
An aldehyde on oxidation gives
(A) an acid
(B) an alcohol
(C) an ether
(D) a ketone
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Aldehydes are containing –CHO functional group and this is one of the types of carbonyl compounds in organic chemistry. The IUPAC nomenclature for aldehydes assigns suffix as –al and suffix for –aldehyde used for the common method for naming aldehydes. Organic compounds like aldehydes, carboxylic acids are oxidized by using oxidizing agents.
Complete answer:
-CHO group in aldehydes are a highly oxidized functional group than $-C{{H}_{2}}OH$, because in aldehydes – CHO group contains one hydrogen atom.
Aldehydes can be oxidized by using oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate, chromic acid, etc. In aldehydes, there is no such importance for oxidation reactions than reduction reactions.
Aldehydes (RCHO) can easily be oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH) even in the presence of oxygen in the air.
\[RCHO\overset{[O]}{\mathop{\to }}\,RCOOH\]
Only aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acid, under these conditions ketones are not oxidized due to lack of critical H atoms for the elimination to occur. The mechanism of oxidation of aldehydes as follows,
Step-1: The reactive species during the oxidation of aldehyde, hydrate will be formed when the aldehyde reacts with water.
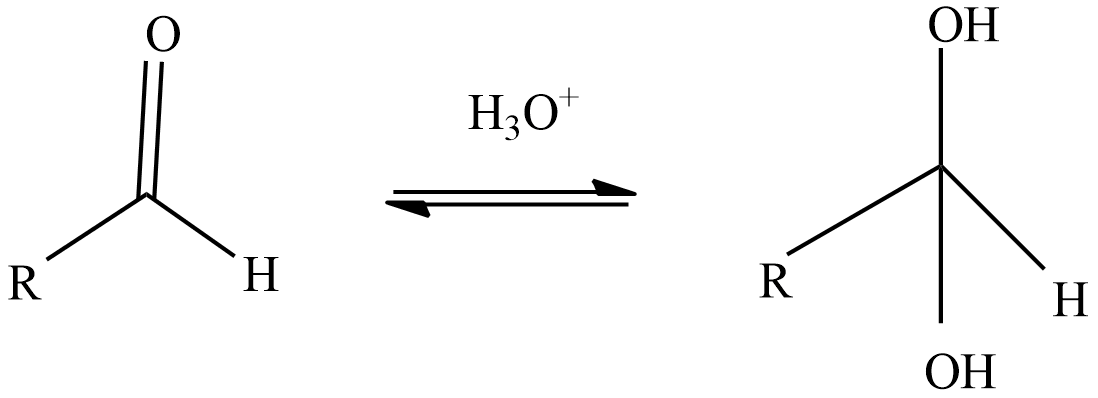
Step-2: React with oxidizing agent chromic acid which forms an intermediate chromate ester.
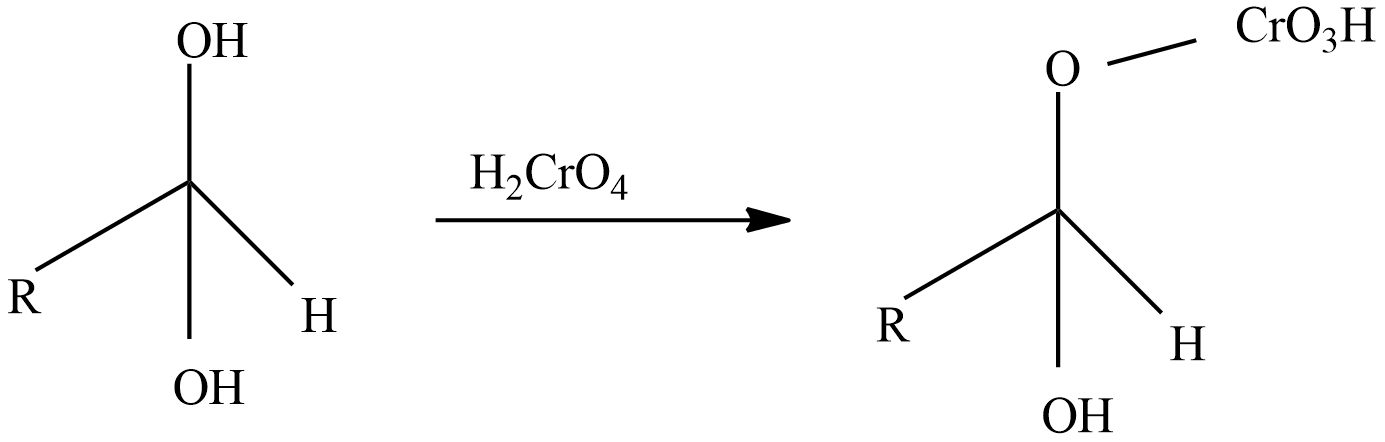
Step-3: A base like water molecule extracts protons from the chromate ester.
