
Among formic acid, acetic acid, propanoic acid, and phenol, the strongest acid in water is-
[A] Formic acid
[B] Acetic acid
[C] Propanoic acid
[D] Phenol
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, approach using the factors that affect the acidity of an acid in a solvent. Consider the strength of the bond that is being broken and also consider the strength of the ions formed.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, three of the given acids are carboxylic acids. Let us see their strength first and then compare them with phenol.
Now, let’s discuss the carboxylic acids-
In the case of carboxylic acids, a positive inductive effect (+I-effect) is present due to the electron-donating tendency of alkyl groups. The +I effect increases with the presence of a higher number of alkyl groups.
This +I effect reduces the acidity. This happens because the +I effect will increase the electron density on carbonyl carbon and thus it reduces the C-O bond polarity. This results in relatively increased O-H bond strength. Thus, due to the increased bond strength it is difficult to furnish the hydrogen ions (property of an acid is the ability to donate the hydrogen ions) and it is responsible for making it less acidic.
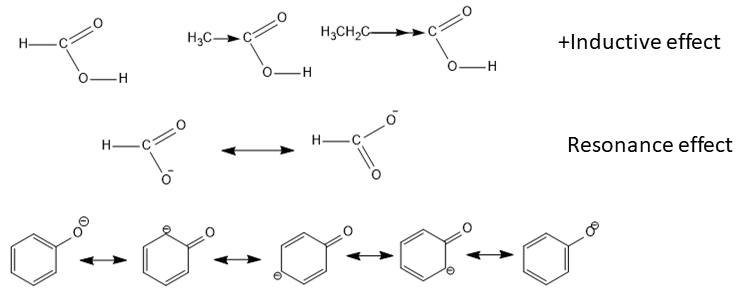
So, we can say among all given alkyl carboxylic acids, the one with the least alkyl group will be more acidic.
Formula of acetic acid is $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ that of propanoic acid is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$ and formic acid is HCHO.
Therefore, we can see that formic acid is the least alkylated. Therefore, the order of acidity of these three carboxylic acids will be - $HCHO>C{{H}_{3}}COOH>{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$
Now, let’s compare formic acid and phenol-
Here, formic is a stronger acid because the delocalization of negative charge after losing proton is more delocalized in formate ions on two oxygen atoms.
Whereas, in phenoxide ion, we can see oxygen being more electronegative will always have higher charge density even after ring delocalization.
In conclusion, formate ions have more powerful resonance compared to phenoxide ion.
Hence, we can say that formic acid is strongest in water.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We have known several theories which explain the concept of acid and bases to us like Arrhenius Theory, Solvent System Theory and many more. These theories explain acid and bases in different ways. In the discussion above we have dealt with the Bronsted Lowry Theory.
Bronsted Lowry theory is also known as the protonic theory because it explains the concept of acid and bases on the bases of a proton or hydrogen ion or${{H}^{+}}$.
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, “any species that tends to give up a proton (hydron) is an acid, and any substance that tends to accept a proton (hydron) is a base.”
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, three of the given acids are carboxylic acids. Let us see their strength first and then compare them with phenol.
Now, let’s discuss the carboxylic acids-
In the case of carboxylic acids, a positive inductive effect (+I-effect) is present due to the electron-donating tendency of alkyl groups. The +I effect increases with the presence of a higher number of alkyl groups.
This +I effect reduces the acidity. This happens because the +I effect will increase the electron density on carbonyl carbon and thus it reduces the C-O bond polarity. This results in relatively increased O-H bond strength. Thus, due to the increased bond strength it is difficult to furnish the hydrogen ions (property of an acid is the ability to donate the hydrogen ions) and it is responsible for making it less acidic.

So, we can say among all given alkyl carboxylic acids, the one with the least alkyl group will be more acidic.
Formula of acetic acid is $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ that of propanoic acid is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$ and formic acid is HCHO.
Therefore, we can see that formic acid is the least alkylated. Therefore, the order of acidity of these three carboxylic acids will be - $HCHO>C{{H}_{3}}COOH>{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$
Now, let’s compare formic acid and phenol-
Here, formic is a stronger acid because the delocalization of negative charge after losing proton is more delocalized in formate ions on two oxygen atoms.
Whereas, in phenoxide ion, we can see oxygen being more electronegative will always have higher charge density even after ring delocalization.
In conclusion, formate ions have more powerful resonance compared to phenoxide ion.
Hence, we can say that formic acid is strongest in water.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We have known several theories which explain the concept of acid and bases to us like Arrhenius Theory, Solvent System Theory and many more. These theories explain acid and bases in different ways. In the discussion above we have dealt with the Bronsted Lowry Theory.
Bronsted Lowry theory is also known as the protonic theory because it explains the concept of acid and bases on the bases of a proton or hydrogen ion or${{H}^{+}}$.
According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, “any species that tends to give up a proton (hydron) is an acid, and any substance that tends to accept a proton (hydron) is a base.”
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




