
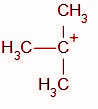
How many $\alpha $ hydrogen does this carbocation have?

Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: In an organic molecule, the carbon atom that is directly bonded to the functional group such as a carbonyl or hydroxyl group is known as the alpha carbon. The hydrogen atom attached to the alpha carbon atom is known as alpha hydrogen. In this case, the functional group is a carbocation.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the carbon atom adjacent to the functional group is the alpha carbon atom. The functional group in the given compound is a carbocation, i.e. the carbon atom carrying the positive charge. This carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms. Hence we can conclude that all three of these carbon atoms (Marked with a star) are alpha carbons.
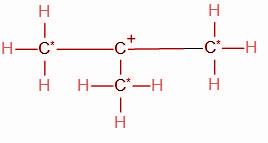
Thus, the total number of alpha hydrogens in the carbocation are 9.
Additional information:
Due to close proximity to the functional group, alpha carbons are highly reactive and are responsible for almost all reactions of an organic compound. For example, in an aldehyde or ketone, the alpha hydrogens are acidic and undergo many reactions. It is acidic due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group. Aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction are among the key reactions showing the reactivity of alpha hydrogens.
Note:
Alpha hydrogens play an important role in the stability of a carbocation. The more the number of alpha hydrogen atoms, more is the stability of the carbocation. This due to hyper conjugation of the alpha hydrogen. The electron bond pair of the alpha carbon hydrogen bond is transferred temporarily to the carbocation, thus, stabilizing it. More the number of alpha hydrogens, more is hyper conjugation and thus more is the stability of the carbocation due to delocalization of charge.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the carbon atom adjacent to the functional group is the alpha carbon atom. The functional group in the given compound is a carbocation, i.e. the carbon atom carrying the positive charge. This carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms. Hence we can conclude that all three of these carbon atoms (Marked with a star) are alpha carbons.

Thus, the total number of alpha hydrogens in the carbocation are 9.
Additional information:
Due to close proximity to the functional group, alpha carbons are highly reactive and are responsible for almost all reactions of an organic compound. For example, in an aldehyde or ketone, the alpha hydrogens are acidic and undergo many reactions. It is acidic due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group. Aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction are among the key reactions showing the reactivity of alpha hydrogens.
Note:
Alpha hydrogens play an important role in the stability of a carbocation. The more the number of alpha hydrogen atoms, more is the stability of the carbocation. This due to hyper conjugation of the alpha hydrogen. The electron bond pair of the alpha carbon hydrogen bond is transferred temporarily to the carbocation, thus, stabilizing it. More the number of alpha hydrogens, more is hyper conjugation and thus more is the stability of the carbocation due to delocalization of charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