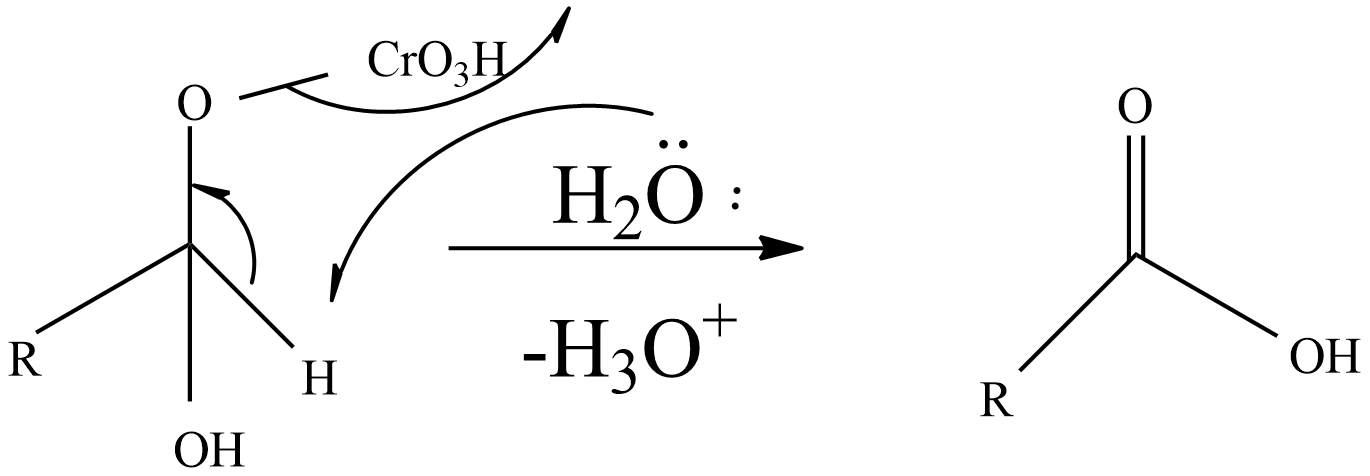
So, an aldehyde on oxidation gives an acid (carboxylic acid).
The correct answer is option A.
Note:
Aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols, in presence of a catalyst as Nickel (Ni), platinum(Pt), and strong reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride, sodium borohydride, or hydrogen gas. Based on the catalysts or reducing agents types of alcohol will be formed as products.
Complete answer:
-CHO group in aldehydes are a highly oxidized functional group than $-C{{H}_{2}}OH$, because in aldehydes – CHO group contains one hydrogen atom.
Aldehydes can be oxidized by using oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate, chromic acid, etc. In aldehydes, there is no such importance for oxidation reactions than reduction reactions.
Aldehydes (RCHO) can easily be oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH) even in the presence of oxygen in the air.
\[RCHO\overset{[O]}{\mathop{\to }}\,RCOOH\]
Only aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acid, under these conditions ketones are not oxidized due to lack of critical H atoms for the elimination to occur. The mechanism of oxidation of aldehydes as follows,
Step-1: The reactive species during the oxidation of aldehyde, hydrate will be formed when the aldehyde reacts with water.
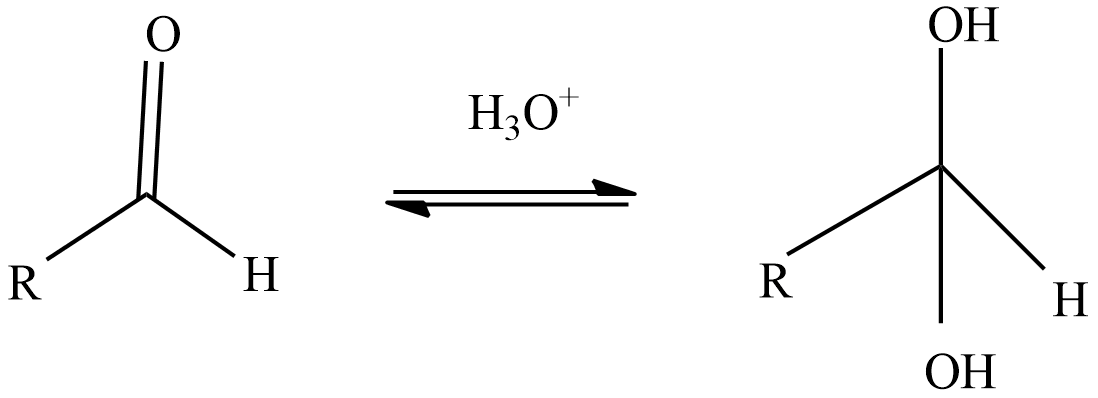
Step-2: React with oxidizing agent chromic acid which forms an intermediate chromate ester.
