
What are the three characteristics of asexual reproduction?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Asexual reproduction is a kind of reproduction process that does not involve fusion of male and female gametes. However, such individuals can be both unicellular or multicellular.
Complete answer:
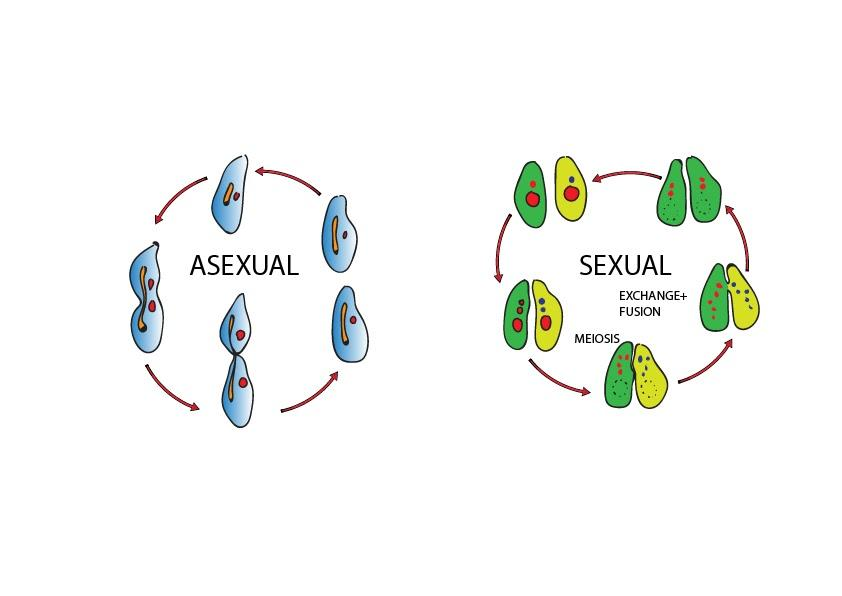
Following are the three characteristics of asexual reproduction:
1. Asexual reproduction involves single parent such that the organism divides itself as a whole or its fragment to form a new individual. Therefore, they grow at a comparatively faster rate.
2. This process of reproduction is quite faster. Usually, the zygote formed in a sexual reproduction takes a quite long gestation period to grow and develop due to which the reproduction period extends whereas the asexual reproduction is doest not require any gestation period so completes faster.
3. The offsprings produced out of asexual reproduction are genetically similar. They look identical to their parents and fellow individuals. However, this might be possible due to the fact that they are just a new version of their parent cells that broke down into two new individuals.
4. Asexual reproduction is common to be observed amongst unicellular organisms. However, it won't be any strange to observe multicellular organisms exhibiting the same procedure. In this process the parent cell undergoes mitotic division to form two daughter cells in case of single celled organisms whereas can involve formation of any bud-like structure on the parent body that eventually matures to separate from the parent body and then lead an individual life.
Note:
This reproduction can even involve spore formation on the parent body as in ferns or it can involve fragmentation taking place on the parent body to form new individuals as in Planaria, or undergo vegetative propagation that commonly takes place in plants such as onions.
Complete answer:
Following are the three characteristics of asexual reproduction:
1. Asexual reproduction involves single parent such that the organism divides itself as a whole or its fragment to form a new individual. Therefore, they grow at a comparatively faster rate.
2. This process of reproduction is quite faster. Usually, the zygote formed in a sexual reproduction takes a quite long gestation period to grow and develop due to which the reproduction period extends whereas the asexual reproduction is doest not require any gestation period so completes faster.
3. The offsprings produced out of asexual reproduction are genetically similar. They look identical to their parents and fellow individuals. However, this might be possible due to the fact that they are just a new version of their parent cells that broke down into two new individuals.
4. Asexual reproduction is common to be observed amongst unicellular organisms. However, it won't be any strange to observe multicellular organisms exhibiting the same procedure. In this process the parent cell undergoes mitotic division to form two daughter cells in case of single celled organisms whereas can involve formation of any bud-like structure on the parent body that eventually matures to separate from the parent body and then lead an individual life.

Note:
This reproduction can even involve spore formation on the parent body as in ferns or it can involve fragmentation taking place on the parent body to form new individuals as in Planaria, or undergo vegetative propagation that commonly takes place in plants such as onions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




