
An acidified ${{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ paper turns green when exposed to $S{{O}_{2}}$. Explain
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Potassium Dichromate is orange in colour and a strong oxidising agent which can exhibit different oxidation states and hence various colours are shown by this compound. It also has a very weak para-magnetism.
Complete Solution :
When acidified ${{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ is exposed to $S{{O}_{2}}$then the following reaction takes place.
${{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}+2{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+3S{{O}_{2}}\to 2C{{r}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}+{{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
- If we look at the reaction then we realise that first the solution is orange in colour and then it changes to green after getting exposed to the gas due to its oxidation state changes to +3 which exhibits colour. There is a very interesting phenomenon which takes place which is called charge-transfer phenomenon. The extra lone pairs present on the oxygen atom to chromate ion which is also called ligand to metal or anion to cation transfer which exhibits the colour orange.
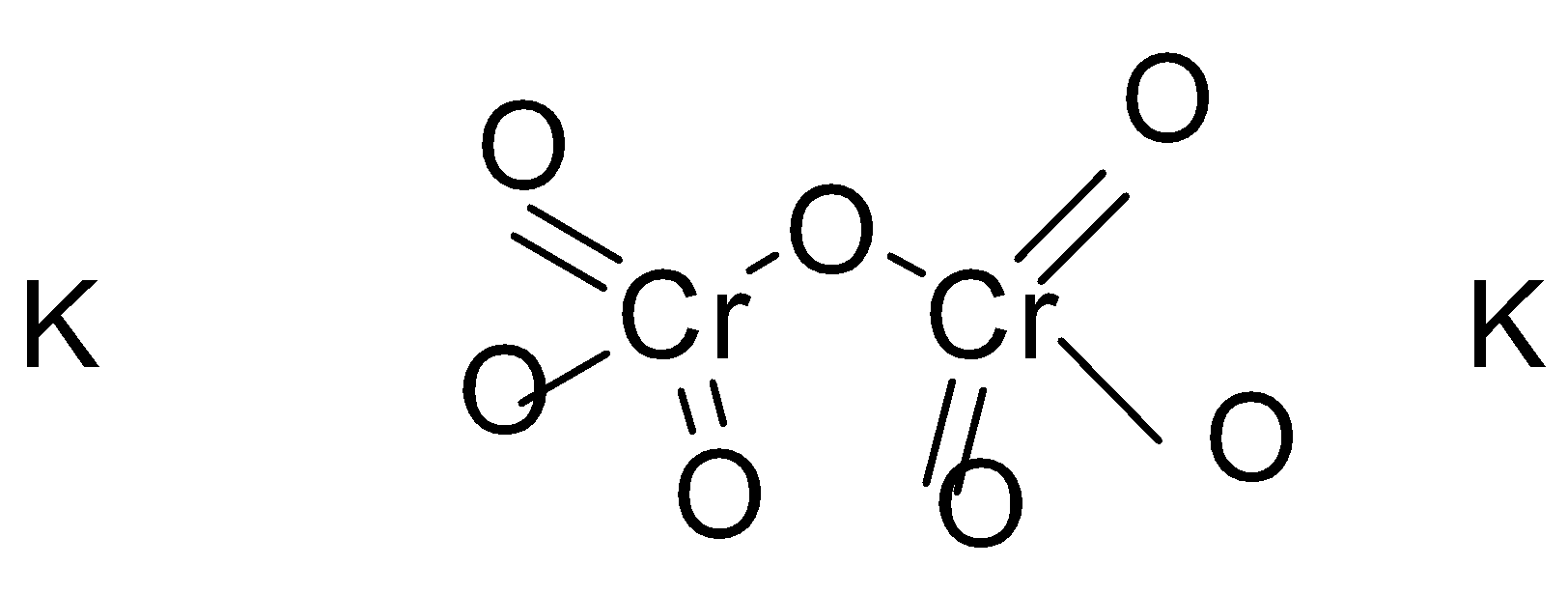
We can clearly see in the diagram and flow of extra lone pairs from oxygen to the chromate ion which generates the colour process .
Note: The d-block elements show colours which generally form complexes due to their nature of bond formation. The colour is shown with the help of two procedures mainly, d-d transition and charge transfer spectra. In d-d transitions the electron in the d-orbital gets excited by a photon and moves to a higher d-orbital arrangement as in the complexes, the d-orbitals generally do not have the same energy level. Hence, once the electrons move it is seen as colour.
- The next phenomenon is of charge transfer spectra where the anion to cation transfer takes place.
Complete Solution :
When acidified ${{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ is exposed to $S{{O}_{2}}$then the following reaction takes place.
${{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}+2{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+3S{{O}_{2}}\to 2C{{r}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}+{{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
- If we look at the reaction then we realise that first the solution is orange in colour and then it changes to green after getting exposed to the gas due to its oxidation state changes to +3 which exhibits colour. There is a very interesting phenomenon which takes place which is called charge-transfer phenomenon. The extra lone pairs present on the oxygen atom to chromate ion which is also called ligand to metal or anion to cation transfer which exhibits the colour orange.

We can clearly see in the diagram and flow of extra lone pairs from oxygen to the chromate ion which generates the colour process .
Note: The d-block elements show colours which generally form complexes due to their nature of bond formation. The colour is shown with the help of two procedures mainly, d-d transition and charge transfer spectra. In d-d transitions the electron in the d-orbital gets excited by a photon and moves to a higher d-orbital arrangement as in the complexes, the d-orbitals generally do not have the same energy level. Hence, once the electrons move it is seen as colour.
- The next phenomenon is of charge transfer spectra where the anion to cation transfer takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life

In Dows process haloarene is converted to phenol with class 11 chemistry CBSE

During the charging of lead storage battery the reaction class 11 chemistry CBSE




