct answer is ‘integument with muscles’.
Note: Connective tissues are mainly classified as loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue.
Areolar tissue consists of a meshwork of collagen, elastic tissue, and reticular fibres. One important area is the skin, which binds the outer layer of skin to the muscle beneath.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Areolar tissues are the most widely distributed connective tissue in the animal body. It is present beneath the skin. It serves as a support framework for epithelium. It joints skin to muscles; it fills space inside organs and is found around muscle blood vessels and nerves. The areolar tissue consists of ground substance, the matrix which is made up of modified polysaccharides (mucopolysaccharides) and proteins (glycoproteins).
Also scattered in the matrix are several kinds of irregular cells that perform different functions in the body. These cells are:
-Fibroblasts: These cells secrete fibres and matrix.
-Macrophages: Ingest cell debris, bacteria, and foreign matter.
-Mast cells: Produces histamine, heparin, and serotonin.
-Plasma cells: Produces antibodies.
Apart from these cells matrix also contains two types of protein fibres:
White collagen fibres: These fibres are made up of collagen proteins. These occur in bundles and are unbranched and inelastic.
Yellow elastic fibres: These fibres are made up of elastin proteins. These are branched and elastic.
The function of areolar tissue is:
- It acts as tissue that supports and packs between organs lying in the cavity of the body.
-It helps in the repair of tissues after an injury.
So, the correct answer is ‘integument with muscles’.
Note: Connective tissues are mainly classified as loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue.
Areolar tissue consists of a meshwork of collagen, elastic tissue, and reticular fibres. One important area is the skin, which binds the outer layer of skin to the muscle beneath.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




