
Addition of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$to trans$ - 2 - $butene would give a product which is:
A. achiral
B. racemic
C. meso
D. optical active
Answer
551.1k+ views
Hint:To determine the answer we should know the type of addition shown by bromine. The stereo of the product depends upon the type of addition and stereo of the reactant. We should also know the meaning of achiral, racemic, meso and optical active. The reagent bromine gives the anti-addition on alkene.
Complete step-by-step answer:The reagent bromine is used for bromination of the alkene. Initially, the pi bond electron density of alkene attacks at bromine, so bromine gets attached from the pi electron density by forming a three membered cyclic structure.
Then bromide ion attacks from the opposite side of the ring and gets added simultaneously; the ring opening takes place, so a dibromide product forms.
The reaction of bromine with trans$ - 2 - $butene is shown as follows:
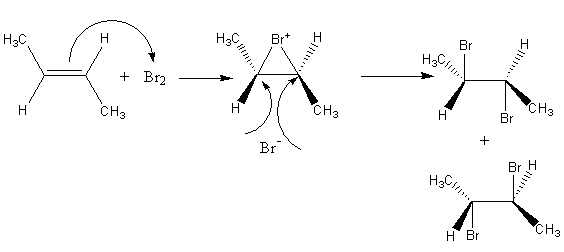
Bromide ion can attack any one of the carbon of the double bond so, a mixture of two product forms. Now we will write the fischer projection formula of the product to find the relation between them.
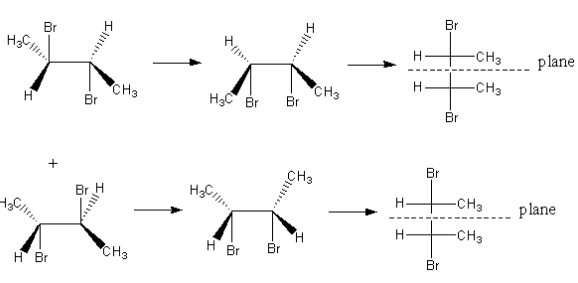
As both carbon centres of the product are chiral centres but the compound has a plane of symmetry. So, the formed compound is meso.
So, addition of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$to Trans$ - 2 - $butene would give a product which is meso.
Therefore, option (C) meso, is correct.
Note: The anti-addition of reagent to Trans alkene results in a meso compound. A carbon centre having four different substituents is known as a chiral centre. For a compound to be optically active, the presence of a chiral centre is necessary. The compound having no chiral centre is known as optical inactive. The compound having a chiral centre can also be achiral if it possesses a plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry and these compounds are known as meso.
Complete step-by-step answer:The reagent bromine is used for bromination of the alkene. Initially, the pi bond electron density of alkene attacks at bromine, so bromine gets attached from the pi electron density by forming a three membered cyclic structure.
Then bromide ion attacks from the opposite side of the ring and gets added simultaneously; the ring opening takes place, so a dibromide product forms.
The reaction of bromine with trans$ - 2 - $butene is shown as follows:

Bromide ion can attack any one of the carbon of the double bond so, a mixture of two product forms. Now we will write the fischer projection formula of the product to find the relation between them.

As both carbon centres of the product are chiral centres but the compound has a plane of symmetry. So, the formed compound is meso.
So, addition of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$to Trans$ - 2 - $butene would give a product which is meso.
Therefore, option (C) meso, is correct.
Note: The anti-addition of reagent to Trans alkene results in a meso compound. A carbon centre having four different substituents is known as a chiral centre. For a compound to be optically active, the presence of a chiral centre is necessary. The compound having no chiral centre is known as optical inactive. The compound having a chiral centre can also be achiral if it possesses a plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry and these compounds are known as meso.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




