
Area under a $v-t$ graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit ?
Answer
525.6k+ views
Hint: Velocity is a vector quantity which has magnitude as well as direction while displacement is also a vector quantity which has magnitude and direction while scalar quantities only have magnitude and no direction.
Complete step by step answer:
Area under the v-t graph means the graph is drawn to show the relation between velocity and time.
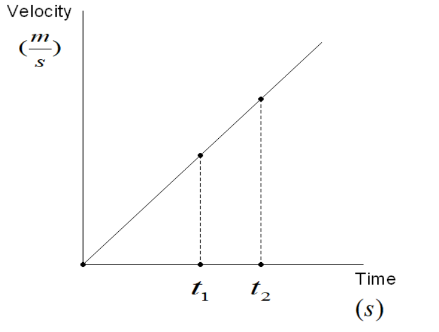
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement that means change in displacement per unit time.
$v=\dfrac{ds}{dt}$
It can be written as:
$ds=vdt$
Take both side integral, we get
$\int{d}s=\int\limits_{{{t}_{1}}}^{{{t}_{2}}}{vdt}$
$\Rightarrow s=\int\limits_{{{t}_{1}}}^{{{t}_{2}}}{vdt}$
$\Rightarrow s=v({{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}})$
Integration of $vdt$ shows area under v-t graph.
From the above analysis we can say the area under the v-t graph shows displacement. We cannot say the area of the v-t graph shows distance because distance is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity, so the area of the v-t graph has magnitude as well as direction. It means that the area of the v-t graph shows a vector quantity. The S.I unit of velocity is $\dfrac{meter}{\sec ond}(\dfrac{m}{s})$ and the S.I unit of time is $\sec ond(s)$.
Unit of the area under v-t graph is ,
$\text{area under v-t graph }=\text{Velocity}\times \text{Time}$
$\Rightarrow \text{area under v-t graph }=(\dfrac{m}{s})\times (s)$
$\therefore \text{area under v-t graph }=m$
Hence, area under the v-t graph shows displacement and its S.I unit is meters.
Note:We should know units of all physical quantities like in the above question we take units of velocity is $\dfrac{meter}{\sec ond}(\dfrac{m}{s})$. We should know some basic concepts of integration which are used in the above question.
Complete step by step answer:
Area under the v-t graph means the graph is drawn to show the relation between velocity and time.

Velocity is the rate of change of displacement that means change in displacement per unit time.
$v=\dfrac{ds}{dt}$
It can be written as:
$ds=vdt$
Take both side integral, we get
$\int{d}s=\int\limits_{{{t}_{1}}}^{{{t}_{2}}}{vdt}$
$\Rightarrow s=\int\limits_{{{t}_{1}}}^{{{t}_{2}}}{vdt}$
$\Rightarrow s=v({{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}})$
Integration of $vdt$ shows area under v-t graph.
From the above analysis we can say the area under the v-t graph shows displacement. We cannot say the area of the v-t graph shows distance because distance is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity, so the area of the v-t graph has magnitude as well as direction. It means that the area of the v-t graph shows a vector quantity. The S.I unit of velocity is $\dfrac{meter}{\sec ond}(\dfrac{m}{s})$ and the S.I unit of time is $\sec ond(s)$.
Unit of the area under v-t graph is ,
$\text{area under v-t graph }=\text{Velocity}\times \text{Time}$
$\Rightarrow \text{area under v-t graph }=(\dfrac{m}{s})\times (s)$
$\therefore \text{area under v-t graph }=m$
Hence, area under the v-t graph shows displacement and its S.I unit is meters.
Note:We should know units of all physical quantities like in the above question we take units of velocity is $\dfrac{meter}{\sec ond}(\dfrac{m}{s})$. We should know some basic concepts of integration which are used in the above question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




