
An infinite ladder network of resistances is constructed with \[1\,\Omega \] and \[2\,\Omega \] resistances as shown in the figure. The 6 V battery between A and B has negligible internal resistance. The equivalent resistance between A and B is?
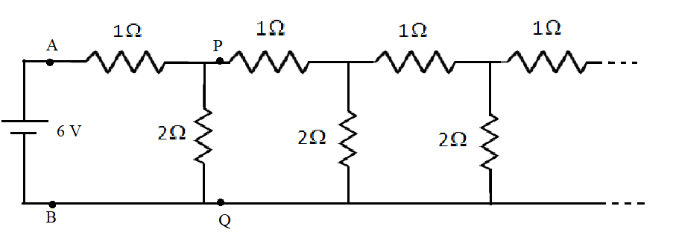

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint:: Assume the equivalent resistance of the circuit beyond the first loop of the circuit as R, then find the equivalent resistance of the whole network.
Formula used:
The equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of resistors \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\]:
\[{R_{12}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}\]
The equivalent resistance of the series combination of resistors \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\]:
\[{R_{12}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
The above circuit diagram of infinite ladder network is,
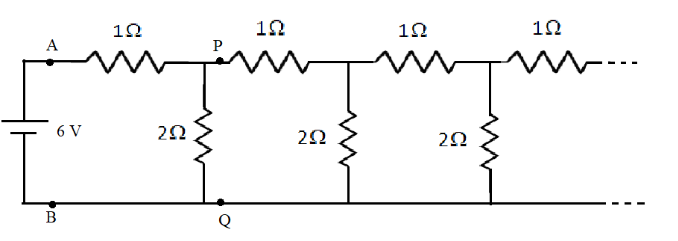
Let the equivalent resistance of the above circuit is R. Since the circuit is infinitely long, removing the loop ABDC from the circuit will not affect the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the circuit beyond PQ is also R.
Now, the revised circuit diagram for this case will become,
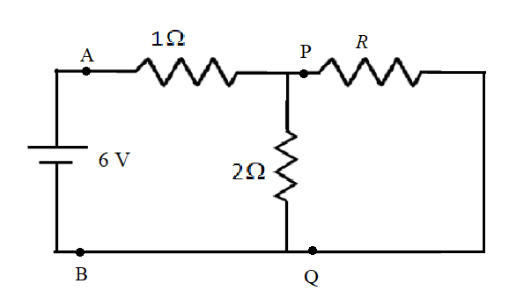
In the above circuit diagram, the resistors R and \[2\,\Omega \] are in parallel combination to each other. The equivalent resistance of these two is,
\[{R_1} = \dfrac{{\left( R \right)\left( {2\,} \right)}}{{R + 2\,}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {R_1} = \dfrac{{2R}}{{R + 2}}\]
Now, \[{R_1}\] is in series with \[1\,\Omega \] resistance of the first loop and we know that the equivalent resistance of these two resistors is R. therefore,
\[R = \dfrac{{2R}}{{R + 2}} + 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow R\left( {R + 2} \right) = 2R + \left( {R + 2} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {R^2} - R + 2 = 0\]
Solve this second order equation to get the value of equivalent resistance as follows,
\[R = \dfrac{{1 \pm \sqrt {{1^2} + 4\left( 2 \right)} }}{2}\]
\[\therefore R = + 2\,\,{\text{or}}\, - 2\]
But resistance can never be negative. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the circuit is \[2\,\Omega \].
Note: We cannot find the equivalent resistance of the infinite ladder network by determining the equivalent resistance of each loop in the circuit. Always assume the equivalent resistance of the network excluding the first loop as R.
Formula used:
The equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of resistors \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\]:
\[{R_{12}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}\]
The equivalent resistance of the series combination of resistors \[{R_1}\] and \[{R_2}\]:
\[{R_{12}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
The above circuit diagram of infinite ladder network is,

Let the equivalent resistance of the above circuit is R. Since the circuit is infinitely long, removing the loop ABDC from the circuit will not affect the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the circuit beyond PQ is also R.
Now, the revised circuit diagram for this case will become,

In the above circuit diagram, the resistors R and \[2\,\Omega \] are in parallel combination to each other. The equivalent resistance of these two is,
\[{R_1} = \dfrac{{\left( R \right)\left( {2\,} \right)}}{{R + 2\,}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {R_1} = \dfrac{{2R}}{{R + 2}}\]
Now, \[{R_1}\] is in series with \[1\,\Omega \] resistance of the first loop and we know that the equivalent resistance of these two resistors is R. therefore,
\[R = \dfrac{{2R}}{{R + 2}} + 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow R\left( {R + 2} \right) = 2R + \left( {R + 2} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {R^2} - R + 2 = 0\]
Solve this second order equation to get the value of equivalent resistance as follows,
\[R = \dfrac{{1 \pm \sqrt {{1^2} + 4\left( 2 \right)} }}{2}\]
\[\therefore R = + 2\,\,{\text{or}}\, - 2\]
But resistance can never be negative. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the circuit is \[2\,\Omega \].
Note: We cannot find the equivalent resistance of the infinite ladder network by determining the equivalent resistance of each loop in the circuit. Always assume the equivalent resistance of the network excluding the first loop as R.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




