
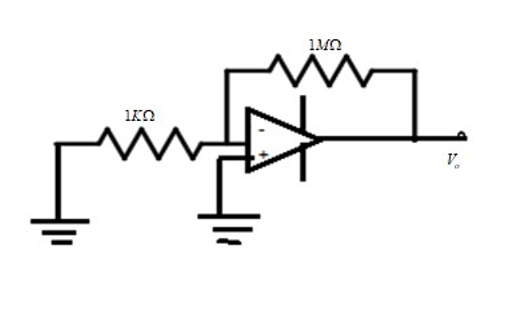
An op-amp has an offset voltage of $1mV$and is ideal in all other aspects. If this op-amp is used in the circuit shown in the figure, the output voltage will be
A) $1mV$
B) $1V$
C) $0.1V$
D) $0V$

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: The inverting amplifier is then one which gives the inverted form of its input that depends on the resistance at the feedback and the input resistance.
Formula used:
\[{V_o} = - \left( {\dfrac{{{R_f}}}{{{R_i}}}} \right){V_i}\]
Where,
\[{V_o}\]=output voltage,
\[{R_f}\]=feedback resistance
\[{R_i}\]=input resistance
\[{V_i}\]=input voltage
The negative sign represents the inverted output of the op-amp.
Complete step by step answer:
We want to find the output voltage of the given inverting op-amp. We find it is the inverting op-amp as it gives its input to pin 2.From the figure, we have
\[{R_f} = 1M\Omega \]
\[ \Rightarrow {R_f} = 1 \times {10^6}\Omega \]
${R_i} = 1K\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow {R_i} = 1 \times {10^3}\Omega $
${V_i} = 1mV$
$ \Rightarrow {V_i} = 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}V$
We can apply all the given values in the formula.
\[ \Rightarrow {V_o} = - \left( {\dfrac{{{R_f}}}{{{R_i}}}} \right){V_i}\]
Substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {V_o} = - \left( {\dfrac{{1 \times {{10}^6}}}{{1 \times {{10}^3}}}} \right) \times 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}$
We can subtract the power because the base number is same. We get,
$ \Rightarrow {V_o} = - \left( {1 \times {{10}^3}} \right) \times 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}$
$\therefore {V_o} = - 1V$
As we don’t care about the sign, because in the question they don’t mention it is an inverting op-amp and there is no option having negative sign too. So by ignoring the sign, we have${V_o} = - 1V$.
Hence the correct option is option B.
Additional information:
(i) Op-amps are the amplifiers that perform specific operations regarding its construction. Hence these amplifiers are called operation amplifiers we simply calling it op-amp.
(ii) There are basically two types of op-amps which are inverting and non-inverting amplifiers. The inverting op-amp alters the sign of the input.
(iii) Some of the other op-amps are adders, subtractors, differentiators, integrators, etc. These are all performing the operations regarding its names by just constructing the op-amps using the two basic op-amps.
(iv) The only difference between the inverting and non-inverting amplifiers is the pin no. through which we give the inputs. For the inverting amplifier, we give input to the inverting input pin of the IC (integrated chip). For the non-inverting amplifier, we give the input to the non-inverting pin of the IC.
Note:
If we give input to one of the two pins either inverting or non-inverting, another one needs to be grounded. We don’t worry about the polarity of the output voltage when the input voltage polarity is not given. Op-amps are also used as a comparator in the circuit.
Formula used:
\[{V_o} = - \left( {\dfrac{{{R_f}}}{{{R_i}}}} \right){V_i}\]
Where,
\[{V_o}\]=output voltage,
\[{R_f}\]=feedback resistance
\[{R_i}\]=input resistance
\[{V_i}\]=input voltage
The negative sign represents the inverted output of the op-amp.
Complete step by step answer:
We want to find the output voltage of the given inverting op-amp. We find it is the inverting op-amp as it gives its input to pin 2.From the figure, we have
\[{R_f} = 1M\Omega \]
\[ \Rightarrow {R_f} = 1 \times {10^6}\Omega \]
${R_i} = 1K\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow {R_i} = 1 \times {10^3}\Omega $
${V_i} = 1mV$
$ \Rightarrow {V_i} = 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}V$
We can apply all the given values in the formula.
\[ \Rightarrow {V_o} = - \left( {\dfrac{{{R_f}}}{{{R_i}}}} \right){V_i}\]
Substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {V_o} = - \left( {\dfrac{{1 \times {{10}^6}}}{{1 \times {{10}^3}}}} \right) \times 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}$
We can subtract the power because the base number is same. We get,
$ \Rightarrow {V_o} = - \left( {1 \times {{10}^3}} \right) \times 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}$
$\therefore {V_o} = - 1V$
As we don’t care about the sign, because in the question they don’t mention it is an inverting op-amp and there is no option having negative sign too. So by ignoring the sign, we have${V_o} = - 1V$.
Hence the correct option is option B.
Additional information:
(i) Op-amps are the amplifiers that perform specific operations regarding its construction. Hence these amplifiers are called operation amplifiers we simply calling it op-amp.
(ii) There are basically two types of op-amps which are inverting and non-inverting amplifiers. The inverting op-amp alters the sign of the input.
(iii) Some of the other op-amps are adders, subtractors, differentiators, integrators, etc. These are all performing the operations regarding its names by just constructing the op-amps using the two basic op-amps.
(iv) The only difference between the inverting and non-inverting amplifiers is the pin no. through which we give the inputs. For the inverting amplifier, we give input to the inverting input pin of the IC (integrated chip). For the non-inverting amplifier, we give the input to the non-inverting pin of the IC.
Note:
If we give input to one of the two pins either inverting or non-inverting, another one needs to be grounded. We don’t worry about the polarity of the output voltage when the input voltage polarity is not given. Op-amps are also used as a comparator in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




