
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and plane mirror is 30cm, it is found that there is no parallax between the images formed by the two mirrors. What is the radius of curvature of the convex mirror?
A. 25cm
B. 7cm
C. 18cm
D. 27cm
Answer
522.3k+ views
Hint: Draw the ray diagram of the system. Determine the position of the image due to the plane mirror. If there is no parallax between the images formed, then the image due to the convex mirror also falls at the same location. Use the formula for spherical mirrors to determine the focal length and radius of curvature.
Formula Used: For spherical mirrors,
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where,
$u$ is the distance of the object from the pole
$v$ is the distance of the image from the pole
$f$ is the distance of the focal point from the pole
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following diagram shows the system.
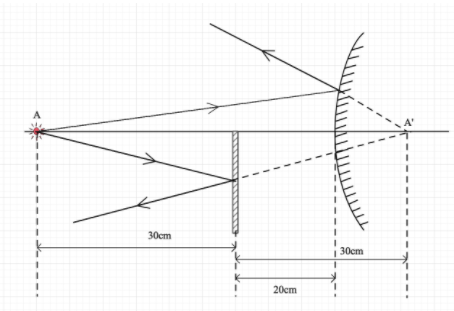
The distance between the object and the convex mirror is 50 cm.
The plane mirror is introduced at a distance of 30cm from the object.
Hence, the distance between the plane mirror and the spherical mirror is 20 cm.
Now, the image due to the plane mirror is formed at a distance of 30cm towards the right of the plane mirror.
So, the image A’ will be formed at a distance of (30-20)cm =10cm towards the right of the convex mirror.
It is given that there is no parallax between the images.
We can conclude that the image due to plane mirror and the convex mirror coincide.
Hence, we know the final image distance due to the convex mirror.
Which is given by, v = +10cm
The image was 50cm on the left of the pole of the convex mirror.
Hence, u = -50cm
We can write the formula for the spherical mirror,
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$....................(1)
We can put the values of u and v in equation (1), we get,
$\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{-50}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{5-1}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2}{25}$
$\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{25}{2}$
Hence, the focal length of the mirror is $\dfrac{25}{2}$ cm
So, the radius of curvature = f × 2 = 25cm
The correct choice is (A).
Note:
If the images due to the two mirrors did not coincide with each other, there would have been two images, and we could have seen a parallax. A parallax is a second image which is not the actual image of the system.
Formula Used: For spherical mirrors,
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where,
$u$ is the distance of the object from the pole
$v$ is the distance of the image from the pole
$f$ is the distance of the focal point from the pole
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following diagram shows the system.

The distance between the object and the convex mirror is 50 cm.
The plane mirror is introduced at a distance of 30cm from the object.
Hence, the distance between the plane mirror and the spherical mirror is 20 cm.
Now, the image due to the plane mirror is formed at a distance of 30cm towards the right of the plane mirror.
So, the image A’ will be formed at a distance of (30-20)cm =10cm towards the right of the convex mirror.
It is given that there is no parallax between the images.
We can conclude that the image due to plane mirror and the convex mirror coincide.
Hence, we know the final image distance due to the convex mirror.
Which is given by, v = +10cm
The image was 50cm on the left of the pole of the convex mirror.
Hence, u = -50cm
We can write the formula for the spherical mirror,
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$....................(1)
We can put the values of u and v in equation (1), we get,
$\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{-50}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{5-1}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2}{25}$
$\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{25}{2}$
Hence, the focal length of the mirror is $\dfrac{25}{2}$ cm
So, the radius of curvature = f × 2 = 25cm
The correct choice is (A).
Note:
If the images due to the two mirrors did not coincide with each other, there would have been two images, and we could have seen a parallax. A parallax is a second image which is not the actual image of the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




