
What are electron deficient and electron rich compounds of hydrogen? Give examples.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: In a stable atom there are total eight electrons in the outermost shell of the atom. On the basis of outermost shell electrons it is concluded that if the compound is electron deficient, electron rich or electron precise compound.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that there are a total eight electrons in the outermost shell of an atom and these electrons define whether the compound is electron deficient or electron rich. Electron deficient compounds are those compounds which don't have sufficient number of electrons for the formation of covalent bonds. Covalent bond is the bond in which atoms are joined by the sharing of electrons. This bond is formed when two atoms share their electrons with each other. In such compounds central metal atoms don't have a filled octet. Number of electrons in the outermost shell of such compounds is less than eight. Group $13$ compounds generally form such compounds. Examples of electron deficient compounds of hydrogen are $B{H_3}$ and $Al{H_3}$. These compounds generally exist in polymorphic form like ${B_2}{H_6}$, ${\left( {Al{H_3}} \right)_n}$ etc. Polymorphism is defined as the ability of a compound to exist in more than one crystalline form. These forms have different arrangements of the atoms in the structure. Electron deficient compounds exist in polymorphic forms in order to complete their electron deficiency.
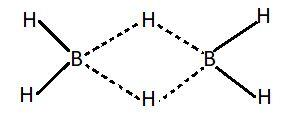
This picture shows the structure of ${B_2}{H_6}$.
Electron rich hydrides are those hydrides which have excess electrons. These compounds usually have more electrons than needed for the formation of bonds. These excess electrons are because of the presence of lone pairs on the central atom. Elements of group $15,16$ and $17$ have lone pairs after. Electron rich compounds are made by the elements which belong to the group $15,16$ and $17$. Examples of electron rich hydrides are $N{H_3}$, $P{H_3}$ etc.
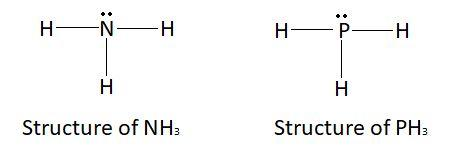
This picture shows the structure of $N{H_3}$ and $P{H_3}$ respectively.
Note: Like electron rich and electron-deficient compounds, there exists electron precise compounds as well. Electron precise compounds are those compounds which have an exact number of electrons that are required for bond formation. Examples of electron precise compounds are $C{H_4},Si{H_4}$ etc.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that there are a total eight electrons in the outermost shell of an atom and these electrons define whether the compound is electron deficient or electron rich. Electron deficient compounds are those compounds which don't have sufficient number of electrons for the formation of covalent bonds. Covalent bond is the bond in which atoms are joined by the sharing of electrons. This bond is formed when two atoms share their electrons with each other. In such compounds central metal atoms don't have a filled octet. Number of electrons in the outermost shell of such compounds is less than eight. Group $13$ compounds generally form such compounds. Examples of electron deficient compounds of hydrogen are $B{H_3}$ and $Al{H_3}$. These compounds generally exist in polymorphic form like ${B_2}{H_6}$, ${\left( {Al{H_3}} \right)_n}$ etc. Polymorphism is defined as the ability of a compound to exist in more than one crystalline form. These forms have different arrangements of the atoms in the structure. Electron deficient compounds exist in polymorphic forms in order to complete their electron deficiency.

This picture shows the structure of ${B_2}{H_6}$.
Electron rich hydrides are those hydrides which have excess electrons. These compounds usually have more electrons than needed for the formation of bonds. These excess electrons are because of the presence of lone pairs on the central atom. Elements of group $15,16$ and $17$ have lone pairs after. Electron rich compounds are made by the elements which belong to the group $15,16$ and $17$. Examples of electron rich hydrides are $N{H_3}$, $P{H_3}$ etc.
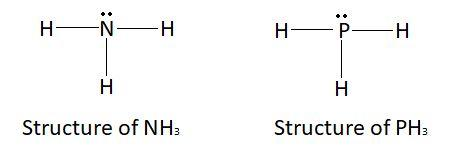
This picture shows the structure of $N{H_3}$ and $P{H_3}$ respectively.
Note: Like electron rich and electron-deficient compounds, there exists electron precise compounds as well. Electron precise compounds are those compounds which have an exact number of electrons that are required for bond formation. Examples of electron precise compounds are $C{H_4},Si{H_4}$ etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




