
Among the following species, the most stable carbonium ion is:
A) ${C_6}{H_5}{C^+ }H{C_6}{H_5}$
B) ${C_6}{H_5}{C^+ }{H_2}$
C) $C{H_3}C{H_2}^+ $
D) ${C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}{C^+ }{H_2}$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint:Carbocations are positively charged carbon atoms which have only six electrons in its outermost shell. When a heterocyclic fission of C-X bond in an organic molecule, generates negatively charged anion and positively charged species carbocation. Stability of carbocation increases when electron donating groups are present.
Complete answer:
The reason for the alkyl carbocation stability is simply as inductive stabilization of the positively charged carbon by its attached electron releasing alkyl substituents and by hyperconjugation or no bond resonance. And therefore in alkyl carbocation tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary which is more stable than primary alkyl carbocation.
But the presence of electron withdrawing groups like nitro and carboxyl groups adjacent to carbon atoms bearing positive charge makes the carbocation less stable.
The resonance effect can further stabilize the carbocations. By resonance effect, positive charge on carbocation atoms gets displaced over other carbon atoms and hence give stability to the carbocation. The more canonical structures of carbocation, the more will be the stability.Here in question, in option C we have alkyl carbocation and there is no possibility of conjugation, hence alkyl carbocations are least stable.
Next we have option D. in this carbocation, the carbon bearing positive charge is alkyl, hence no possibility of resonance. Hence is less stable than aromatic carbocation.
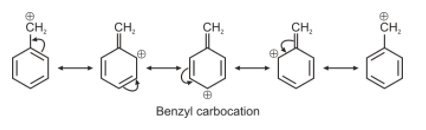
For option B. the carbon bearing positive charge is attached directly to the aromatic system. Hence resonance can occur and this carbocation will have 4 canonical structures. This carbocation is also known as benzyl carbocation.
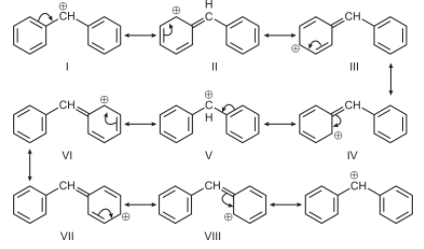
For option A, the carbon bearing positive charge is attached to 2 aromatic systems, therefore resonance will occur but since it has 2 benzene rings attached to the carbocation, hence it will have more canonical structure than the benzyl carbocation. Therefore it is most stable among all.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note:The carbocation stability also increases by the presence of heteroatoms having an unshared pair of electrons for example nitrogen, oxygen adjacent to the cation. Such carbocations are also stabilized by resonance. The triphenylmethyl carbocation is more stable than option A above, because it has 3 benzene rings, hence it will have more canonical structure.
Complete answer:
The reason for the alkyl carbocation stability is simply as inductive stabilization of the positively charged carbon by its attached electron releasing alkyl substituents and by hyperconjugation or no bond resonance. And therefore in alkyl carbocation tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary which is more stable than primary alkyl carbocation.
But the presence of electron withdrawing groups like nitro and carboxyl groups adjacent to carbon atoms bearing positive charge makes the carbocation less stable.
The resonance effect can further stabilize the carbocations. By resonance effect, positive charge on carbocation atoms gets displaced over other carbon atoms and hence give stability to the carbocation. The more canonical structures of carbocation, the more will be the stability.Here in question, in option C we have alkyl carbocation and there is no possibility of conjugation, hence alkyl carbocations are least stable.
Next we have option D. in this carbocation, the carbon bearing positive charge is alkyl, hence no possibility of resonance. Hence is less stable than aromatic carbocation.
For option B. the carbon bearing positive charge is attached directly to the aromatic system. Hence resonance can occur and this carbocation will have 4 canonical structures. This carbocation is also known as benzyl carbocation.

For option A, the carbon bearing positive charge is attached to 2 aromatic systems, therefore resonance will occur but since it has 2 benzene rings attached to the carbocation, hence it will have more canonical structure than the benzyl carbocation. Therefore it is most stable among all.

Hence the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note:The carbocation stability also increases by the presence of heteroatoms having an unshared pair of electrons for example nitrogen, oxygen adjacent to the cation. Such carbocations are also stabilized by resonance. The triphenylmethyl carbocation is more stable than option A above, because it has 3 benzene rings, hence it will have more canonical structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