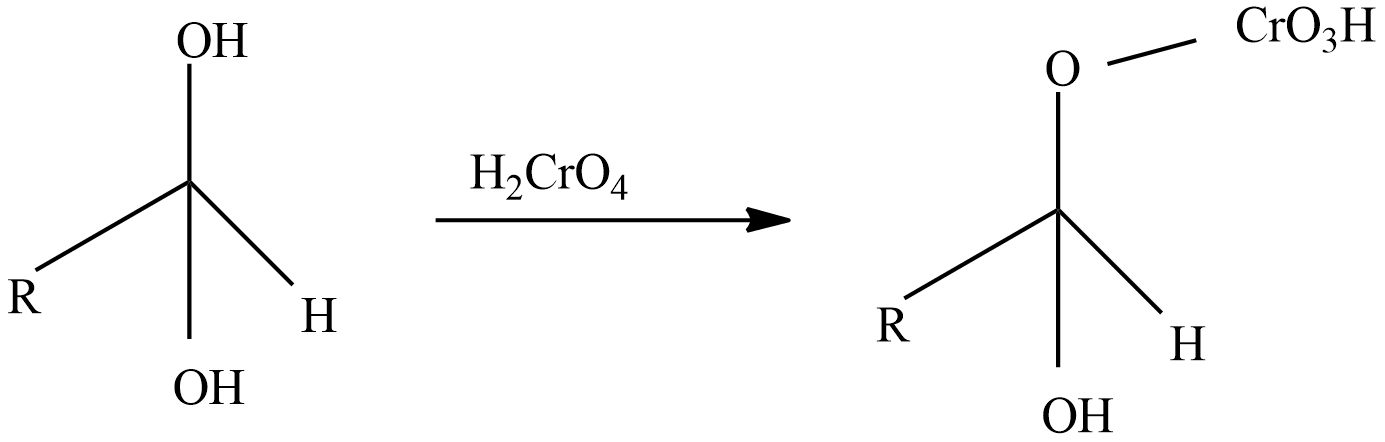
Step-3: A base like water molecule extracts protons from the chromate ester.
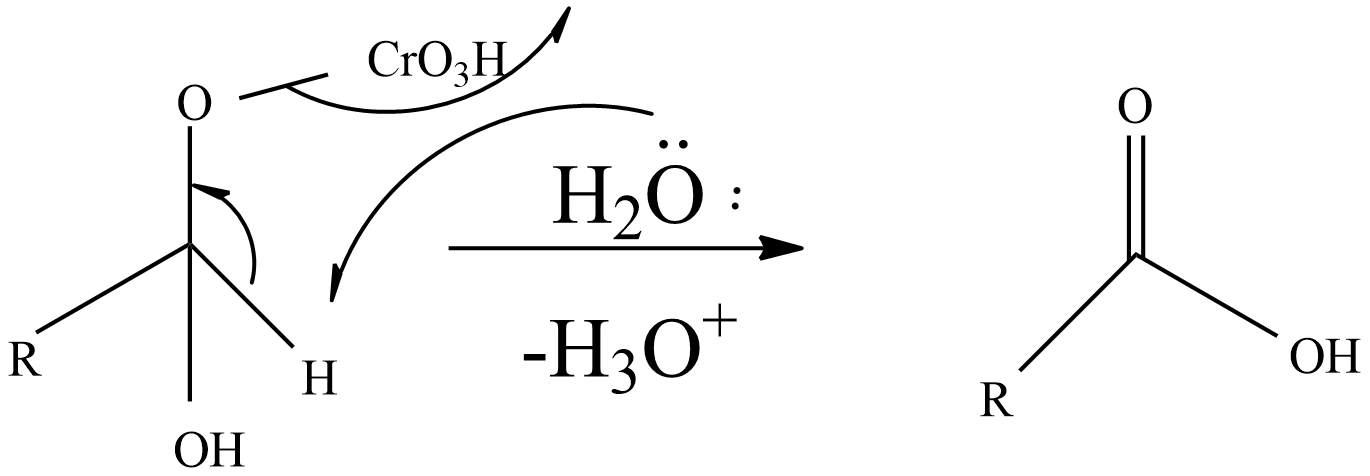
So, an aldehyde on oxidation gives an acid (carboxylic acid).
The correct answer is option A.
Note:
Aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols, in presence of a catalyst as Nickel (Ni), platinum(Pt), and strong reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride, sodium borohydride, or hydrogen gas. Based on the catalysts or reducing agents types of alcohol will be formed as products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




