
What are the three types of RNA?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: RNA stands for RiboNucleic Acid. It is a compound found in every cell. It is majorly concerned with synthesis of proteins whereas it also plays a major role in DNA replication.
Complete answer:
RNA plays a significant role in conduction of many genetic and protein synthesising processes. Therefore, it is found in many different forms. However, out of many three types of RNA are most common. Those are:
mRNA: stands for messenger RNA (RiboNucleic Acid). It is a single stranded structure that is concerned with carrying genetic information of the replicating DNA. It carries this information in the form of some basic codes describing respective amino acid requirements in protein synthesising or DNA replicating process. As the name suggests they work as messengers between replicating DNA and protein synthesising sites in the cytoplasm.
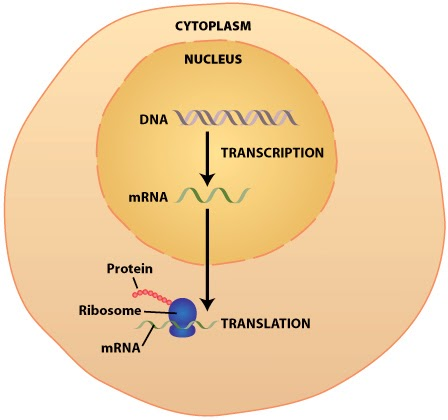
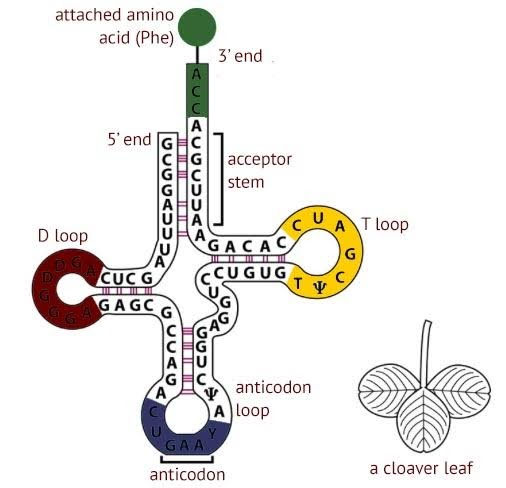
tRNA: stands for transfer RNA (RiboNucleic Acid). It works as a helping hand for mRNA in decoding the information being carried by it. Basically, its activity can be termed as translation of mRNA data into protein synthesis. Therefore, it is specifically found in the ribosomal areas of the cytoplasm.
rRNA stands for ribosomal RNA (RiboNucleic Acid). It functions as a catalyst in protein synthesising processes. It plays a crucial role in binding of amino acids together as a single unit in order to frame several protein molecules.
Note:
RNA must not be confused with DNA. Though they are both involved in genetic processes yet are quite different in terms of structure. RNA are single stranded sugar ribose molecules whereas DNA is a double stranded oxygen lacking ribose molecule.
Complete answer:
RNA plays a significant role in conduction of many genetic and protein synthesising processes. Therefore, it is found in many different forms. However, out of many three types of RNA are most common. Those are:
mRNA: stands for messenger RNA (RiboNucleic Acid). It is a single stranded structure that is concerned with carrying genetic information of the replicating DNA. It carries this information in the form of some basic codes describing respective amino acid requirements in protein synthesising or DNA replicating process. As the name suggests they work as messengers between replicating DNA and protein synthesising sites in the cytoplasm.

tRNA: stands for transfer RNA (RiboNucleic Acid). It works as a helping hand for mRNA in decoding the information being carried by it. Basically, its activity can be termed as translation of mRNA data into protein synthesis. Therefore, it is specifically found in the ribosomal areas of the cytoplasm.

rRNA stands for ribosomal RNA (RiboNucleic Acid). It functions as a catalyst in protein synthesising processes. It plays a crucial role in binding of amino acids together as a single unit in order to frame several protein molecules.
Note:
RNA must not be confused with DNA. Though they are both involved in genetic processes yet are quite different in terms of structure. RNA are single stranded sugar ribose molecules whereas DNA is a double stranded oxygen lacking ribose molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




