
An object of height 1.5 cm is situated at a distance of 15cm from a concave mirror. The concave mirror forms its real image of height 3.0cm. The focal length of the mirror will be:
A. -10 cm
B. -20 cm
C. 20 cm
D. 30 cm
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Keeping in mind the cases of image formation by a concave mirror, we can say that the real image formed by it is always situated below the axis of the mirror. According to the sign conventions, the distance measured left of the mirror and below the axis of mirror is to be taken negative while the distance in the right of the mirror and above the principal axis is to be taken positive.
Formula used: magnification (m) = $\dfrac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}$=$- \dfrac{v}{u}$, $\dfrac1f=\dfrac 1u+\dfrac 1v$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
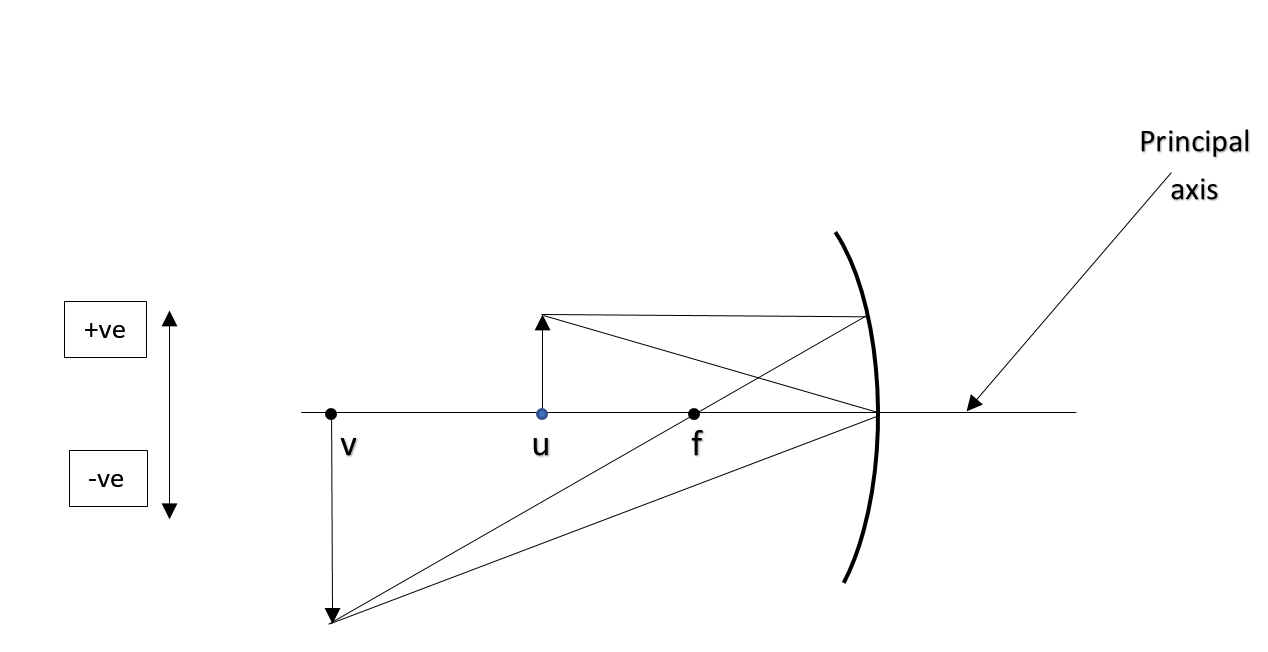
u (object distance) = -15cm [ -ve, as measured in the left of pole ]
$h_{i}$(height of image) = - 3cm [ -ve as measured below principle axis ]
$h_{o}$(height of object) = 1.5cm [ +ve as kept above principle axis ]
From the above data, m= $\dfrac{-3}{1.5}$=$- \dfrac{v}{u}$
$- \dfrac{v}{-15}$=$\dfrac{-3}{1.5}$ or $v=-30cm$
Now using mirror formula;
$\dfrac1f=\dfrac 1u+\dfrac 1v$
$\dfrac1f=\dfrac 1{-15}+\dfrac 1{-30}$
$f=-10cm$
Hence option A. is correct
Additional information:
Though if one proceeds with taking proper care of sign conventions, focal length of concave mirror will always come out to be negative, but in multiple questions like these, we must have the knowledge that focal length of concave mirror is negative whereas that of a convex mirror is positive.
Note: In optics lens and mirror problems, the first and foremost thing is to understand the sign conventions properly and then proceed, otherwise the topic will seem very difficult. Students are also advised to understand the diagrams of image formation in various cases of lens and mirror.
Formula used: magnification (m) = $\dfrac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}$=$- \dfrac{v}{u}$, $\dfrac1f=\dfrac 1u+\dfrac 1v$.
Complete step-by-step solution -

u (object distance) = -15cm [ -ve, as measured in the left of pole ]
$h_{i}$(height of image) = - 3cm [ -ve as measured below principle axis ]
$h_{o}$(height of object) = 1.5cm [ +ve as kept above principle axis ]
From the above data, m= $\dfrac{-3}{1.5}$=$- \dfrac{v}{u}$
$- \dfrac{v}{-15}$=$\dfrac{-3}{1.5}$ or $v=-30cm$
Now using mirror formula;
$\dfrac1f=\dfrac 1u+\dfrac 1v$
$\dfrac1f=\dfrac 1{-15}+\dfrac 1{-30}$
$f=-10cm$
Hence option A. is correct
Additional information:
Though if one proceeds with taking proper care of sign conventions, focal length of concave mirror will always come out to be negative, but in multiple questions like these, we must have the knowledge that focal length of concave mirror is negative whereas that of a convex mirror is positive.
Note: In optics lens and mirror problems, the first and foremost thing is to understand the sign conventions properly and then proceed, otherwise the topic will seem very difficult. Students are also advised to understand the diagrams of image formation in various cases of lens and mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




