
What are duplication and translocation in connection with chromosomal mutation?
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: The alteration or change in the DNA sequence is called mutation. It is a spontaneous process which is inheritable from parents to offspring. Both internal and external factors are responsible for chromosomal mutation.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the chromosomal mutation.
Mutation means any change in the DNA sequence. The change can be in the nucleotide bases(A, G, C, T) due to the faulty translation or due to the DNA replication errors or due to any environmental factor like exposure to radiations, chemicals or may be due to microorganisms.
When a chromosome undergoes mutation, it is called chromosomal mutation. In human beings there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in which half is from the mother and half is from the father. Chromosome mutations can be of due to-
Duplication-It happens when the extra copies of genes or regions of chromosome are generated due to which two homologous chromosomes have different genetic material. Gene duplication occurs in the interphase. This duplication leads to evolution of new species.
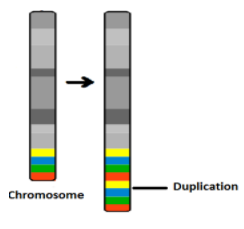
Translocation- It is an abnormality which happens because a part of chromosome breaks and reattaches to another chromosome. The translocation can be detected by finding the karyotype of the affected cells.
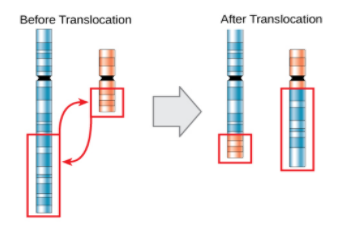
Note:An example of duplication is Pallister Killian syndrome in which the part of the 12th chromosome is duplicated. It is a rare genetic disorder. Chromosomal translocation can cause serious diseases like leukaemia. Down’s syndrome is caused by the translocation in chromosome 24.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the chromosomal mutation.
Mutation means any change in the DNA sequence. The change can be in the nucleotide bases(A, G, C, T) due to the faulty translation or due to the DNA replication errors or due to any environmental factor like exposure to radiations, chemicals or may be due to microorganisms.
When a chromosome undergoes mutation, it is called chromosomal mutation. In human beings there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in which half is from the mother and half is from the father. Chromosome mutations can be of due to-
Duplication-It happens when the extra copies of genes or regions of chromosome are generated due to which two homologous chromosomes have different genetic material. Gene duplication occurs in the interphase. This duplication leads to evolution of new species.

Translocation- It is an abnormality which happens because a part of chromosome breaks and reattaches to another chromosome. The translocation can be detected by finding the karyotype of the affected cells.

Note:An example of duplication is Pallister Killian syndrome in which the part of the 12th chromosome is duplicated. It is a rare genetic disorder. Chromosomal translocation can cause serious diseases like leukaemia. Down’s syndrome is caused by the translocation in chromosome 24.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




