
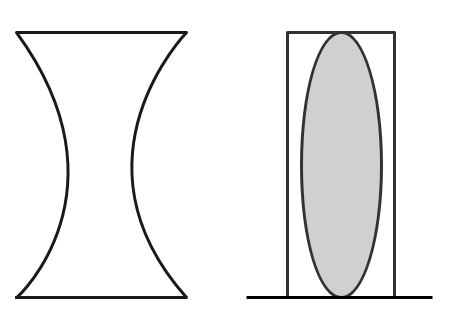
An equi concave diverging lens of focal length $F$ is cut into two equal halves. The two halves are turned around and joined with some liquid between them. The lens obtained is converging with a focal length $F$. If the refractive index of the liquid is $3$, then what is the refractive index of the lens?
\[\begin{align}
& A.4 \\
& B.2 \\
& C.5 \\
& D.1.5 \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: We know that the lens makers formula for thin lenses, where $F$ is the focal length, also $R=2F$, $\mu$ is the refractive index of the lens and $R_{1}$ and $R_{2}$ is the radius of curvature of the spheres of surfaces 1 and 2 respectively.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{F}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R_{1}}-\dfrac{1}{R_{2}}\right)$
Complete step by step answer:
We also know that the focal length $F$ of the concave lens given by the lens makers formula is expressed as $\dfrac{1}{F}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$, where $\mu$ is the refractive index of the concave lens and $R$ is its radius of curvature.
Now consider the focal length of the combination of two halves of the concave lens and the liquid with refractive index $\mu_{l}=3$.
Then clearly $\dfrac{1}{f_{1}}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{\infty}-\dfrac{1}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
Similarly, $\dfrac{1}{f_{3}}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{\infty}-\dfrac{1}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
But since the $f_{2}$ has some liquid between them, then we get, $\dfrac{1}{f_{2}}=(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{R}\right)=(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$
We can write it as $\dfrac{1}{f_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{3}}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)+(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)+(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
An equiconvex lens of focal length $F$ is cut into two equal halves and the joined with some liquid between them, we can say that $\dfrac{1}{F}=\dfrac{1}{f_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{3}}$
Then we can get, $(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)+(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)+(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
$\Rightarrow (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{-R}\right)+(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$
$ \Rightarrow (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)=[(-1)(\mu-1)+(\mu_{l}-1)]\times\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$
$\Rightarrow \mu-1=-\mu+\mu_{l}$
$2\mu=\mu_{l}+1$
Given $\mu_{l}=3$
$\mu=\dfrac{4}{2}=2$
Thus the refractive index of the lens $2$
Hence the answer is \[B.2\]
Note:
The lens makers formula as the name suggests is used in the making of the lens. Also clearly, more the refractive index of the lens or combination of lens and liquid, less the focal length. Whereas, the more the radius of curvature of the spherical lens, the more is the focal length of the lens.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{F}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R_{1}}-\dfrac{1}{R_{2}}\right)$
Complete step by step answer:
We also know that the focal length $F$ of the concave lens given by the lens makers formula is expressed as $\dfrac{1}{F}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$, where $\mu$ is the refractive index of the concave lens and $R$ is its radius of curvature.
Now consider the focal length of the combination of two halves of the concave lens and the liquid with refractive index $\mu_{l}=3$.
Then clearly $\dfrac{1}{f_{1}}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{\infty}-\dfrac{1}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
Similarly, $\dfrac{1}{f_{3}}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{\infty}-\dfrac{1}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
But since the $f_{2}$ has some liquid between them, then we get, $\dfrac{1}{f_{2}}=(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{R}\right)=(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$
We can write it as $\dfrac{1}{f_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{3}}=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)+(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)+(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
An equiconvex lens of focal length $F$ is cut into two equal halves and the joined with some liquid between them, we can say that $\dfrac{1}{F}=\dfrac{1}{f_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{f_{3}}$
Then we can get, $(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)+(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)+(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{-R}\right)$
$\Rightarrow (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)=(\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{-R}\right)+(\mu_{l}-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$
$ \Rightarrow (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)=[(-1)(\mu-1)+(\mu_{l}-1)]\times\left(\dfrac{2}{R}\right)$
$\Rightarrow \mu-1=-\mu+\mu_{l}$
$2\mu=\mu_{l}+1$
Given $\mu_{l}=3$
$\mu=\dfrac{4}{2}=2$
Thus the refractive index of the lens $2$
Hence the answer is \[B.2\]
Note:
The lens makers formula as the name suggests is used in the making of the lens. Also clearly, more the refractive index of the lens or combination of lens and liquid, less the focal length. Whereas, the more the radius of curvature of the spherical lens, the more is the focal length of the lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




