
Among the members of V A group (N, P, As, S and Bi), which of the following properties shows an increase as we go down from nitrogen to bismuth?
(A) Stability of +3 oxidation state
(B) Reducing character of hydrides
(C) Electronegativity
(D) Acidic nature of the pentoxide
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: The question has multiple correct answers. As we know that the size of the atom increases along a group, since new shells are introduced, compare how the properties given in the options change with the size increasing factor of elements involved in a group.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question it is asked that which periodic property given in the options have an increasing trend as we go down the group in group V A i.e. the Nitrogen down.
We are very familiar with the periodic table from lower class. The 118 elements are arranged in various periods and groups. We have 7 periods and 18 groups in a periodic table in which the Nitrogen family is placed on the right side of the periodic table where the non-metals are placed. We also know that the group V A is the group 15 in the periodic table. Since the first element in group-15 is Nitrogen, it is also called the nitrogen family.
Now let’s write the elements in the nitrogen group as such they are placed in the periodic table.
- We know that in a group, all the elements will have the same outer electronic configuration i.e. each group will possess a general electronic configuration. All the elements in the group will have the same number of valence electrons and the group will have the group number same as the number of valence electrons.
- The general electronic configuration of group V A is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{3}}$
And hence will have 5 valence electrons and the valence electrons are the electrons that take part actively in bond formation. But as we move down the group the two electrons in ns orbital will not take part in bond formation. The elements on the bottom of the group will show the +3 oxidation state only. Hence we could say that as we go down the group the stability of +3 oxidation state increases which is due to the inert pair effect.
- If we consider reducing property of hydride of the group-15. We know that the reducing property of the hydrides is the property to liberate hydrogen from the hydrides. Since the atomic size is increasing down the group, the distance between H and the central atom increases down the group i.e. bond length increases down the group. Therefore the bond breaking is easier and the reducing property of hydrides increases down the group.
- If we see the electronegativity trend then it decreases down the group since the atomic size is increasing.
- Then comes the acidic nature of pentoxide (${{M}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$), we know since the electronegativity is decrease down the group, then the electropositivity is increasing down the group, so the tendency to lose electrons increases and the acidic character of pentoxide is decreasing.
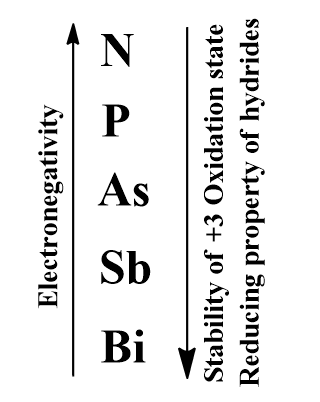
The correct answer is option “A” and “B” .
Note: If in the option the periodic trend in increase of the +5 oxidation state was given then it might have been the wrong option, since only the first three elements i.e. N,P and As will show the common oxidation states of +3 and +5. For other two elements ,the inert pair effect comes into action.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question it is asked that which periodic property given in the options have an increasing trend as we go down the group in group V A i.e. the Nitrogen down.
We are very familiar with the periodic table from lower class. The 118 elements are arranged in various periods and groups. We have 7 periods and 18 groups in a periodic table in which the Nitrogen family is placed on the right side of the periodic table where the non-metals are placed. We also know that the group V A is the group 15 in the periodic table. Since the first element in group-15 is Nitrogen, it is also called the nitrogen family.
Now let’s write the elements in the nitrogen group as such they are placed in the periodic table.

- We know that in a group, all the elements will have the same outer electronic configuration i.e. each group will possess a general electronic configuration. All the elements in the group will have the same number of valence electrons and the group will have the group number same as the number of valence electrons.
- The general electronic configuration of group V A is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{3}}$
And hence will have 5 valence electrons and the valence electrons are the electrons that take part actively in bond formation. But as we move down the group the two electrons in ns orbital will not take part in bond formation. The elements on the bottom of the group will show the +3 oxidation state only. Hence we could say that as we go down the group the stability of +3 oxidation state increases which is due to the inert pair effect.
- If we consider reducing property of hydride of the group-15. We know that the reducing property of the hydrides is the property to liberate hydrogen from the hydrides. Since the atomic size is increasing down the group, the distance between H and the central atom increases down the group i.e. bond length increases down the group. Therefore the bond breaking is easier and the reducing property of hydrides increases down the group.
- If we see the electronegativity trend then it decreases down the group since the atomic size is increasing.
- Then comes the acidic nature of pentoxide (${{M}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$), we know since the electronegativity is decrease down the group, then the electropositivity is increasing down the group, so the tendency to lose electrons increases and the acidic character of pentoxide is decreasing.

The correct answer is option “A” and “B” .
Note: If in the option the periodic trend in increase of the +5 oxidation state was given then it might have been the wrong option, since only the first three elements i.e. N,P and As will show the common oxidation states of +3 and +5. For other two elements ,the inert pair effect comes into action.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




