
What are tetrads? Are they formed in mitosis?
Answer
480.3k+ views
Hint: Tetrads are a group of two homologous chromosomes, which come together undergoing the crossover event. Concerning homologous chromosomes, one homologous chromosome comes from the mother and the other one comes from the father. When they pair up for the preparation of crossing over events, they form a tetrad shape. As tetra stands for four, there are four sister chromatids.
Complete answer:
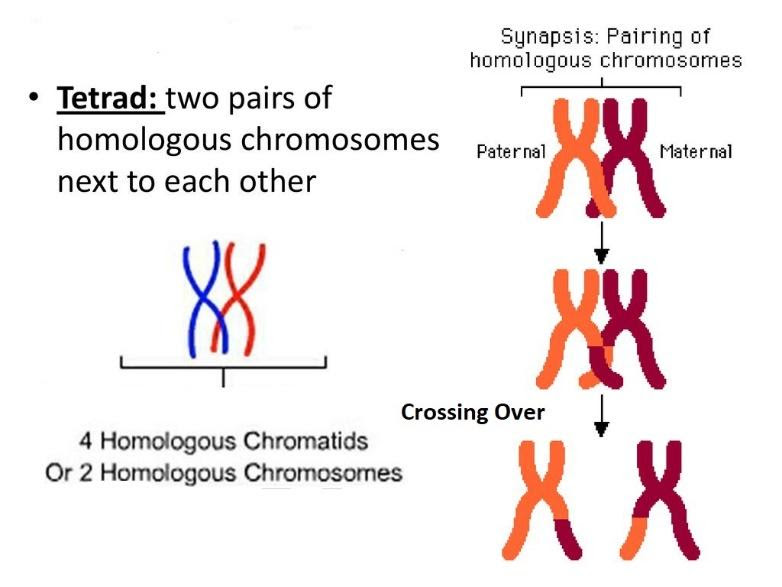
Fig.: Tetrads (Chromosomes)
In the interphase stage of meiosis, DNA has already been duplicated and condensed into chromosomes and each chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids. When a chromosome is paired with a similar chromosome, which is also made of two identical sister chromatids, the chromosomes become homologous.
Homologous chromosomes are similar, but not identical. This is similar to the case of human hair. Though the structure of the hair is the same for everyone, some people possess black hair, some have white hair, and some exhibit blonde hair.
A mitosis is a form of cell division, which is used for healing injuries in the body. In mitosis, a single parental cell divides to give two identical daughter cells. Tetrads do not appear in mitosis as there is no crossing-over event. Without crossing over, the chromosomes are brought to the equator of the cell in mitosis. There is no exchange of genetic information that takes place between the chromosomes.
In meiosis – I, the pairing of homologous chromosomes happens. Crossing over happens between homologous chromosomes and separation of homologous chromosomes occurs so that each daughter cell has one-half the chromosome number when compared to the parent cell. The tetrads are formed in the prophase stage of meiosis –I.
Note:
Tetrads are also called bivalents. For the crossing over to occur, the presence of tetrads is mandatory. When the separation of homologous chromosomes takes place in meiosis –I, the tetrads break apart. They are held together at a point known as chiasmata. Tetrads are attached to microtubules from the poles, with one homologous chromosome facing each pole at the end of the prophase – I stage.
Complete answer:

Fig.: Tetrads (Chromosomes)
In the interphase stage of meiosis, DNA has already been duplicated and condensed into chromosomes and each chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids. When a chromosome is paired with a similar chromosome, which is also made of two identical sister chromatids, the chromosomes become homologous.
Homologous chromosomes are similar, but not identical. This is similar to the case of human hair. Though the structure of the hair is the same for everyone, some people possess black hair, some have white hair, and some exhibit blonde hair.
A mitosis is a form of cell division, which is used for healing injuries in the body. In mitosis, a single parental cell divides to give two identical daughter cells. Tetrads do not appear in mitosis as there is no crossing-over event. Without crossing over, the chromosomes are brought to the equator of the cell in mitosis. There is no exchange of genetic information that takes place between the chromosomes.
In meiosis – I, the pairing of homologous chromosomes happens. Crossing over happens between homologous chromosomes and separation of homologous chromosomes occurs so that each daughter cell has one-half the chromosome number when compared to the parent cell. The tetrads are formed in the prophase stage of meiosis –I.
Note:
Tetrads are also called bivalents. For the crossing over to occur, the presence of tetrads is mandatory. When the separation of homologous chromosomes takes place in meiosis –I, the tetrads break apart. They are held together at a point known as chiasmata. Tetrads are attached to microtubules from the poles, with one homologous chromosome facing each pole at the end of the prophase – I stage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




